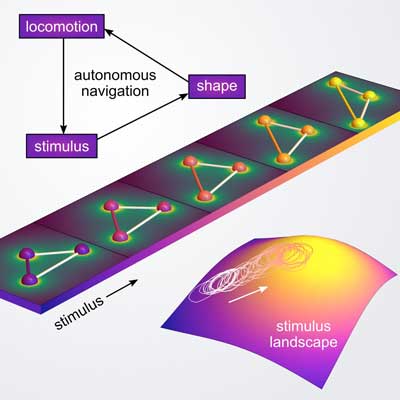
 Engineers propose a strategy for microscale robots that can sense symptoms of a material defect and navigate autonomously to the defect site, where corrective actions could be performed.
Engineers propose a strategy for microscale robots that can sense symptoms of a material defect and navigate autonomously to the defect site, where corrective actions could be performed.
Tuesday, December 10, 2019
Self-driving microrobots
 Engineers propose a strategy for microscale robots that can sense symptoms of a material defect and navigate autonomously to the defect site, where corrective actions could be performed.
Engineers propose a strategy for microscale robots that can sense symptoms of a material defect and navigate autonomously to the defect site, where corrective actions could be performed.
New laser technique images quantum world in a trillionth of a second
 Technique captures a process that commonly causes electrical resistance in materials while, in others, can cause the absence of resistance, or superconductivity.
Technique captures a process that commonly causes electrical resistance in materials while, in others, can cause the absence of resistance, or superconductivity.
Getting a closer look inside biomolecules
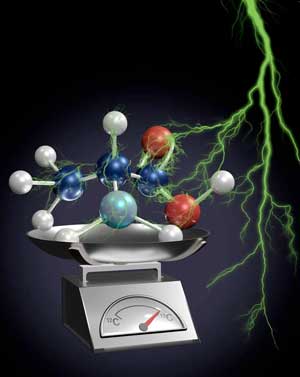 Researchers demonstrated the first use of electron microscopy for non-destructive isotope tracking in an amino acid.
Researchers demonstrated the first use of electron microscopy for non-destructive isotope tracking in an amino acid.
Tiny crystals work better when they double up with designer frameworks
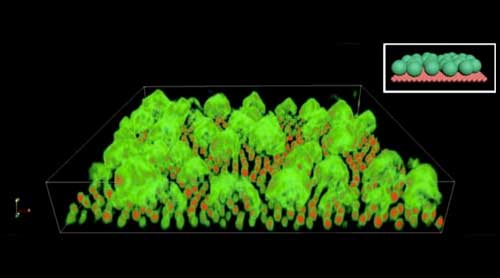 Researchers wrote a set of design rules that they then used to direct the self-assembly of the crystals and the cages into new types sheet-like structures.
Researchers wrote a set of design rules that they then used to direct the self-assembly of the crystals and the cages into new types sheet-like structures.
Pushing the precision of nanoscale mapping
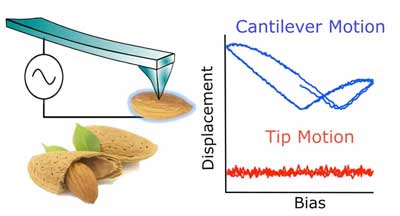 Like all scanning probe microscopes, AFM is susceptible to instrument 'crosstalk', or background signals that can mask the true atomic force measurement of interest and create misleading results. For the first time, researchers offer a new, easy-to-implement approach to overcoming crosstalk challenges in VM-AFM measurements.
Like all scanning probe microscopes, AFM is susceptible to instrument 'crosstalk', or background signals that can mask the true atomic force measurement of interest and create misleading results. For the first time, researchers offer a new, easy-to-implement approach to overcoming crosstalk challenges in VM-AFM measurements.
Researchers close in on new nonvolatile memory
 Researchers came up with a unique method for measuring the electric potential distribution across a ferroelectric capacitor - the device underlying the memory of the future, which would be orders of magnitude faster than the current flash and solid-state drives, withstanding 1 million times as many rewrite cycles.
Researchers came up with a unique method for measuring the electric potential distribution across a ferroelectric capacitor - the device underlying the memory of the future, which would be orders of magnitude faster than the current flash and solid-state drives, withstanding 1 million times as many rewrite cycles.
How to induce magnetism in graphene
 Researchers have succeeded in synthesizing a unique nanographene predicted in the 1970s, which conclusively demonstrates that carbon in very specific forms has magnetic properties that could permit future spintronic applications.
Researchers have succeeded in synthesizing a unique nanographene predicted in the 1970s, which conclusively demonstrates that carbon in very specific forms has magnetic properties that could permit future spintronic applications.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
