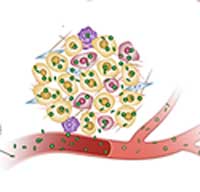
 Scientists propose a bioinspired lipoproteins (bLP)-mediated strategy, aiming at inducing photothermia to disrupt the tumor stromal microenvironments (TSM) barriers and augmenting the accessibility of second-wave nanoparticles to cancer cells to suppress tumor relapse and metastasis.
Scientists propose a bioinspired lipoproteins (bLP)-mediated strategy, aiming at inducing photothermia to disrupt the tumor stromal microenvironments (TSM) barriers and augmenting the accessibility of second-wave nanoparticles to cancer cells to suppress tumor relapse and metastasis.
Friday, July 26, 2019
Bioinspired nanoparticles remodel tumor stroma to enhance nanoparticle accessibility to cancer cells
 Scientists propose a bioinspired lipoproteins (bLP)-mediated strategy, aiming at inducing photothermia to disrupt the tumor stromal microenvironments (TSM) barriers and augmenting the accessibility of second-wave nanoparticles to cancer cells to suppress tumor relapse and metastasis.
Scientists propose a bioinspired lipoproteins (bLP)-mediated strategy, aiming at inducing photothermia to disrupt the tumor stromal microenvironments (TSM) barriers and augmenting the accessibility of second-wave nanoparticles to cancer cells to suppress tumor relapse and metastasis.
Yellow is not the new black: Discovery paves way for new generation of solar cells
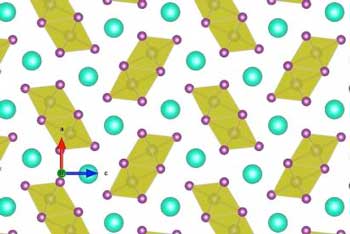 A study for the first time explains how a promising type of perovskites - man-made crystals that can convert sunlight into electricity - can be stabilized. As a result, the crystals turn black, enabling them to absorb sunlight.
A study for the first time explains how a promising type of perovskites - man-made crystals that can convert sunlight into electricity - can be stabilized. As a result, the crystals turn black, enabling them to absorb sunlight.
Shaping light with a smartlens
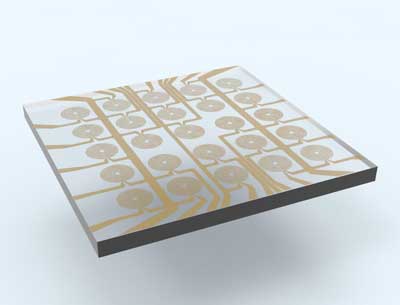 A team of researchers reports on a dynamically tuneable lens capable of achieving almost any complex optical function.
A team of researchers reports on a dynamically tuneable lens capable of achieving almost any complex optical function.
New quantum phenomenon helps to understand fundamental limits of graphene electronics
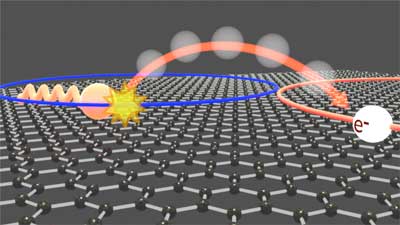 A new study describes how electrons in a single atomically-thin sheet of graphene scatter off the vibrating carbon atoms which make up the hexagonal crystal lattice.
A new study describes how electrons in a single atomically-thin sheet of graphene scatter off the vibrating carbon atoms which make up the hexagonal crystal lattice.
Next-generation graphene membranes for carbon capture
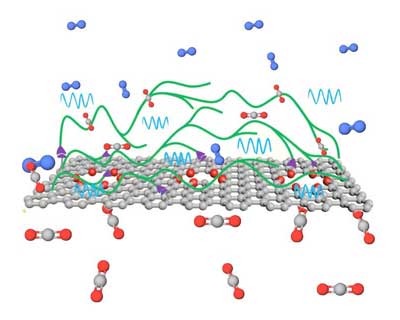 Chemical engineers have developed a new class of high-performance membranes for carbon capture that greatly exceed current targets.
Chemical engineers have developed a new class of high-performance membranes for carbon capture that greatly exceed current targets.
Listening to the whispers of individual cells
 A new method developed by biophysicists has made it possible for the first time to detect and analyse signals between individual cells.
A new method developed by biophysicists has made it possible for the first time to detect and analyse signals between individual cells.
Synthetic biology enables protein origami
 Engineers find new way to create single-chain protein nanostructures using synthetic biology and protein-assembly techniques.
Engineers find new way to create single-chain protein nanostructures using synthetic biology and protein-assembly techniques.
Physicists discover new quantum trick for graphene: magnetism
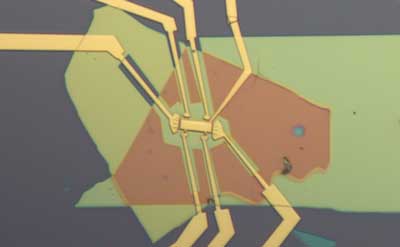 Physicists were stunned when two twisted sheets of graphene showed signs of superconductivity. Now scientists have shown that the material also generates a type of magnetism once only dreamed of theoretically.
Physicists were stunned when two twisted sheets of graphene showed signs of superconductivity. Now scientists have shown that the material also generates a type of magnetism once only dreamed of theoretically.
Designed switch allows unprecedented control over living cells
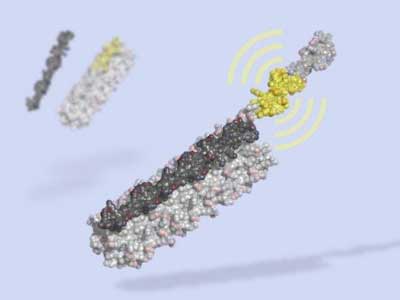 From modifying gene expression to cell signaling, dynamic designer proteins may usher in a new era of synthetic biology.
From modifying gene expression to cell signaling, dynamic designer proteins may usher in a new era of synthetic biology.
Mimicking lizard skin to save energy on an industrial scale
 The LABIONICS project is set to drive the commercial development of breakthrough laser-engineered products inspired by the unique skin and scale textures of animals and insects, potentially leading to entirely new applications across industry, energy and medicine.
The LABIONICS project is set to drive the commercial development of breakthrough laser-engineered products inspired by the unique skin and scale textures of animals and insects, potentially leading to entirely new applications across industry, energy and medicine.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
