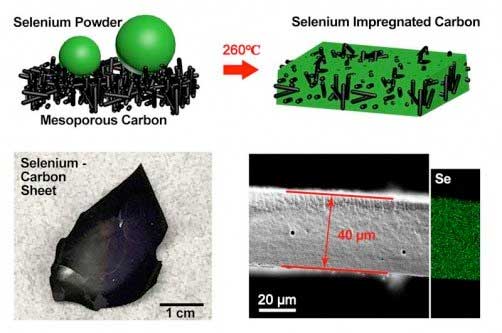
 New self-supporting composite metal material doubles the volumetric energy and achieves fast charging rates in batteries.
New self-supporting composite metal material doubles the volumetric energy and achieves fast charging rates in batteries.
Thursday, June 27, 2019
Novel electrodes enhance battery capacity
 New self-supporting composite metal material doubles the volumetric energy and achieves fast charging rates in batteries.
New self-supporting composite metal material doubles the volumetric energy and achieves fast charging rates in batteries.
New technology gives insight into how nanomaterials form and grow
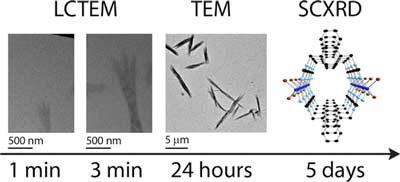 A new form of electron microscopy allows researchers to examine nanoscale tubular materials while they are 'alive' and forming liquids - a first in the field.
A new form of electron microscopy allows researchers to examine nanoscale tubular materials while they are 'alive' and forming liquids - a first in the field.
Portable gas detection shrinks to new dimensions
 The banknote-size sensor can identify each ingredient of a 29-compound mixture in seven seconds. The system also reliably detected compounds that simulate mustard gas and phosphonate-based nerve agents during 40 days of continuous operation.
The banknote-size sensor can identify each ingredient of a 29-compound mixture in seven seconds. The system also reliably detected compounds that simulate mustard gas and phosphonate-based nerve agents during 40 days of continuous operation.
Bursts of light shape walls between waves of charge
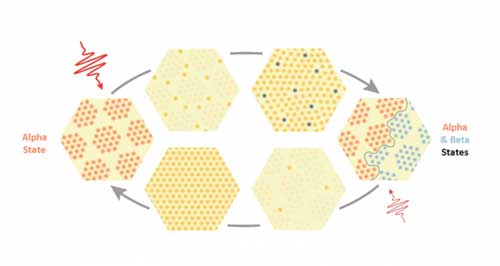 New method provides ultrafast switching of electronic structure and illuminates fundamentals of charge ordering, potentially offering a simple path for next-generation data storage.
New method provides ultrafast switching of electronic structure and illuminates fundamentals of charge ordering, potentially offering a simple path for next-generation data storage.
A new way to make droplets bounce away
 Engineers design surfaces that send rain flying away, potentially preventing icing or soaking.
Engineers design surfaces that send rain flying away, potentially preventing icing or soaking.
Thermoelectric nanomaterial turns waste heat back into electricity
 A low-temperature method for making high-performance thermoelectric materials could recapture lost energy.
A low-temperature method for making high-performance thermoelectric materials could recapture lost energy.
Printing graphene inks in space
 Studying the different self-assembly modes of graphene into functional patterns in zero-gravity will enable the fabrication of graphene electronic devices during long-term space missions, as well as help understand fundamental properties of graphene printing on Earth.
Studying the different self-assembly modes of graphene into functional patterns in zero-gravity will enable the fabrication of graphene electronic devices during long-term space missions, as well as help understand fundamental properties of graphene printing on Earth.
Improved technique for using magnetic nanoclusters to kill hard-to-reach tumors
 Researchers developed nanoclusters, multiatom collections of nanoparticles, with enhanced heating efficiency. The nanoclusters are hexagon-shaped iron oxide nanoparticles doped with cobalt and manganese and loaded into biodegradable nanocarriers.
Researchers developed nanoclusters, multiatom collections of nanoparticles, with enhanced heating efficiency. The nanoclusters are hexagon-shaped iron oxide nanoparticles doped with cobalt and manganese and loaded into biodegradable nanocarriers.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
