 Scientists have come up with a systematic method for studying and even predicting gene expression - without using cells. Using their innovative, quantitative approach, they measured important parameters governing gene regulation. This allowed them to design and construct a synthetic biological logic gate, which could one day be used to introduce new functions into cells.
Scientists have come up with a systematic method for studying and even predicting gene expression - without using cells. Using their innovative, quantitative approach, they measured important parameters governing gene regulation. This allowed them to design and construct a synthetic biological logic gate, which could one day be used to introduce new functions into cells.
Monday, March 25, 2019
Engineering cellular function without living cells
 Scientists have come up with a systematic method for studying and even predicting gene expression - without using cells. Using their innovative, quantitative approach, they measured important parameters governing gene regulation. This allowed them to design and construct a synthetic biological logic gate, which could one day be used to introduce new functions into cells.
Scientists have come up with a systematic method for studying and even predicting gene expression - without using cells. Using their innovative, quantitative approach, they measured important parameters governing gene regulation. This allowed them to design and construct a synthetic biological logic gate, which could one day be used to introduce new functions into cells.
Cellulose nanofiber hydrogel for enhanced cell encapsulation and delivery
 Cellulose nanofibers hydrogel has great potential as a cell-encapsulation delivery carrier for sustained release of paracrine factors and for tissue regeneration, with unique versatility for injection, scaffolding, and 3D bioprinting.
Cellulose nanofibers hydrogel has great potential as a cell-encapsulation delivery carrier for sustained release of paracrine factors and for tissue regeneration, with unique versatility for injection, scaffolding, and 3D bioprinting.
Nanocellulose-based material gives three sensors in one
 Cellulose soaked in a carefully designed polymer mixture acts as a sensor to measure pressure, temperature and humidity -- at the same time. The measurements are completely independent of each other. The sensor may be highly significant in fields such as robotics, healthcare and security.
Cellulose soaked in a carefully designed polymer mixture acts as a sensor to measure pressure, temperature and humidity -- at the same time. The measurements are completely independent of each other. The sensor may be highly significant in fields such as robotics, healthcare and security.
Physicists shatter Bose-Einstein condensate, get different pieces every time
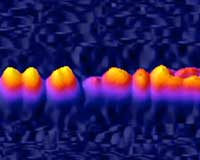 Physicists have shown that shaking ultracold Bose-Einstein condensates can cause them to either divide into uniform segments or shatter into unpredictable splinters, depending on the frequency of the shaking.
Physicists have shown that shaking ultracold Bose-Einstein condensates can cause them to either divide into uniform segments or shatter into unpredictable splinters, depending on the frequency of the shaking.
Extremely accurate measurements of atom states for quantum computing
 A new method allows the quantum state of atomic qubits to be measured with twenty times less error than was previously possible, without losing any atoms.
A new method allows the quantum state of atomic qubits to be measured with twenty times less error than was previously possible, without losing any atoms.
Wood-based technology creates electricity from heat
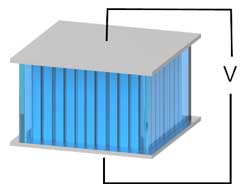 Researchers have created a heat-to-electricity device that runs on ions and which could someday harness the body?s heat to provide energy.
Researchers have created a heat-to-electricity device that runs on ions and which could someday harness the body?s heat to provide energy.
Gold soaks up boron, spits out borophene
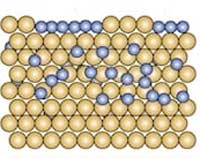 In the heat of a furnace, boron atoms happily dive into a bath of gold. And when things get cool, they resurface as coveted borophene.
In the heat of a furnace, boron atoms happily dive into a bath of gold. And when things get cool, they resurface as coveted borophene.
Optimizing the energy production of photovoltaic panels using artificial intelligence
 Researchers have developed a method based on artificial intelligence techniques that consider the atmospheric variations when designing the solar cells to produce more energy.
Researchers have developed a method based on artificial intelligence techniques that consider the atmospheric variations when designing the solar cells to produce more energy.
Scientists squeeze catalysts inside host materials like a ship into a bottle
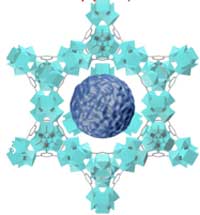 Scientists have found a way to place catalysts inside the tiniest pores of different host materials, a bit like when model ships are unfolded inside a bottle.
Scientists have found a way to place catalysts inside the tiniest pores of different host materials, a bit like when model ships are unfolded inside a bottle.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
