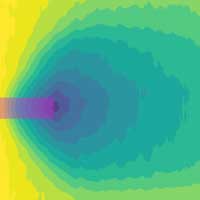
 In a step toward making more accurate and uniform 3D-printed parts such as personalized prosthetics and dental materials, researchers have demonstrated a method of measuring the rate at which microscopic regions of a liquid raw material harden into a solid plastic when exposed to light.
In a step toward making more accurate and uniform 3D-printed parts such as personalized prosthetics and dental materials, researchers have demonstrated a method of measuring the rate at which microscopic regions of a liquid raw material harden into a solid plastic when exposed to light.
Thursday, December 10, 2020
Nanocylinder vibrations help quantify polymer curing for 3D printing
 In a step toward making more accurate and uniform 3D-printed parts such as personalized prosthetics and dental materials, researchers have demonstrated a method of measuring the rate at which microscopic regions of a liquid raw material harden into a solid plastic when exposed to light.
In a step toward making more accurate and uniform 3D-printed parts such as personalized prosthetics and dental materials, researchers have demonstrated a method of measuring the rate at which microscopic regions of a liquid raw material harden into a solid plastic when exposed to light.
Researchers identify the physical mechanism that can kill bacteria with gold nanoparticles
 The research opens the door to the development of new bactericide materials as an alternative to antibiotics.
The research opens the door to the development of new bactericide materials as an alternative to antibiotics.
Researchers demonstrate nondestructive mid-infrared imaging using entangled photons
 Researchers have shown that entangled photons can be used to improve the penetration depth of optical coherence tomography (OCT) in highly scattering materials. The method represents a way to perform OCT with mid-infrared wavelengths and could be useful for non-destructive testing and analysis of materials such as ceramics and paint samples.
Researchers have shown that entangled photons can be used to improve the penetration depth of optical coherence tomography (OCT) in highly scattering materials. The method represents a way to perform OCT with mid-infrared wavelengths and could be useful for non-destructive testing and analysis of materials such as ceramics and paint samples.
Femtochip: paving the way to innovative lasers
 Major advances in laser physics, microtechnology and materials science are needed before an integrated short-pulse laser can be realised on a chip, and a newly funded research project is striving to make these advances.
Major advances in laser physics, microtechnology and materials science are needed before an integrated short-pulse laser can be realised on a chip, and a newly funded research project is striving to make these advances.
Topological insulators for quantum simulators
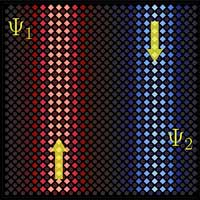 A recent study reports on how the many-body interactions in topological insulators can be of great advantage for quantum simulations of complex systems.
A recent study reports on how the many-body interactions in topological insulators can be of great advantage for quantum simulations of complex systems.
Making cheaper, biocompatible E-skin electrodes
 Materials scientists have improved electrical conductivity in a polymer electrode for E-skin applications. Their approach is simple and cheap, but further enhancements are needed for the polymer to become a viable alternative to more expensive gold electrodes.
Materials scientists have improved electrical conductivity in a polymer electrode for E-skin applications. Their approach is simple and cheap, but further enhancements are needed for the polymer to become a viable alternative to more expensive gold electrodes.
Tiny bubbles on electrodes key to speeding up chemical processes
 New research has shown the formation of bubbles on electrodes, usually thought to be a hindrance, can be beneficial, with deliberately added bubbles, or oil droplets, able to accelerate processes such as the removal of pollutants including hydrocarbons from contaminated water and the production of chlorine.
New research has shown the formation of bubbles on electrodes, usually thought to be a hindrance, can be beneficial, with deliberately added bubbles, or oil droplets, able to accelerate processes such as the removal of pollutants including hydrocarbons from contaminated water and the production of chlorine.
Researchers control multiple wavelengths of light from a single source
 Researchers have synthesized a collection of nanoparticles, known as carbon dots, capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of light from a single particle. Additionally, the team discovered that the dispersion of the carbon dots, or the interparticle distance between each dot, influences the properties of the light the carbon dots emit.
Researchers have synthesized a collection of nanoparticles, known as carbon dots, capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of light from a single particle. Additionally, the team discovered that the dispersion of the carbon dots, or the interparticle distance between each dot, influences the properties of the light the carbon dots emit.
A comprehensive review of biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages
 Bioengineers conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms.
Bioengineers conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
