Thursday, February 28, 2019
Organic electronics: A high-performance unipolar n-type thin-film transistor
Layering titanium oxide's different mineral forms for better solar cells
An easier way to engineer plants
Nanotechnology makes it possible for mice to see in infrared
Hall effect becomes viscous in graphene
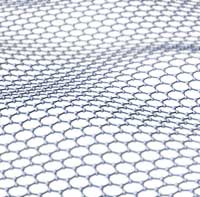
New blueprint for understanding, predicting and optimizing complex nanoparticles
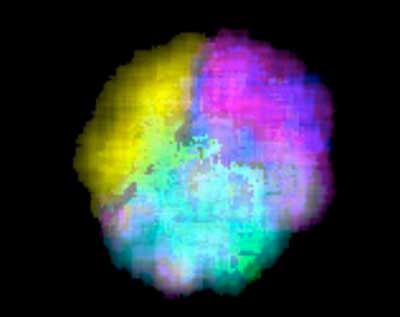
Hybrid material may outperform graphene in several applications
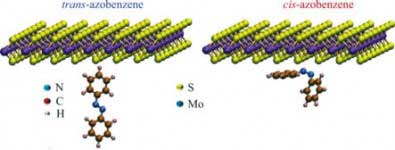
Zips on the nanoscale
In-depth insights into glass corrosion
Easing bacterial traffic jams
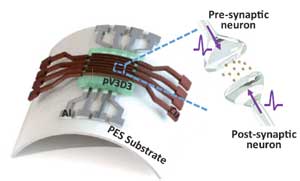
Researchers develop analog memristive synapses for neuromorphic chips
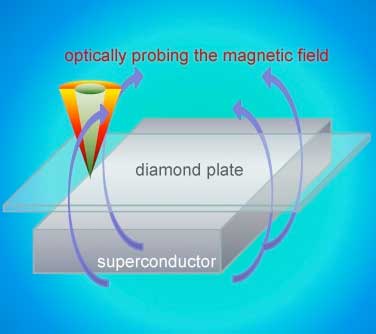
Scientists measure exact edge between superconducting and magnetic states
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
