Wednesday, January 31, 2018
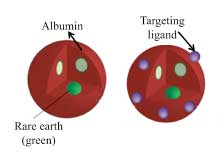
Surveillance nanotechnology tracks cancer metastasis to multiple organs
Tests in mice show the particles are better than MRI and CT at tracking cancer's progress.
Materials research team lights the way for more efficient LEDs
New research ha revealed that nanocrystals made of cesium lead halide perovskites is the first discovered material which the ground exciton state is 'bright', making it an attractive candidate for more efficient solid-state lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs).

Clustered quantum dots could improve HD TV
Scientists have been working to develop a new process, which could lead to a new generation of high-definition (HD), paving the way for brighter, lighter and more energy efficient TVs and smart devices.
Silk fibers could be high-tech 'natural metamaterials' (w/video)
New research has demonstrated how the nano-architecture of a silkworm?s fiber causes 'Anderson localization of light', a discovery that could lead to various innovations and a better understanding of light transport and heat transfer.

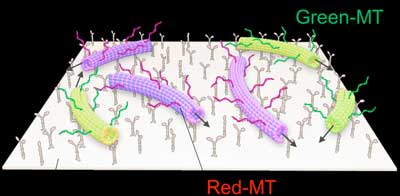
Letting molecular robots swarm like birds
Researchers have developed DNA-assisted molecular robots that autonomously swarm in response to chemical and physical signals, paving the way for developing future nano-machines.
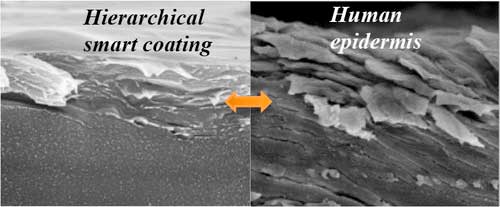
Skin-inspired graphene oxide based coating that's as hard as teeth and can heal itself
Researchers have reported the development of a smart coating that is as hard as tooth enamel on the outside but can heal itself like skin can.
Lab-on-a-chip for tracking single bacterial cells (w/video)
This integrated setup can be used to study gene regulation in single bacterial cells in response to dynamically controlled environmental changes.
Chemists follow molecules down 'nanowells', track catalytic reactions in nanoconfinement
Chemists have measured the effects of nanoconfinement in catalysis by tracking single molecules as they dive down 'nanowells' and react with catalysts at the bottom.
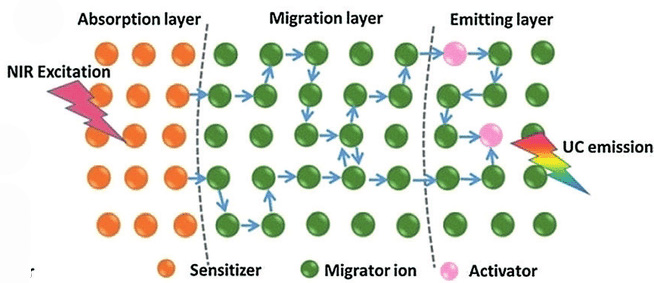
Precisely tailoring the dynamics of upconversion luminescence in nanoparticles
Through a collaborative approach of advanced spectroscopy and theoretical modelling, researchers were able to establish that the migration of excitation energy greatly affects the upconversion dynamics.
Tuesday, January 30, 2018
The fight against tooth decay gets help with a new nanocomposite smart material
Dentistry researchers have developed a filling material with tiny particles made by self-assembly of antimicrobial drugs, designed to stop bacteria in its tracks.
A customizable, fabric-like power source for wearable electronics
Researchers have created a customizable, fabric-like power source that can be cut, folded or stretched without losing its function.

Monday, January 29, 2018
'Chemical net' could be key to capturing pure hydrogen
MXene material could help produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel.
New molecular muscle responds to visible light
Picture a tiny, makeshift muscle that can curl a 20 milligram suspended weight when exposed to light. Under the right conditions, another mix packs enough power to bench-press a dime.

Diamonds show promise for spintronic devices
Scientists have measured how strongly a charge carrier's spin interacts with a magnetic field in diamond. This crucial property shows diamond as a promising material for spintronic devices.

