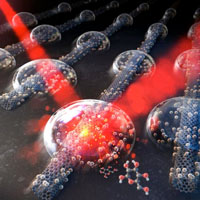
 A novel technology, capable of analyzing nanomaterials in our daily lives with the use of common 'salt' has been developed. This allows various molecules to amplify up to hundreds of times the signals they produce in response to light, thereby making them very useful for nanomaterial research.
A novel technology, capable of analyzing nanomaterials in our daily lives with the use of common 'salt' has been developed. This allows various molecules to amplify up to hundreds of times the signals they produce in response to light, thereby making them very useful for nanomaterial research.
Friday, March 13, 2020
New study presents hygroscopic micro/nanolenses along carbon nanotube ion channels
 A novel technology, capable of analyzing nanomaterials in our daily lives with the use of common 'salt' has been developed. This allows various molecules to amplify up to hundreds of times the signals they produce in response to light, thereby making them very useful for nanomaterial research.
A novel technology, capable of analyzing nanomaterials in our daily lives with the use of common 'salt' has been developed. This allows various molecules to amplify up to hundreds of times the signals they produce in response to light, thereby making them very useful for nanomaterial research.
Discovery of zero-energy bound states at both ends of a one-dimensional atomic line defect
 Scientists discovered Majorana zero modes at both ends of 1D atomic line defects in two-dimensional iron-based high-temperature superconductors.
Scientists discovered Majorana zero modes at both ends of 1D atomic line defects in two-dimensional iron-based high-temperature superconductors.
Pathways toward realizing the promise of all-solid-state batteries
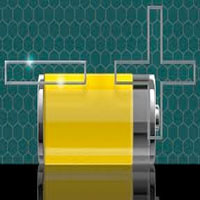 Nanoengineers offer a research roadmap that includes four challenges that need to be addressed in order to advance a promising class of batteries - all-solid-state batteries - to commercialization.
Nanoengineers offer a research roadmap that includes four challenges that need to be addressed in order to advance a promising class of batteries - all-solid-state batteries - to commercialization.
3D Hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst helps efficiently reduce CO2
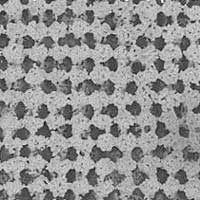 Researchers developed a three-dimensional hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst with carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide conversion rate up to 3.96 times higher than that of conventional nanoporous gold catalysts.
Researchers developed a three-dimensional hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst with carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide conversion rate up to 3.96 times higher than that of conventional nanoporous gold catalysts.
A scalable production system for MXenes
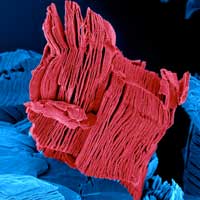 Researchers have designed a system that can be used to make large quantities of the material while preserving its unique properties. The lab-scale reactor system can convert a ceramic precursor material into a pile of the powdery black MXene titanium carbide, in quantities as large as 50 grams per batch.
Researchers have designed a system that can be used to make large quantities of the material while preserving its unique properties. The lab-scale reactor system can convert a ceramic precursor material into a pile of the powdery black MXene titanium carbide, in quantities as large as 50 grams per batch.
Water-free way to make MXenes could mean new uses for the promising nanomaterials
 The new discovery removes water from the MXene-making process, which means the materials can be used in applications in which water is a contaminant or hampers performance, such as battery electrodes and next-generation solar cells.
The new discovery removes water from the MXene-making process, which means the materials can be used in applications in which water is a contaminant or hampers performance, such as battery electrodes and next-generation solar cells.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
