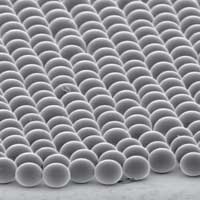
 Researchers have developed a new material able to cool another one by emitting infrared radiation. The results are expected to be used in devices where an increase in temperature has drastic effects on performance, like solar panels and computer systems, among other applications.
Researchers have developed a new material able to cool another one by emitting infrared radiation. The results are expected to be used in devices where an increase in temperature has drastic effects on performance, like solar panels and computer systems, among other applications.
Friday, November 8, 2019
Self-assembled microspheres of silica to cool surfaces without energy consumption
 Researchers have developed a new material able to cool another one by emitting infrared radiation. The results are expected to be used in devices where an increase in temperature has drastic effects on performance, like solar panels and computer systems, among other applications.
Researchers have developed a new material able to cool another one by emitting infrared radiation. The results are expected to be used in devices where an increase in temperature has drastic effects on performance, like solar panels and computer systems, among other applications.
Team uses golden 'lollipop' to observe elusive interference effect at the nanoscale
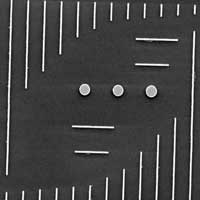 Researchers used a nanoscale electron probe to directly observe infrared plasmonic Fano antiresonances.
Researchers used a nanoscale electron probe to directly observe infrared plasmonic Fano antiresonances.
Machine learning analyses help unlock secrets of stable 'supercrystal'
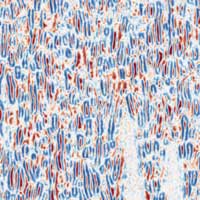 Beyond solids, liquids, gases, plasma, and other examples only accessible under extreme conditions, scientists are constantly searching for other states of matter. Although newly discovered states tend to be short-lived, a recent experiment transformed a mixture of two materials into a novel state of matter with a much longer lifetime - a supercrystal.
Beyond solids, liquids, gases, plasma, and other examples only accessible under extreme conditions, scientists are constantly searching for other states of matter. Although newly discovered states tend to be short-lived, a recent experiment transformed a mixture of two materials into a novel state of matter with a much longer lifetime - a supercrystal.
Strain-induced isomerisation of molecular chains
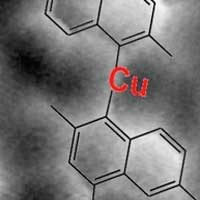 Scientists have demonstrated a strain-induced structural rearrangement of one-dimensional (1D) metal-organic molecular chains for potential use in fabricating functional nanostructures.
Scientists have demonstrated a strain-induced structural rearrangement of one-dimensional (1D) metal-organic molecular chains for potential use in fabricating functional nanostructures.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
