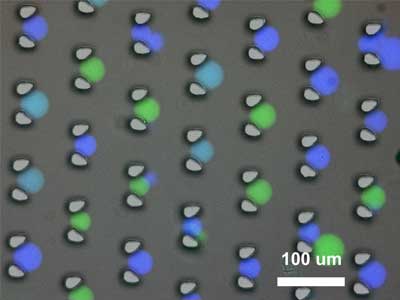
 The work provides a step towards chemical cognition in synthetic protocells and could be useful in biosensing and therapeutics.
The work provides a step towards chemical cognition in synthetic protocells and could be useful in biosensing and therapeutics.
Monday, March 4, 2019
Protocells use DNA logic to communicate and compute
 The work provides a step towards chemical cognition in synthetic protocells and could be useful in biosensing and therapeutics.
The work provides a step towards chemical cognition in synthetic protocells and could be useful in biosensing and therapeutics.
Exploring charge flow through proteins
 In a new study, scientists explore a surprising property of proteins -- one that has only recently come to light. The group demonstrates electrical conductance through proteins poised between a pair of electrodes.
In a new study, scientists explore a surprising property of proteins -- one that has only recently come to light. The group demonstrates electrical conductance through proteins poised between a pair of electrodes.
Assembly in the air: Using sound to defy gravity
 Researchers have levitated particles using sound in an experiment which could have applications in soft robotics and help reveal how planets start to form.
Researchers have levitated particles using sound in an experiment which could have applications in soft robotics and help reveal how planets start to form.
Right electrolyte doubles novel two-dimensional material's ability to store energy
 Scientists have discovered a way to improve the energy density of promising energy-storage materials, conductive two-dimensional ceramics called MXenes.
Scientists have discovered a way to improve the energy density of promising energy-storage materials, conductive two-dimensional ceramics called MXenes.
New shapes of laser beam 'sneak' through opaque media
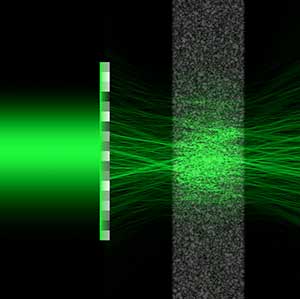 Researchers have found a way to pre-treat a laser beam so that it enters opaque surfaces without dispersing - like a headlight that?s able to cut through heavy fog at full strength.
Researchers have found a way to pre-treat a laser beam so that it enters opaque surfaces without dispersing - like a headlight that?s able to cut through heavy fog at full strength.
Chemists print sensors for nano-objects
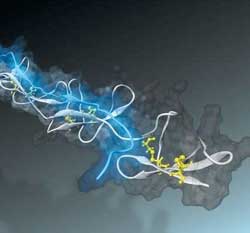 The optical nanosensors' operating principle is based on the interaction of light in thin films: a similar effect can be observed in soap bubbles. Such sensors can be quickly manufactured using an inkjet printer and special ink made of titanium dioxide.
The optical nanosensors' operating principle is based on the interaction of light in thin films: a similar effect can be observed in soap bubbles. Such sensors can be quickly manufactured using an inkjet printer and special ink made of titanium dioxide.
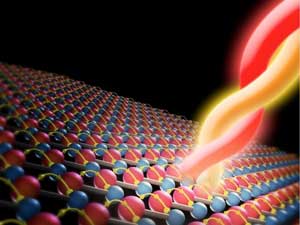
New quantum sensor could improve cancer treatment
 A new quantum sensor has proven it can outperform existing technologies and promises significant advancements in long-range 3D imaging and monitoring the success of cancer treatments.
A new quantum sensor has proven it can outperform existing technologies and promises significant advancements in long-range 3D imaging and monitoring the success of cancer treatments.
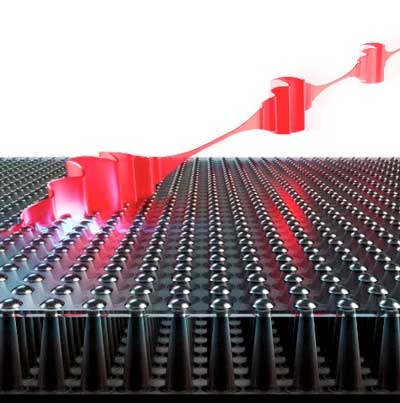
Chirality yields colossal photocurrent
 Unique Weyl semimetal delivers largest intrinsic conversion of light to electricity.