Interstellar fullerenes may help find solutions for earthly matters
Fullerenes were first discovered by Harry Kroto in the 1970s, a feat for which he and his colleagues received a Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Recently, they have been found in winds emitted by red giants and in interstellar medium.
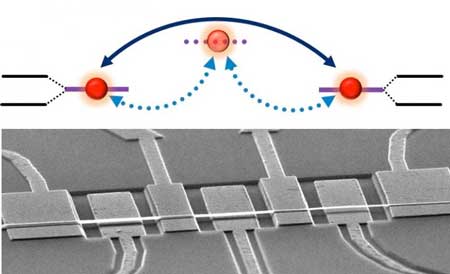
Scientists realize strong indirect coupling in distant graphene-based nanomechanical resonators
A research team has realized strong coupling between distant phonon modes, by introducing a third resonator as a phonon cavity mode. Varying the resonant frequency of the phonon cavity mode, the coupling strength between distant phonon modes can be continuous tuned.
Researchers develop flexible vertical micro LED (w/video)
Researchers have developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology.

Light-steering of spin-polarized currents in topological insulators
Topological insulators are a fascinating group of materials. A spin-polarization occurs, as soon as an electric current flows in the material. Scientists have measured this now for the first time optically at room temperature.
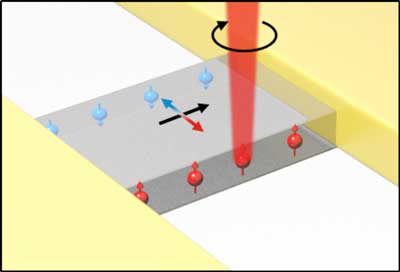
Synthetic 'virus' to kill bacteria
Scientists have developed a synthetic 'virus' that kills bacteria on first contact.
Superconducting synapse may be missing piece for 'artificial brains'
Researchers have built a superconducting switch that 'learns' like a biological system and could connect processors and store memories in future computers operating like the human brain.
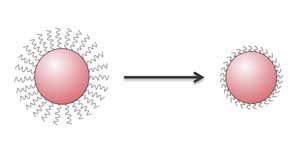
New nanomedicine methode prevents premature nanoparticle breakdown
Nanoparticles that transport medicines to a specific part of the human body are usually broken down in the liver prematurely. Researchers have discovered a new method to prevent this from happening.
Antiferromagnets prove their potential for spin-based information technology
Physicists demonstrate technologically feasible read-out and writing of digital information in antiferromagnets / Basic principle for ultrafast and stable magnetic memory.
Flexing for the next silicon wave
Ultrathin, rigid silicon segments that are wired through interdigitated metal contacts produce ultraflexible high-performance solar cells.

Let liquid fingers point the way
Gold nanospheres can be manipulated on surfaces with nanometer precision using the effects of solvent evaporation.

Friday, January 26, 2018
Scientists catch light squeezing and stretching next-gen data storage material
Combining X-ray and electron data, researchers observe the rapid atomic response of iron-platinum nanoparticles to light, which could help control future magnetic data storage devices.
Research boosts efficiency and stability of optical rectennas
Recent improvements could allow rectennas - which convert electromagnetic fields at optical frequencies directly to electrical current - to operate low-power devices such as temperature sensors.

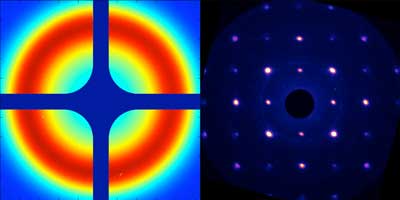
X-ray experiments suggest high tunability of 2-D material
Scientists use a new x-ray platform to see microscale details in monolayer material's electronic structure.
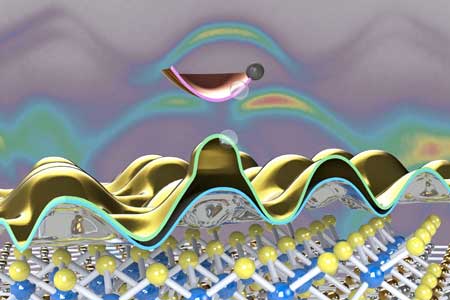
Tiny scales could serve as safe material in implants to reinforce bones and joints
Researchers have designed a system of minuscule two-ended hooks, made out of calcite, that can 'grow' from silicone into tissue to fix themselves into place.

