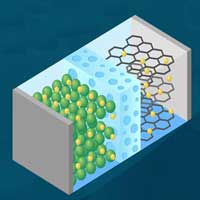
 Doping carbon anode material with different atoms increases the performance of sodium-ion batteries.
Doping carbon anode material with different atoms increases the performance of sodium-ion batteries.
Monday, January 25, 2021
Revolutionizing rechargeable sodium-ion batteries with doped carbon anodes
 Doping carbon anode material with different atoms increases the performance of sodium-ion batteries.
Doping carbon anode material with different atoms increases the performance of sodium-ion batteries.
Better bundled: new principle for generating X-rays
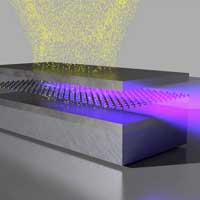 Physicists develop method in which beams are simultaneously generated and guided by sandwich structure.
Physicists develop method in which beams are simultaneously generated and guided by sandwich structure.
Scientists design stretchable electronics to perform better under strain
 By incorporating a patterned material that optimizes strain distribution among transistors, researchers have created stretchable electronics that are less compromised by deformation. They also created several circuit elements with the design, which could lead to even more types of stretchable electronics.
By incorporating a patterned material that optimizes strain distribution among transistors, researchers have created stretchable electronics that are less compromised by deformation. They also created several circuit elements with the design, which could lead to even more types of stretchable electronics.
Research network aims to drive generation of nanostructures with finely focused ion beams
 A finely focused ion beam (FIB) is a very useful tool in nanotechnology and analytics. Until now, scientists have mainly used FIB technology to prepare samples for certain microscopic techniques, such as troubleshooting in the semiconductor industry. But FIBs can do much more.
A finely focused ion beam (FIB) is a very useful tool in nanotechnology and analytics. Until now, scientists have mainly used FIB technology to prepare samples for certain microscopic techniques, such as troubleshooting in the semiconductor industry. But FIBs can do much more.
Optimal information about the invisible
 Scientists show that meaningful laser measurement data results can be obtained even in complicated environments.
Scientists show that meaningful laser measurement data results can be obtained even in complicated environments.
New study claims graphene manufacturing is mature enough to produce prototypes and some real-life niche applications
 Two new papers roadmap the expected future mass introduction of graphene and related materials in the market.
Two new papers roadmap the expected future mass introduction of graphene and related materials in the market.
Nanomedicine's 'crown' is ready for its close up
 An international team of researchers has developed a new method to better understand how nanomedicines interact with patients' biomolecules.
An international team of researchers has developed a new method to better understand how nanomedicines interact with patients' biomolecules.
Atomically precise noble metal nanoclusters: New emerging metal nanomaterials
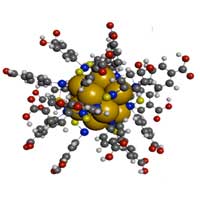 Unlike plasmon gold nanoparticles, which have continuous or semi-continuous energy levels, gold nanoclusters have a distinctive discrete electronic structure and molecular-like properties, such as enhanced photoluminescence, intrinsic magnetism, intrinsic chirality and discrete redox behavior.
Unlike plasmon gold nanoparticles, which have continuous or semi-continuous energy levels, gold nanoclusters have a distinctive discrete electronic structure and molecular-like properties, such as enhanced photoluminescence, intrinsic magnetism, intrinsic chirality and discrete redox behavior.
Microswimmers can learn from bubbles how to swim efficiently
 Researchers show that the secret to optimal micro-swimming is out there in the nature. They prove that a microswimmer can increase its swimming efficiency by learning the swimming techniques from an unexpected mentor: an air bubble.
Researchers show that the secret to optimal micro-swimming is out there in the nature. They prove that a microswimmer can increase its swimming efficiency by learning the swimming techniques from an unexpected mentor: an air bubble.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
