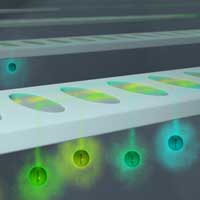
 A team of researchers has developed a new way to control and measure atoms that are so close together no optical lens can distinguish them.
A team of researchers has developed a new way to control and measure atoms that are so close together no optical lens can distinguish them.
Friday, October 30, 2020
A new spin on atoms gives scientists a closer look at quantum weirdness
 A team of researchers has developed a new way to control and measure atoms that are so close together no optical lens can distinguish them.
A team of researchers has developed a new way to control and measure atoms that are so close together no optical lens can distinguish them.
A world record in detecting extremely low levels of gas impurities
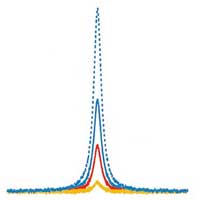 Scientists used photoacoustic spectroscopy applied to background-free analyses to measure unprecedentedly small trace gas concentrations.
Scientists used photoacoustic spectroscopy applied to background-free analyses to measure unprecedentedly small trace gas concentrations.
Plastic waste comes back in black as pristine graphene
 In a process they call ACDC, researchers expose plastic waste to around eight seconds of high-intensity alternating current, followed by the DC jolt. The products are high-quality turbostratic graphene, a valuable and soluble substance that can be used to enhance electronics, composites, concrete and other materials, and carbon oligomers, molecules that can be vented away from the graphene for use in other applications.
In a process they call ACDC, researchers expose plastic waste to around eight seconds of high-intensity alternating current, followed by the DC jolt. The products are high-quality turbostratic graphene, a valuable and soluble substance that can be used to enhance electronics, composites, concrete and other materials, and carbon oligomers, molecules that can be vented away from the graphene for use in other applications.
Thursday, October 29, 2020
Order in the disorder: density fluctuations in amorphous silicon discovered
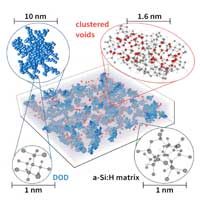 For the first time, scientists have identified the atomic substructure of amorphous silicon with a resolution of 0.8 nanometres. The results show that three different phases form within the amorphous matrix, which dramatically influences the quality and lifetime of the semiconductor layer.
For the first time, scientists have identified the atomic substructure of amorphous silicon with a resolution of 0.8 nanometres. The results show that three different phases form within the amorphous matrix, which dramatically influences the quality and lifetime of the semiconductor layer.
Scientists launch quest to develop quantum sensors for probing quantum materials
 The newly created Center for Quantum Sensing and Quantum Materials aims to unravel mysteries associated with exotic superconductors, topological insulators and strange metals.
The newly created Center for Quantum Sensing and Quantum Materials aims to unravel mysteries associated with exotic superconductors, topological insulators and strange metals.
Researchers find path to nanodiamond from graphene
 A spot of pressure enables chemical conversion to hardened 2D material.
A spot of pressure enables chemical conversion to hardened 2D material.
Predictive model reveals function of promising energy harvester device
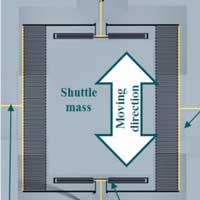 A small energy harvesting device that can transform subtle mechanical vibrations into electrical energy could be used to power wireless sensors and actuators for use in anything from temperature and occupancy monitoring in smart environments, to biosensing within the human body.
A small energy harvesting device that can transform subtle mechanical vibrations into electrical energy could be used to power wireless sensors and actuators for use in anything from temperature and occupancy monitoring in smart environments, to biosensing within the human body.
Breakthrough quantum-dot transistors create a flexible alternative to conventional electronics
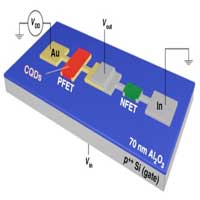 Quantum dot logic circuits provide the long-sought building blocks for innovative devices, including printable electronics, flexible displays, and medical diagnostics.
Quantum dot logic circuits provide the long-sought building blocks for innovative devices, including printable electronics, flexible displays, and medical diagnostics.
Scientists discover new structures in the smallest ice cube
 Scientists have revealed the coexistence of five cubic isomers in the smallest ice cube, including two with chirality.
Scientists have revealed the coexistence of five cubic isomers in the smallest ice cube, including two with chirality.
