
Monday, April 30, 2018
Magnetic nanoparticles leap from lab bench to breast cancer clinical trials
Magnetic nanoparticles will be used for their first breast cancer clinical trial later this year.
Water-repellent surfaces can efficiently boil water, keep electronics cool
Surfaces that repel water can support efficient boiling if all air and vapor is removed from a system first.

Scientists create nanomaterials that reconfigure in response to biochemical signals
Researchers are developing self-assembling electronic nanomaterials that can respond to biochemical signals for potential therapeutic use.
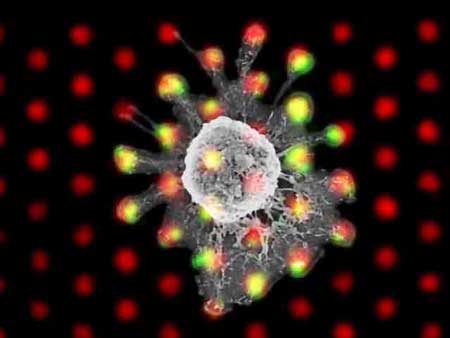
Geometry is key to T-cell triggering
Engineers discover geometric underpinnings of T-cell stimulation through precise engineering of T-cell receptor geometry, building a 3D nanofabricated biomimetic surface that simulates the key components of an antigen-presenting cell.
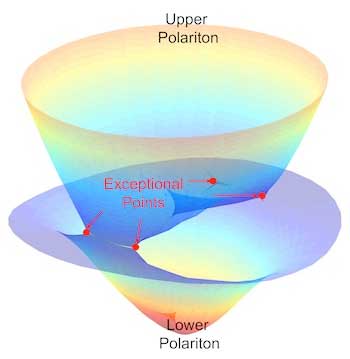
Scientists make tunable light-matter couplings in nanotube films
Researchers discover exceptional points in a unique material they created.
Stagediving with biomolecules improves optical microscopy
Physicists have developed a novel method for optical microscopy. Using biological motors and single quantum dots, they acquire ultra-high-resolution images.
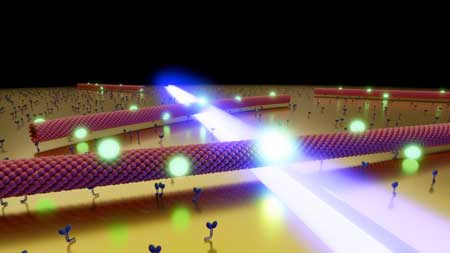
Topological insulator 'flips' for superconductivity
Topology meets superconductivity through innovative reverse-order sample preparation.
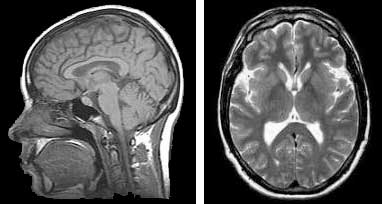
Nanoparticles developed to improve magnetic resonance scan images
Clinical use of these nanoparticles in MRI scans could facilitate the diagnosis of hepatic, pulmonary and cardiovascular pathologies, as well as many types of tumours.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