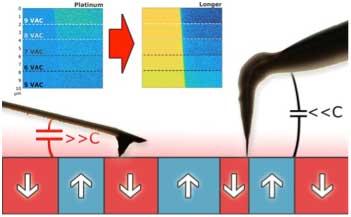
New technology aiming to improve trueness in the piezoelectric microscopy characterization of ceramic materials
Scientists have proved that unconventional AFM probes are suitable to acquire a trueness piezoelectric signal in Piezoresponse Force Microscopy.
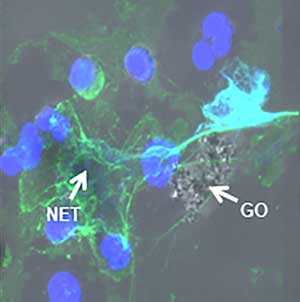
Graphene oxide is 'sensed' by specialised cells of the immune system
A new study shows that our immune system handles graphene oxide in a manner similar to pathogens, paving the way for safer biomedical applications of this two-dimensional material.
New research yields super-strong aluminum alloy
Researchers have demonstrated how to create a super-strong aluminum alloy that rivals the strength of stainless steel, an advance with potential industrial applications.
Thursday, January 25, 2018
Quantum race accelerates development of silicon quantum chip
Researchers showed that quantum information of an electron spin can be transported to a photon, in a silicon quantum chip. This is important in order to connect quantum bits across the chip and allowing to scale up to large numbers of qubits.

Researchers combine spintronics and nanophotonics in 2D material
The discovery brings the worlds of spintronics and nanophotonics closer together and might lead to the development of an energy-efficient way of processing data, in data centres, for example.

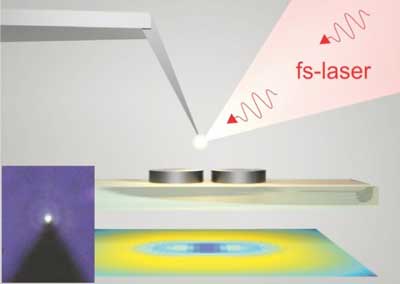
'Nanobulb' helps see subwavelength-size objects with ordinary microscope
Scientists have proven that a silicon-gold nanoparticle can act as an effective source of white light when agitated by a pulse laser in IR band.
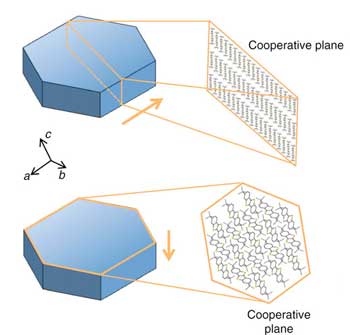
Shape-shifting organic crystals use memory to improve plastic electronics
Researchers have identified a mechanism that triggers shape-memory phenomena in organic crystals used in plastic electronics.
Novel methods of synthesizing quantum dot materials
Scientists are optimizing nanostructures for energy devices such as solar cells.
World's smallest sensor measures growth force of plants, animals and humans
Researchers have experimented with a combination of laser technology and chemical knowledge, coming up with a sensor consisting of one single molecule that is a few hundred times more accurate than existing devices used to measure nano-forces on the molecular level.
From quasiparticles to highly sensitive sensors
A new ERC grant allows a chemist to deal with ultrafast time- and space-resolved dynamics in molecular-plasmonic hybrid systems.

