Wednesday, February 13, 2019
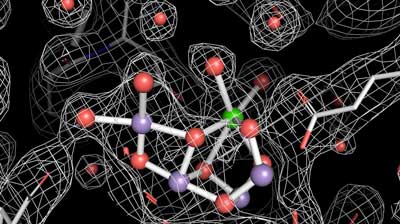
Atomic snapshots of photosynthesis
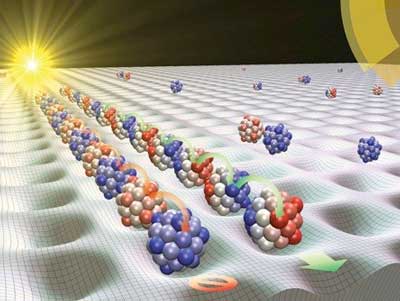
First direct view of an electron's short, speedy trip across a border
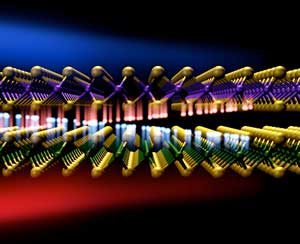
Too close for comfort: Nanoparticles need some space to transfer energy
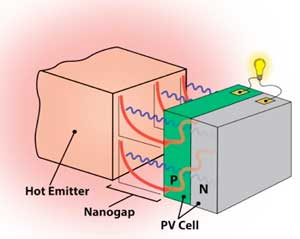
Running an LED in reverse could cool future computers
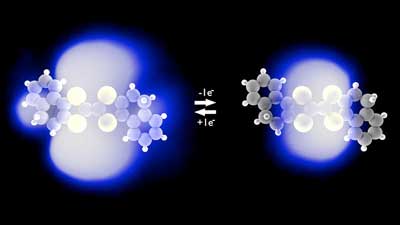
Physicists watch electron transfer in a single molecule
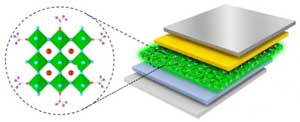
New approach improving stability and optical properties of perovskite films
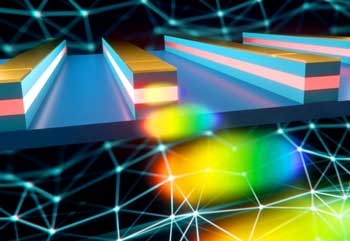
Engineers develop high-performance quantum dot mode-locked laser on silicon
Graphene and 2D materials on track to innovative applications

Sensitive biosensor detects Down syndrome DNA
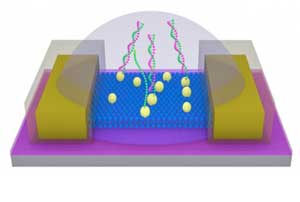
Customized mix of materials for three-dimensional micro- and nanostructures
What happens to magnetic nanoparticles once in cells?
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
