 Silicon single-electron/hole transistors (SETs/SHTs) and super-high frequency nanoelectromechanical resonators show great potentials in quantum computation, sensing and many other areas.
Silicon single-electron/hole transistors (SETs/SHTs) and super-high frequency nanoelectromechanical resonators show great potentials in quantum computation, sensing and many other areas.
Tuesday, December 15, 2020
Researchers develop Si-based super-high frequency nanoelectromechanical resonator
 Silicon single-electron/hole transistors (SETs/SHTs) and super-high frequency nanoelectromechanical resonators show great potentials in quantum computation, sensing and many other areas.
Silicon single-electron/hole transistors (SETs/SHTs) and super-high frequency nanoelectromechanical resonators show great potentials in quantum computation, sensing and many other areas.
Novel type of nanoparticle efficiently and selectively kills cancer cells
 Researchers report the development of a class of novel amorphous nanoparticles made up of calcium and citrate, which are capable of breaching the barriers to uptake, and killing tumor cells in a targeted fashion.
Researchers report the development of a class of novel amorphous nanoparticles made up of calcium and citrate, which are capable of breaching the barriers to uptake, and killing tumor cells in a targeted fashion.
Novel computer modeling techniques to predict the properties of 2D materials
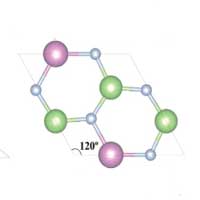 Cutting-edge computer modeling techniques to predict the properties of 2D materials that haven't yet been made in real life.
Cutting-edge computer modeling techniques to predict the properties of 2D materials that haven't yet been made in real life.
Weak force has strong impact on nanosheets
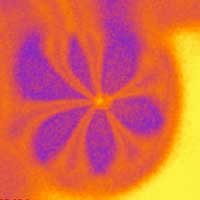 Scientists found that nature's ubiquitous 'weak' force is sufficient to indent rigid nanosheets, extending their potential for use in nanoscale optics or catalytic systems.
Scientists found that nature's ubiquitous 'weak' force is sufficient to indent rigid nanosheets, extending their potential for use in nanoscale optics or catalytic systems.
New fullerene crystal production method 50 times faster than predecessor
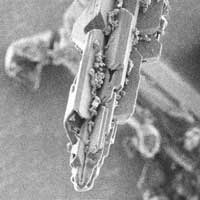 Researchers have developed a highly efficient technique for producing a unique fullerene crystal, called fullerene finned-micropillar (FFMP), that is of significant use for next-generation electronics.
Researchers have developed a highly efficient technique for producing a unique fullerene crystal, called fullerene finned-micropillar (FFMP), that is of significant use for next-generation electronics.
Earable computing: A new research area in the making
 Researchers believe that earphones will be the next significant milestone in wearable devices, and that new hardware, software, and apps will all run on this platform.
Researchers believe that earphones will be the next significant milestone in wearable devices, and that new hardware, software, and apps will all run on this platform.
Three-dimensional view of catalysts in action
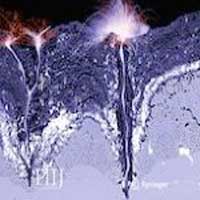 A new diagnostic tool, operando X-ray spectroscopy, visualizes the structure and gradients of complex technical catalysts in three dimensions, thus allowing us to look into functioning chemical reactors.
A new diagnostic tool, operando X-ray spectroscopy, visualizes the structure and gradients of complex technical catalysts in three dimensions, thus allowing us to look into functioning chemical reactors.
Catalytic activity of individual cobalt oxide nanoparticles determined
 Researchers have developed a method using a robotic arm that allows them to select individual particles under an electron microscope and place them on a nanoelectrode for electrochemical analysis.
Researchers have developed a method using a robotic arm that allows them to select individual particles under an electron microscope and place them on a nanoelectrode for electrochemical analysis.
Nanoengineered cement shows promise for sealing leaky gas wells
 Leaking natural gas wells are considered a potential source of methane emissions, and a new nanomaterial cement mixture could provide an effective, affordable solution for sealing these wells.
Leaking natural gas wells are considered a potential source of methane emissions, and a new nanomaterial cement mixture could provide an effective, affordable solution for sealing these wells.
How water helps the substrate into the enzyme
 Scientists have investigated why cages can increase the catalytic activity of enclosed molecules. Using terahertz spectroscopy and complex computer simulations, they showed that water encapsulated in a tiny cage has special properties - that are structurally and dynamically distinct from any known phase of water.
Scientists have investigated why cages can increase the catalytic activity of enclosed molecules. Using terahertz spectroscopy and complex computer simulations, they showed that water encapsulated in a tiny cage has special properties - that are structurally and dynamically distinct from any known phase of water.
Novel nanomaterial strain sensors are ultra-thin, battery-free and can transmit data wirelessly
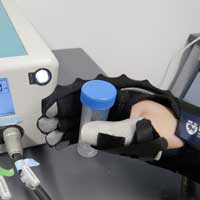 Researchers have taken the first step towards improving the safety and precision of industrial robotic arms by developing a new range of nanomaterial strain sensors that are 10 times more sensitive when measuring minute movements, compared to existing technology.
Researchers have taken the first step towards improving the safety and precision of industrial robotic arms by developing a new range of nanomaterial strain sensors that are 10 times more sensitive when measuring minute movements, compared to existing technology.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