Chemical scissors snip 2D transition metal dichalcogenides into nanoribbon
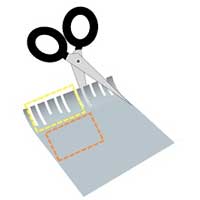 Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative - and an innovative way to produce them using chemical 'scissors' - that could make hydrogen production more economical.
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative - and an innovative way to produce them using chemical 'scissors' - that could make hydrogen production more economical.
Graphene-based memory resistors show promise for brain-based computing
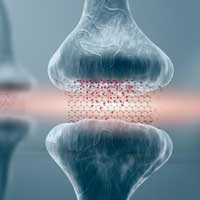 Engineers are attempting to pioneer a type of computing that mimics the efficiency of the brain's neural networks while exploiting the brain's analog nature.
Engineers are attempting to pioneer a type of computing that mimics the efficiency of the brain's neural networks while exploiting the brain's analog nature.
Smart fluorescent molecular switches based on boron-based compounds
 Scientists have developed extremely stable molecular switches of high luminosity that self-assemble into 1D nanostructures and form gel-like materials. These molecular switches can be used in biomedicine as fluorescent probes for imaging or sensing, in fluorescent displays, or in memories and information processing devices.
Scientists have developed extremely stable molecular switches of high luminosity that self-assemble into 1D nanostructures and form gel-like materials. These molecular switches can be used in biomedicine as fluorescent probes for imaging or sensing, in fluorescent displays, or in memories and information processing devices.
A new method to measure optical absorption in semiconductor crystals
 Scientists reveal more details about omnidirectional photoluminescence (ODPL) spectroscopy - a method for probing semiconducting crystals with light to detect defects and impurities.
Scientists reveal more details about omnidirectional photoluminescence (ODPL) spectroscopy - a method for probing semiconducting crystals with light to detect defects and impurities.
Wednesday, October 28, 2020
Reliable quality-control of graphene and other 2D materials is routinely possible
 Researchers have discovered and confirmed a method which could serve as an easy but reliable way to test the quality of graphene and other 2D materials. It takes advantage of the very broad background in surface electron diffraction, named the Bell-Shaped-Component, which strongly correlates to uniformly patterned, or 'perfect' graphene.
Researchers have discovered and confirmed a method which could serve as an easy but reliable way to test the quality of graphene and other 2D materials. It takes advantage of the very broad background in surface electron diffraction, named the Bell-Shaped-Component, which strongly correlates to uniformly patterned, or 'perfect' graphene.
Liquid nanofoam could be a game changer for future football helmets
 A liquid nanofoam liner undergoing testing could prolong the safe use of football helmets.
A liquid nanofoam liner undergoing testing could prolong the safe use of football helmets.
Turning a coronavirus protein into a nanoparticle could be key for COVID-19 vaccine
 Changing makeup of a specific protein has the potential to neutralize the virus.
Changing makeup of a specific protein has the potential to neutralize the virus.
Direct observation of a single electron's butterfly-shaped distribution in titanium oxide
 A valence electron in titanium oxide has been imaged at a resolution of 0.2 Angstroms using synchrotron X-ray diffraction and a new Fourier synthesis method that can determine the orbital states in materials regardless of their physical properties.
A valence electron in titanium oxide has been imaged at a resolution of 0.2 Angstroms using synchrotron X-ray diffraction and a new Fourier synthesis method that can determine the orbital states in materials regardless of their physical properties.
Tuesday, October 27, 2020
Enabling the data-driven future of microscopy
 Data-infused artificial intelligence could speed materials discovery.
Data-infused artificial intelligence could speed materials discovery.
Tailoring 2D materials to improve electronic and optical devices
 New possibilities for future developments in electronic and optical devices have been unlocked by recent advancements in two-dimensional (2D) materials.
New possibilities for future developments in electronic and optical devices have been unlocked by recent advancements in two-dimensional (2D) materials.
Scientists explain the paradox of Casimir forces in nanodevices
 Researchers propose a new approach to describe the interaction of metals with electromagnetic fluctuations i.e., with random bursts of electric and magnetic fields.
Researchers propose a new approach to describe the interaction of metals with electromagnetic fluctuations i.e., with random bursts of electric and magnetic fields.
