 Researchers have developed an all-glass, centimeter-scale metalens in the visible spectrum that can be manufactured using conventional chip fabrication methods.
Researchers have developed an all-glass, centimeter-scale metalens in the visible spectrum that can be manufactured using conventional chip fabrication methods.
Tuesday, December 3, 2019
Metalens grows up
 Researchers have developed an all-glass, centimeter-scale metalens in the visible spectrum that can be manufactured using conventional chip fabrication methods.
Researchers have developed an all-glass, centimeter-scale metalens in the visible spectrum that can be manufactured using conventional chip fabrication methods.
Bending an organic semiconductor can boost electrical flow
 Slightly bending semiconductors made of organic materials can roughly double the speed of electricity flowing through them and could benefit next-generation electronics such as sensors and solar cells.
Slightly bending semiconductors made of organic materials can roughly double the speed of electricity flowing through them and could benefit next-generation electronics such as sensors and solar cells.
Diamonds in your devices: Powering the next generation of energy storage
 Using conductive nanodiamond as electrode material in a water-based cell significantly increases its energy storage capacity.
Using conductive nanodiamond as electrode material in a water-based cell significantly increases its energy storage capacity.
Towards high quality ZnO quantum dots prospective for biomedical applications
 Scientists have moved a step closer to creating stable, high quality colloidal zinc oxide quantum dots (ZnO QDs) for use in modern technologies and nanomedicine. Using advanced DNP-enhanced NMR spectroscopy they have clearly proved the superiority of the developed organometallic approach over the traditional sol-gel procedure both in terms of stability and the highly-ordered organic shell of the resulting ZnO QDs.
Scientists have moved a step closer to creating stable, high quality colloidal zinc oxide quantum dots (ZnO QDs) for use in modern technologies and nanomedicine. Using advanced DNP-enhanced NMR spectroscopy they have clearly proved the superiority of the developed organometallic approach over the traditional sol-gel procedure both in terms of stability and the highly-ordered organic shell of the resulting ZnO QDs.
Imaging technique gives catalytic 2D material engineering a better view
 A scanning electrochemical cell imaging technique shows how nanoscale structural features affect the catalytic activity of MoS2 monolayers for hydrogen evolution reactions.
A scanning electrochemical cell imaging technique shows how nanoscale structural features affect the catalytic activity of MoS2 monolayers for hydrogen evolution reactions.
Electron correlations in carbon nanostructures
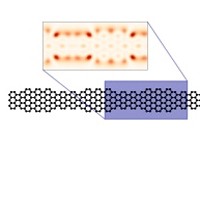 Physicists elucidate the behaviour of electrons in graphene nanoribbons.
Physicists elucidate the behaviour of electrons in graphene nanoribbons.
Grain boundaries in graphene do not affect spin transport
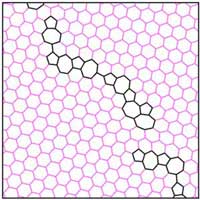 Researchers have used numerical simulations to show that spin diffusion length is independent of grain size. The results have implications for the optimisation of graphene-based spintronic devices.
Researchers have used numerical simulations to show that spin diffusion length is independent of grain size. The results have implications for the optimisation of graphene-based spintronic devices.
Magnetic nanoparticles for water purification
 Scientists have introduced a new water purification method based on magnetic nanoparticles coated with a so-called 'ionic liquid' that simultaneously remove organic, inorganic, and microbial contaminants, as well as microplastics. The nanoparticles are then easily removed with magnets.
Scientists have introduced a new water purification method based on magnetic nanoparticles coated with a so-called 'ionic liquid' that simultaneously remove organic, inorganic, and microbial contaminants, as well as microplastics. The nanoparticles are then easily removed with magnets.
Hiring antibodies as nanotechnology builders
 Researchers recruit antibodies as molecular builders to assemble nanoscale structures made of synthetic DNA.
Researchers recruit antibodies as molecular builders to assemble nanoscale structures made of synthetic DNA.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