Unique Weyl semimetal delivers largest intrinsic conversion of light to electricity.
How to catch a magnetic monopole in the act
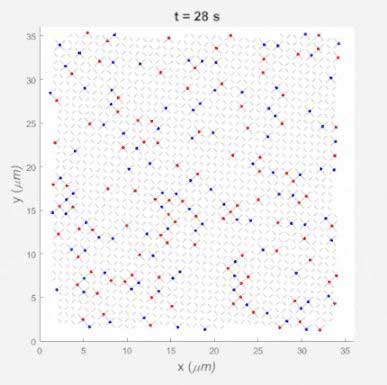 A research team has created a nanoscale 'playground' on a chip that simulates the formation of exotic magnetic particles called 'monopoles'. The study could unlock the secrets to ever-smaller, more powerful memory devices, microelectronics, and next-generation hard drives that employ the power of magnetic spin to store data.
A research team has created a nanoscale 'playground' on a chip that simulates the formation of exotic magnetic particles called 'monopoles'. The study could unlock the secrets to ever-smaller, more powerful memory devices, microelectronics, and next-generation hard drives that employ the power of magnetic spin to store data.
Magnonic devices can replace electronics without much noise
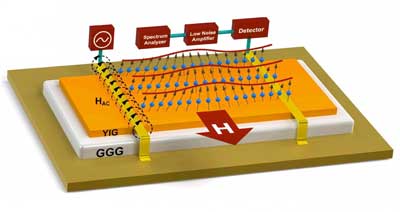 Magnonic devices of the future could use low power to avoid performance losses.
Magnonic devices of the future could use low power to avoid performance losses.
The force is with us, always? Tuning quantum vacuum forces from attractive to repulsive
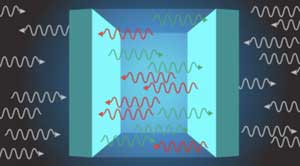 A physicist has shown for the first time that the Casimir force can be reversed and made repulsive, tunable or enhanced, based on the material inserted in between the plates.
A physicist has shown for the first time that the Casimir force can be reversed and made repulsive, tunable or enhanced, based on the material inserted in between the plates.
Ultracold atoms could provide 2D window to exotic 1D physics
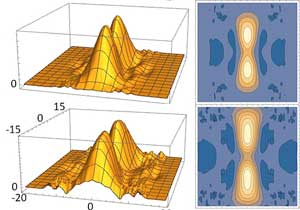 Physicists propose new vantage point to observe quantum fractionalization.
Physicists propose new vantage point to observe quantum fractionalization.
Step right up for bigger 2D sheets
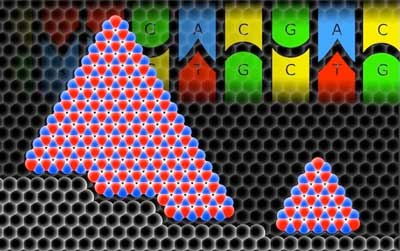 Theory shows how monocrystals of hexagonal boron nitride come together.
Theory shows how monocrystals of hexagonal boron nitride come together.
Researchers look toward nature to beat cancer
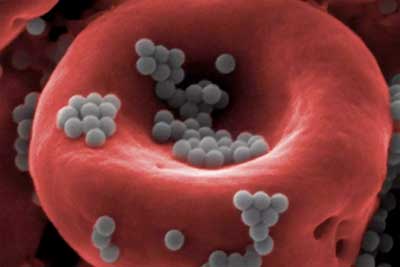 Researchers are inventing new ways to fight the deadly disease.
Researchers are inventing new ways to fight the deadly disease.
First scalable graphene yarns for wearable textiles produced
 The newly developed process has the potential produce tonnes of conductive graphene-based yarn, using existing textile machineries and without adding to production costs.
The newly developed process has the potential produce tonnes of conductive graphene-based yarn, using existing textile machineries and without adding to production costs.
Quality problems in nanomaterials curb development
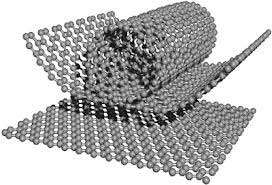 The problem is that it is difficult to analyse the crystal structure and there are no established standard methods for classifying the materials.
The problem is that it is difficult to analyse the crystal structure and there are no established standard methods for classifying the materials.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