Titanate nanotubes composites enhance photocatalysis of hydrogen
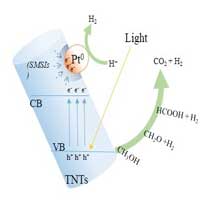 Scientists examined the photocatalytic performances of titanate nanotubes (TNTs) against commonly-used titanium dioxide and discovered superior performance of TNTs.
Scientists examined the photocatalytic performances of titanate nanotubes (TNTs) against commonly-used titanium dioxide and discovered superior performance of TNTs.
High-resolution lithography for metal-organic framework films
 Researchers have developed a high-resolution lithography process to pattern metal-organic framework (MOF) films. This work will speed up the integration of these materials into microchips.
Researchers have developed a high-resolution lithography process to pattern metal-organic framework (MOF) films. This work will speed up the integration of these materials into microchips.
New type of graphene photodetector enables low-cost cameras for self-driving cars and robots
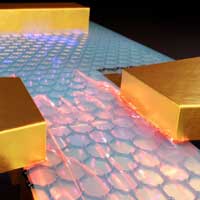 Researchers integrated three concepts to achieve a novel graphene photodetector: metallic plasmonic antennas, ultra sub-wavelength waveguiding of light and graphene photodetection.
Researchers integrated three concepts to achieve a novel graphene photodetector: metallic plasmonic antennas, ultra sub-wavelength waveguiding of light and graphene photodetection.
New insights into how alkali-metal doped flexible solar cells work
 Scientists place another piece of the puzzle on how introducing alkali metals into crystals of thin-film flexible solar cells improves their efficiency.
Scientists place another piece of the puzzle on how introducing alkali metals into crystals of thin-film flexible solar cells improves their efficiency.
Monday, October 26, 2020
On-surface synthesis of graphene nanoribbons could advance quantum devices
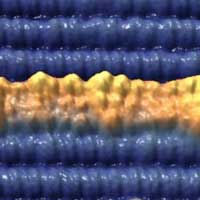 Scientists has synthesized graphene nanoribbons on a titanium dioxide surface using an atomically precise method that removes a barrier for custom-designed carbon nanostructures required for quantum information sciences.
Scientists has synthesized graphene nanoribbons on a titanium dioxide surface using an atomically precise method that removes a barrier for custom-designed carbon nanostructures required for quantum information sciences.
Researchers roll out the next generation of single-molecule race cars
 Nanoengineers are getting ready to rev their engines for the second international Nanocar Race.
Nanoengineers are getting ready to rev their engines for the second international Nanocar Race.
Could a nasal spray repair brain cells?
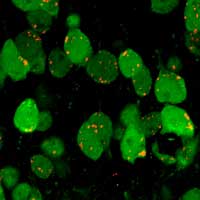 An inexpensive, accessible and non-invasive therapy for diseases and injuries of the brain may be slowly emerging: tiny particles called extracellular vesicles (EVs). Unlike stem cell therapies for repairing brain damage, EVs may safely regenerate brain cells and reduce inflammation.
An inexpensive, accessible and non-invasive therapy for diseases and injuries of the brain may be slowly emerging: tiny particles called extracellular vesicles (EVs). Unlike stem cell therapies for repairing brain damage, EVs may safely regenerate brain cells and reduce inflammation.
A 2D derivative of perovskite shows potential for valleytronics applications
 Engineers have found a 2D material that could make computers faster and more energy-efficient. Their material is a derivative of perovskite that has the surprising ability to enable the valleytronics phenomenon touted as a possible platform for information processing and storage.
Engineers have found a 2D material that could make computers faster and more energy-efficient. Their material is a derivative of perovskite that has the surprising ability to enable the valleytronics phenomenon touted as a possible platform for information processing and storage.
Tiny golden bullets could help tackle asbestos-related cancers
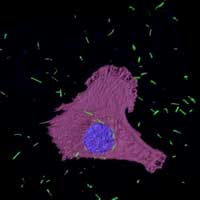 Researchers demonstrate that gold nanotubes could be used to treat mesothelioma, a type of cancer caused by exposure to asbestos.
Researchers demonstrate that gold nanotubes could be used to treat mesothelioma, a type of cancer caused by exposure to asbestos.
A new graphene-based testing system for disease-related antibodies
 The new instrument, based on the principle of a quartz-crystal microbalance combined with a graphene-based bio-interface, offers a cheap, fast, simple and sensitive alternative to currently available antibody tests.
The new instrument, based on the principle of a quartz-crystal microbalance combined with a graphene-based bio-interface, offers a cheap, fast, simple and sensitive alternative to currently available antibody tests.
