 Scientists discover a new, long-hypothesized material state with a signature of quantum disordered liquid-like magnetic moments.
Scientists discover a new, long-hypothesized material state with a signature of quantum disordered liquid-like magnetic moments.
Wednesday, September 4, 2019
Seeking moments of disorder
 Scientists discover a new, long-hypothesized material state with a signature of quantum disordered liquid-like magnetic moments.
Scientists discover a new, long-hypothesized material state with a signature of quantum disordered liquid-like magnetic moments.
Artificial intelligence helps to predict hybrid nanoparticle structures
 New research demonstrates a new algorithm that 'learns' to predict binding sites of molecules at the metal-molecule interface of hybrid nanoparticles by using already published experimental structural information on nanoparticle reference systems.
New research demonstrates a new algorithm that 'learns' to predict binding sites of molecules at the metal-molecule interface of hybrid nanoparticles by using already published experimental structural information on nanoparticle reference systems.
Coating nuclear materials with atomic layer deposition
 Scientists have discovered a new way to coat nuclear materials that supports efforts to minimize use of high-enriched uranium.
Scientists have discovered a new way to coat nuclear materials that supports efforts to minimize use of high-enriched uranium.
New insulation technique paves the way for more powerful and smaller chips
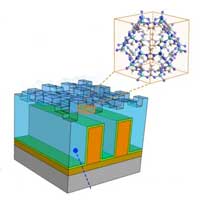 The technique uses metal-organic frameworks, a new type of materials consisting of structured nanopores. In the long term, this method can be used for the development of even smaller and more powerful chips that consume less energy
The technique uses metal-organic frameworks, a new type of materials consisting of structured nanopores. In the long term, this method can be used for the development of even smaller and more powerful chips that consume less energy
A novel recipe for efficiently removing intrinsic defects from hard crystals
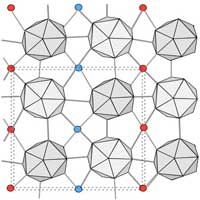 Researchers obtained an ordered phase of boron by adding hydrogen (hydrogenation) at high temperatures and through dehydrogenation by low-temperature annealing.
Researchers obtained an ordered phase of boron by adding hydrogen (hydrogenation) at high temperatures and through dehydrogenation by low-temperature annealing.
Studying heart cells with nanovolcanoes
 Researchers have developed a groundbreaking method for studying the electrical signals of cardiac muscle cells. The technology has numerous potential applications in basic and applied research - such as improving the search for mechanisms underlying cardiac arrhythmias.
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking method for studying the electrical signals of cardiac muscle cells. The technology has numerous potential applications in basic and applied research - such as improving the search for mechanisms underlying cardiac arrhythmias.
Secret messages hidden in light-sensitive polymers
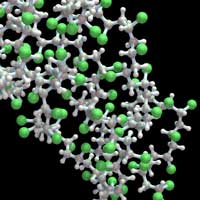 Scientists have shown how valuable light-sensitive macromolecules are: when exposed to the right wavelength of light, they can be transformed so as to change, erase or decode the molecular message that they contain.
Scientists have shown how valuable light-sensitive macromolecules are: when exposed to the right wavelength of light, they can be transformed so as to change, erase or decode the molecular message that they contain.
'Resonance' Raman spectroscopy with 1-nm resolution
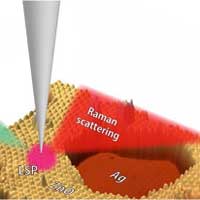 Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy resolved 'resonance' Raman scattering with 1-nm resolution in ultrathin zinc oxide films epitaxially grown on a single-crystal silver surface.
Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy resolved 'resonance' Raman scattering with 1-nm resolution in ultrathin zinc oxide films epitaxially grown on a single-crystal silver surface.
Study reveals 'radical' wrinkle in forming complex carbon molecules in space
 A team of scientists has discovered a new possible pathway toward forming carbon structures in space using a specialized chemical exploration technique.
A team of scientists has discovered a new possible pathway toward forming carbon structures in space using a specialized chemical exploration technique.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
