Wednesday, January 2, 2019
Scientists move quantum optic networks a step closer to reality
New discovery is big on nanoscale
Controlling neurons with light - but without wires or batteries
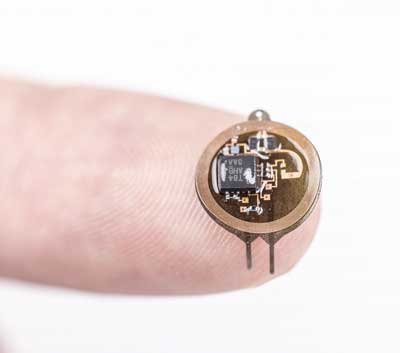
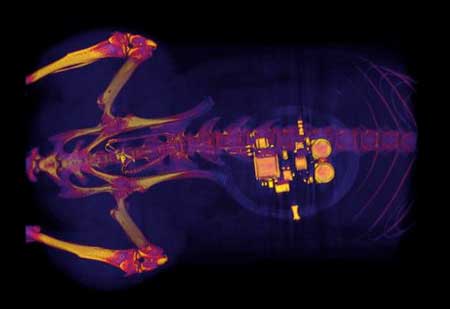
Tiny, implantable device uses light to treat bladder problems
A catalytic flying carpet
Rippling under pressure - when layered materials are pushed to the brink
Quantum chemistry on quantum computers
Graphene-based implant overcomes technical limitation to record brain activity at extremely low frequencies
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