Saturday, October 24, 2020
New imaging technology captures individual molecule's 'wobble'
 Microscopy breakthrough reveals how proteins behave in 3D, enabling new insights into cell behavior and disease progression.
Microscopy breakthrough reveals how proteins behave in 3D, enabling new insights into cell behavior and disease progression.
Friday, October 23, 2020
Building materials from spinning particles
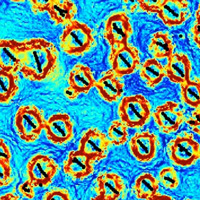 Active particle suspensions are a class of materials with tunable properties. This new research provides insight into fundamental aspects of the dynamics of such systems that act collectively.
Active particle suspensions are a class of materials with tunable properties. This new research provides insight into fundamental aspects of the dynamics of such systems that act collectively.
Topological states caught in the act
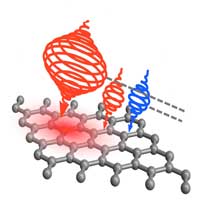 Scientists have shown that short-lived topological states can be tracked with equally short light flashes spiraling like a corkscrew.
Scientists have shown that short-lived topological states can be tracked with equally short light flashes spiraling like a corkscrew.
Thursday, October 22, 2020
Future VR could employ new ultrahigh-res nanophotonic display
 By expanding on existing designs for electrodes of ultra-thin solar panels, researchers have developed a new architecture for OLED - organic light-emitting diode - displays that could enable televisions, smartphones and virtual or augmented reality devices with resolutions of up to 10,000 pixels per inch (PPI).
By expanding on existing designs for electrodes of ultra-thin solar panels, researchers have developed a new architecture for OLED - organic light-emitting diode - displays that could enable televisions, smartphones and virtual or augmented reality devices with resolutions of up to 10,000 pixels per inch (PPI).
Do the twist: Making two-dimensional quantum materials using curved surfaces
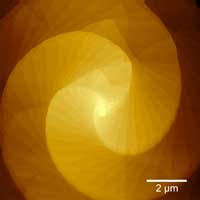 Scientists have discovered a way to control the growth of twisting, microscopic spirals of materials just one atom thick.
Scientists have discovered a way to control the growth of twisting, microscopic spirals of materials just one atom thick.
A first-of-its-kind nanoparticle catalyst mimics natural processes to break down plastic and produce valuable new products
 Researchers have developed a first-of-its-kind catalyst that is able to process polyolefin plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, types of polymers widely used in things like plastic grocery bags, milk jugs, shampoo bottles, toys, and food containers.
Researchers have developed a first-of-its-kind catalyst that is able to process polyolefin plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, types of polymers widely used in things like plastic grocery bags, milk jugs, shampoo bottles, toys, and food containers.
Scientists create three-dimensional nanostructures using ion beams
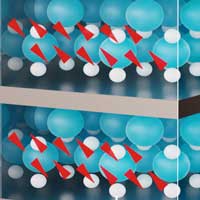 Effects at the interface between magnetic and non-magnetic layers have been exploited for data storage for three decades. This has led to a steady increase in hard drive storage capacity and is one reason why researchers see potential for ushering data processing into a new era.
Effects at the interface between magnetic and non-magnetic layers have been exploited for data storage for three decades. This has led to a steady increase in hard drive storage capacity and is one reason why researchers see potential for ushering data processing into a new era.
Scientists are working on cicada-inspired waterproof surfaces
 A multidisciplinary group that studies the physical and chemical properties of insect wings has demonstrated the ability to reproduce the nanostructures that help cicada wings repel water and prevent bacteria from establishing on the surface.
A multidisciplinary group that studies the physical and chemical properties of insect wings has demonstrated the ability to reproduce the nanostructures that help cicada wings repel water and prevent bacteria from establishing on the surface.
Reviewing multiferroics for future, low-energy data storage
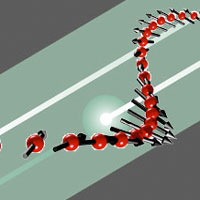 A new study comprehensively reviews the magnetic structure of the multiferroic material bismuth ferrite.
A new study comprehensively reviews the magnetic structure of the multiferroic material bismuth ferrite.
With innovative nanofiber membranes, cloth masks' efficacy goes up to 99%
 Researchers have developed a nanofiber membrane that can be sandwiched between the cloth pieces in a homemade mask. These nanofibers make regular cloth masks as strong as N95 masks.
