
Wednesday, November 28, 2018
New device widens light beams by 400 times
Flexible electronic skin aids human-machine interactions

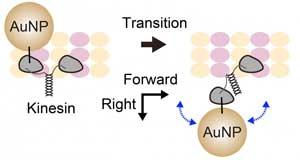
Gold nanoparticle microsecond tracking with atomic-level localization precision
Nanoscale blood test technique set to springboard cancer discoveries
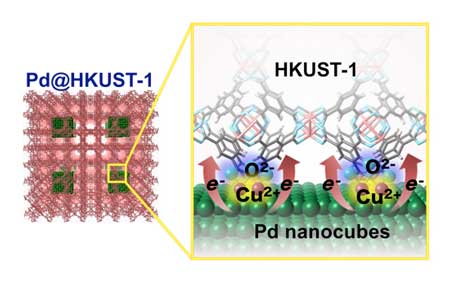
Interfacial electronic state improving hydrogen storage capacity in Pd-MOF materials
A golden age for particle analysis

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
