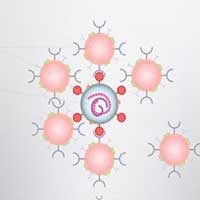
 Nanoparticles cloaked in human lung cell membranes and human immune cell membranes can attract and neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture, causing the virus to lose its ability to hijack host cells and reproduce.
Nanoparticles cloaked in human lung cell membranes and human immune cell membranes can attract and neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture, causing the virus to lose its ability to hijack host cells and reproduce.
Wednesday, June 17, 2020
Nanosponges could intercept coronavirus infection
 Nanoparticles cloaked in human lung cell membranes and human immune cell membranes can attract and neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture, causing the virus to lose its ability to hijack host cells and reproduce.
Nanoparticles cloaked in human lung cell membranes and human immune cell membranes can attract and neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture, causing the virus to lose its ability to hijack host cells and reproduce.
Using tiny electrodes to measure electrical activity in bacteria
 Scientists have developed an organic electrochemical transistor that they can use to measure and study in fine detail a phenomenon known as extracellular electron transfer in which bacteria release electrons.
Scientists have developed an organic electrochemical transistor that they can use to measure and study in fine detail a phenomenon known as extracellular electron transfer in which bacteria release electrons.
New nanoparticle drug combination for atherosclerosis
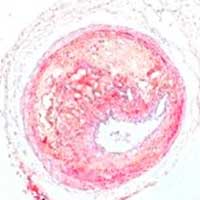 Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
Energy storage using oxygen and MOFs to boost battery performance
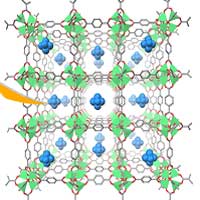 Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air.
Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air.
Physicists develop a new theory for Bose-Einstein condensates
 Bose-Einstein condensates are often described as the fifth state of matter: At extremely low temperatures, gas atoms behave like a single particle. The exact properties of these systems are notoriously difficult to study.
Bose-Einstein condensates are often described as the fifth state of matter: At extremely low temperatures, gas atoms behave like a single particle. The exact properties of these systems are notoriously difficult to study.
Tuesday, June 16, 2020
Nanomaterial gives robots chameleon skin
 A new film made of gold nanoparticles changes color in response to any type of movement. Its unprecedented qualities could allow robots to mimic chameleons and octopi - among other futuristic applications.
A new film made of gold nanoparticles changes color in response to any type of movement. Its unprecedented qualities could allow robots to mimic chameleons and octopi - among other futuristic applications.
Scientists grow optical chips in a petri dish
 Researchers propose a quick and affordable method to create optical chips right in a Petri dish.
Researchers propose a quick and affordable method to create optical chips right in a Petri dish.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