Researchers have developed a nanofiber membrane that can be sandwiched between the cloth pieces in a homemade mask. These nanofibers make regular cloth masks as strong as N95 masks.
World record resolution in cryo electron microscopy
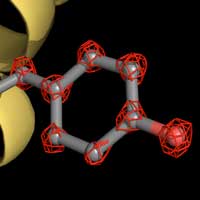 Novel technique visualizes individual atoms in a protein with cryo electron microscopy for the first time.
Novel technique visualizes individual atoms in a protein with cryo electron microscopy for the first time.
Loose nanofiltration membrane is promising for resource recovery
 A new review summarizes the developments in the emerging field of loose nanofiltration, and provides guidance to improve the fabrication of loose nanofiltration membranes and facilitate their applications in resource recovery.
A new review summarizes the developments in the emerging field of loose nanofiltration, and provides guidance to improve the fabrication of loose nanofiltration membranes and facilitate their applications in resource recovery.
Turning streetwear into solar power plants
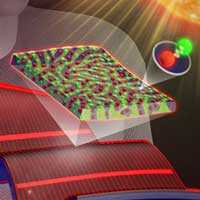 Researchers succeeded in developing a material that works like a luminescent solar concentrator and can even be applied to textiles. This opens up numerous possibilities for producing energy directly where it is needed, i.e. in the use of everyday electronics.
Researchers succeeded in developing a material that works like a luminescent solar concentrator and can even be applied to textiles. This opens up numerous possibilities for producing energy directly where it is needed, i.e. in the use of everyday electronics.
Wednesday, October 21, 2020
Oxygen can do a favor to synthesize metal-organic frameworks
 Researchers have identified how oxygen affects the synthesis of a novel MOF.
Researchers have identified how oxygen affects the synthesis of a novel MOF.
A flexible color-changing film inspired by chameleon skin (w/video)
 Researchers have developed a flexible film that changes color in response to stretching, pressure or humidity.
Researchers have developed a flexible film that changes color in response to stretching, pressure or humidity.
Materials scientists discover design secrets of nearly indestructible insect
 Researchers reveal the material components - and their nano- and microscale blueprints - that make the diabolical ironclad beetle so indestructible, while also demonstrating how engineers can benefit from these designs.
Researchers reveal the material components - and their nano- and microscale blueprints - that make the diabolical ironclad beetle so indestructible, while also demonstrating how engineers can benefit from these designs.
Researchers invent a new atomic layer deposition process
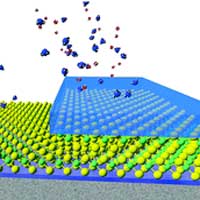 Researchers have invented a new way to deposit thin layers of atoms as a coating onto a substrate material at near room temperatures.
Researchers have invented a new way to deposit thin layers of atoms as a coating onto a substrate material at near room temperatures.
Magic fibers: Creating 'smart fabrics' that can change color
 A researcher is testing new ways to spin liquid crystals into fibers that could be used in camouflage clothing or to create cleaning wipes that can detect the presence of bacteria.
A researcher is testing new ways to spin liquid crystals into fibers that could be used in camouflage clothing or to create cleaning wipes that can detect the presence of bacteria.
Spinning graphene composite spider web architecture into 3D imaging technology
 Researchers are taking cues from nature to develop 3D photodetectors for biomedical imaging. The team used some architectural features from spider webs and combined it with organic-dye-sensitized graphene hybrid composites to develop the technology.
Researchers are taking cues from nature to develop 3D photodetectors for biomedical imaging. The team used some architectural features from spider webs and combined it with organic-dye-sensitized graphene hybrid composites to develop the technology.
Tuesday, October 20, 2020
Kitchen-fridge temperature supercurrents from stacked 2D materials
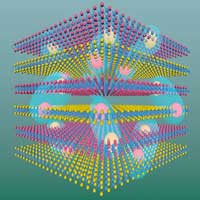 Could a stack of 2D materials allow for supercurrents at ground-breakingly warm temperatures, easily achievable in the household kitchen? An international study opens a new route to high-temperature supercurrents at temperatures as 'warm' as inside a kitchen fridge.
Could a stack of 2D materials allow for supercurrents at ground-breakingly warm temperatures, easily achievable in the household kitchen? An international study opens a new route to high-temperature supercurrents at temperatures as 'warm' as inside a kitchen fridge.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