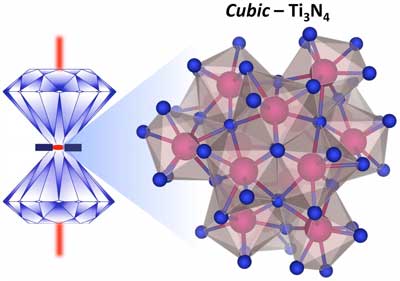
Prediction of titanic nitride proved unsinkable
Long sought-after form of cubic, semiconducting titanium nitride synthesized.
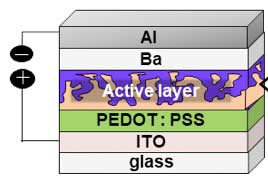
A simple new approach to plastic solar cells
Researchers intelligently design new highly efficient organic solar cells based on amorphous electronic materials with potential for easy printing.
Development of self-crack-healing ceramics capable of quick full strength recovery
Using clues provided by bone healing mechanisms, researchers added a healing activator to crystalline grain boundaries, enabling the ceramic to fully heal cracks in as little as one minute at 1,000 C, the operating temperature of an aircraft engine.
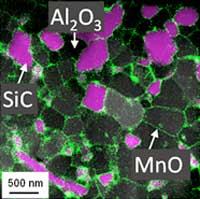
Recycling and reusing worn cathodes to make new lithium ion batteries
Nanoengineers have developed an energy-efficient recycling process that restores used cathodes from spent lithium ion batteries and makes them work just as good as new.

New technology standard could shape the future of electronics design
Scientists have discovered a way of enhancing the capabilities of an emerging nanotechnology that could open the door to a new generation of electronics.
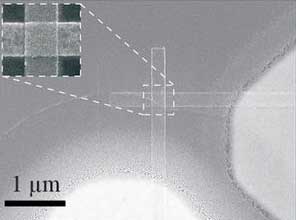
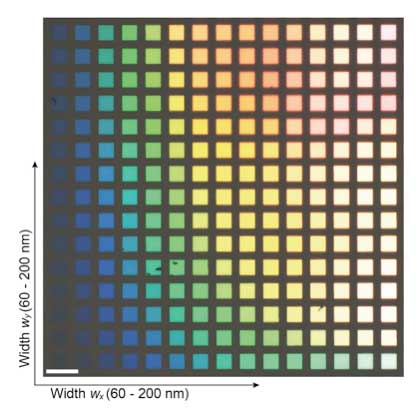
Silicon nanoblock arrays create vivid colors with subwavelength resolution
Researchers demonstrate a silicon metamaterial surface that will allow for color printing with diffraction-limited resolution.
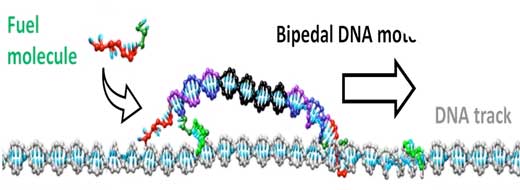
Track-walking molecular motors
Physicists have developed new self-directed molecular motors for nanoscale applications.
Wednesday, January 24, 2018
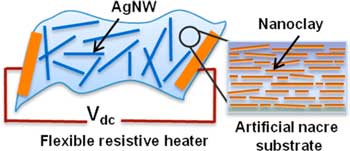
Pearly material for bendable heating elements
Scientists demonstrate a hybrid material consisting of imitation pearl combined with silver nanowires that works as a heater, with the added benefit of high flexibility, suggesting a potential role in wearable devices.
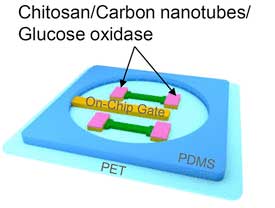
New biosensor could monitor glucose levels in tears and sweat
Researchers report the development of an ultra-thin, flexible sensor that could be incorporated into contact lenses or on the backs of watches for real-time glucose tracking.
Engineers create new architecture for vaporizable electronics
Engineers have demonstrated a new method for remotely vaporizing electronics into thin air, giving devices the ability to vanish ? along with their valuable data ? if they were to get into the wrong hands.

Advances in lasers get to the long and short of it
A new way of modifying the dipole moment of cholesteric liquid crystals allows for researchers to select between the different band-edge modes experimentally for the first time.
Nanoparticle vaccine offers universal protection against influenza a viruses
Researchers have developed a universal vaccine to combat influenza A viruses that produces long-lasting immunity in mice and protects them against the limitations of seasonal flu vaccines.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
