
Thursday, March 15, 2018
Spin memory - Dynamic solution for accurate reading
A sensing scheme that responds dynamically to voltage fluctuations could improve accuracy when reading data from spin-based memory storage.
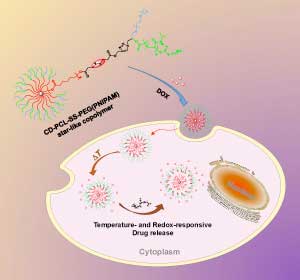
Nanoscale drug delivery particles that can sense their surroundings
Star-shaped nanoparticles that release their drug payload only after entering cells could improve current treatments.
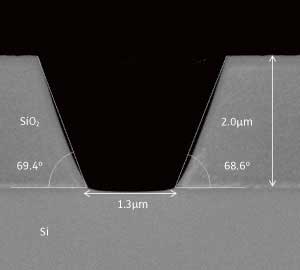
A better angle on microscopic devices
A flexible, low-cost technique could lead to the mass production of microelectromechanical systems for use in a range of applications.
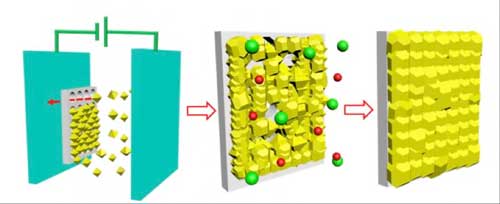
Metal-organic frameworks cut energy consumption of petrochemicals
Chemical Engineers have developed a new method for making meta-organic framework membranes that can be used to considerably improve energy-expensive processes such as propylene-propane separation, which accounts for 40% of energy used in the global petrochemical industry.
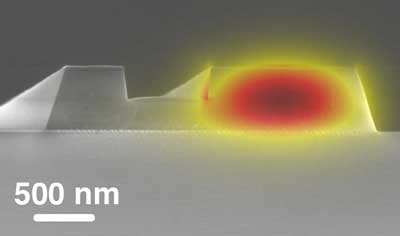
Frequency combs ID chemicals within the mid-infrared spectral region
Our health, safety, and well-being depend on how well we know the chemicals that surround us, and the development of new laser sources will now make it possible to identify chemicals with greater sensitivity.
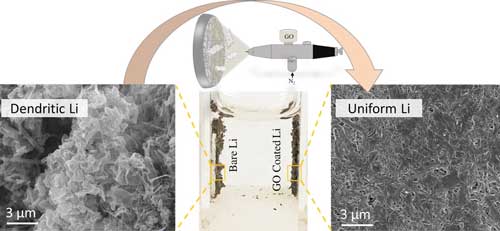
Graphene oxide nanosheets could help bring lithium-metal batteries to market
Researchers have developed a form of a graphene-oxide coated 'nanosheet' that, when placed in between the two electrodes of a lithium-metal battery, prevents uneven plating of lithium and allows the battery to safely function for hundreds of charge/discharge cycles.
Research on bismuth ferrite could lead to new types of electrical devices
New research makes a significant step toward a new kind of electrical device, which would use the natural properties of materials like bismuth ferrite, along with a different type of current, to send electricity quickly through smaller, denser circuits.
Splicing together a thin film in motion
Recent work provides a new approach to imaging thin films on the atomic scale. It is made possible using an algorithm for image recovery that splices together a sequence of frames in time.
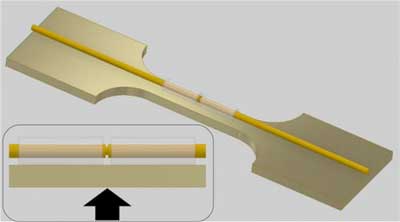
Measuring electrical conductance across a single molecule
Scientists developed a stable mechanical design to measure electrical current across a single molecule that assembles on a noble metal at room temperature.
Graphene finds new application as non-toxic, anti-static hair dye
New formula works as well as commercial permanent dyes without chemically altering hairs.

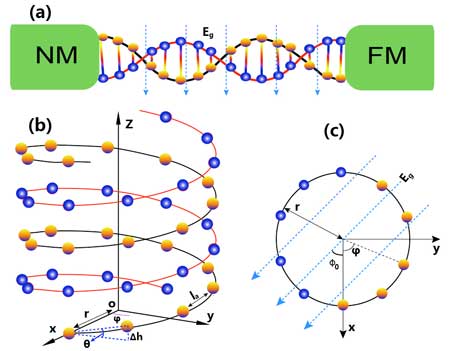
Thermally driven spin current in DNA
Researchers for the first time explore fundamental aspects of unidirectional spin transport along a double-stranded DNA molecule driven by a temperature gradient.
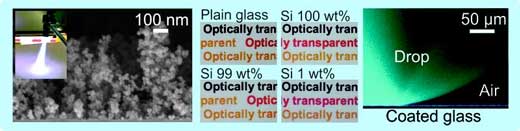
Speedy surfaces
Researchers have found a new way of applying a structured coating for liquid repellency. By using liquid flame spray, the method is extremely fast. Not only water but also oil drops do not adhere to these surfaces but remain spherical and bounce or roll off easily.
New quantum spin liquid predicted by Nobel Laureate prepared for the first time
This achievement is an important step towards building so-called topological quantum computers.
Ultra-white nanocoating modelled on beetle scales
Researchers have developed a super-thin, non-toxic, lightweight, edible ultra-white coating that could be used to make brighter paints and coatings, for use in the cosmetic, food or pharmaceutical industries.

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
