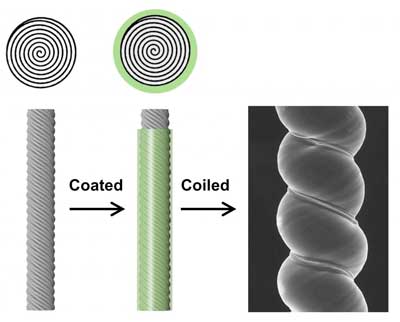
 To form the new muscles, the research team applied a polymer coating to twisted CNT yarns, as well as to inexpensive nylon, silk and bamboo yarns, creating a sheath around the yarn core.
To form the new muscles, the research team applied a polymer coating to twisted CNT yarns, as well as to inexpensive nylon, silk and bamboo yarns, creating a sheath around the yarn core.
Thursday, July 11, 2019
Sheaths drive powerful new artificial muscles
 To form the new muscles, the research team applied a polymer coating to twisted CNT yarns, as well as to inexpensive nylon, silk and bamboo yarns, creating a sheath around the yarn core.
To form the new muscles, the research team applied a polymer coating to twisted CNT yarns, as well as to inexpensive nylon, silk and bamboo yarns, creating a sheath around the yarn core.
Artificial 'muscles' achieve powerful pulling force
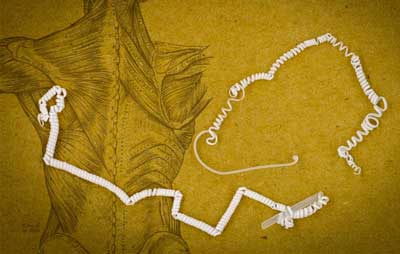 New system of contracting fibers could be a boon for biomedical devices and robotics.
New system of contracting fibers could be a boon for biomedical devices and robotics.
Nanotechnology delivers hepatitis B vaccine
 X-ray imaging shows that nanostructured silica acts as a protective vehicle to deliver intact antigen to the intestine so that it can trigger an immune response. The material can give rise to a polyvaccine against six diseases.
X-ray imaging shows that nanostructured silica acts as a protective vehicle to deliver intact antigen to the intestine so that it can trigger an immune response. The material can give rise to a polyvaccine against six diseases.
Compact atomic gyroscope displays new twists
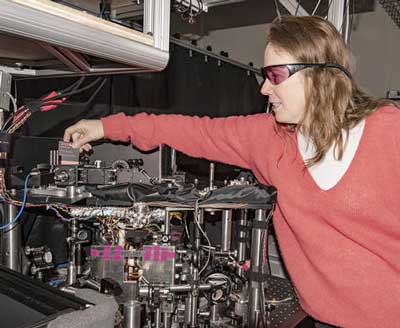 Researchers have upgraded their compact atomic gyroscope to enable multitasking measurement capabilities and measure its performance, important steps toward practical applications.
Researchers have upgraded their compact atomic gyroscope to enable multitasking measurement capabilities and measure its performance, important steps toward practical applications.
New superomniphobic glass soars high on butterfly wings using machine learning
 Engineers develop new superclear, supertransparent, stain-resistant, anti-fogging nanostructured glass based on butterfly wing.
Engineers develop new superclear, supertransparent, stain-resistant, anti-fogging nanostructured glass based on butterfly wing.
A nanoparticle 'EpiPen' for spinal cord injuries
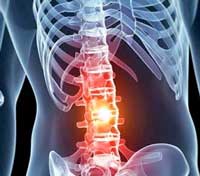 An injection of nanoparticles can prevent the body's immune system from overreacting to trauma, potentially preventing some spinal cord injuries from resulting in paralysis.
An injection of nanoparticles can prevent the body's immune system from overreacting to trauma, potentially preventing some spinal cord injuries from resulting in paralysis.
Designer proteins form wires and lattices on mineral surface
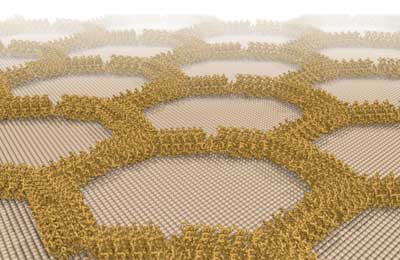 Findings lay foundation for engineered nano-scale circuits, sensors and filters.
Findings lay foundation for engineered nano-scale circuits, sensors and filters.
Trapped light particles: Physicists use nanostructures to free photons for highly efficient white OLEDs
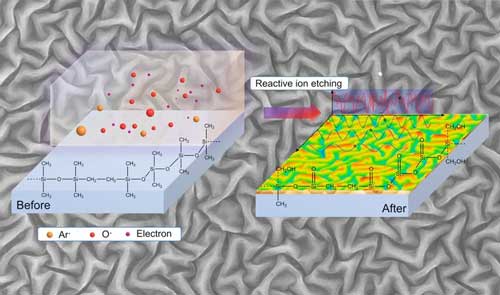 The physicists introduce a facile, scalable and especially lithography-free method for the generation of controllable nanostructures with directional randomness and dimensional order, significantly boosting the efficiency of white OLEDs.
The physicists introduce a facile, scalable and especially lithography-free method for the generation of controllable nanostructures with directional randomness and dimensional order, significantly boosting the efficiency of white OLEDs.
Conductive graphene materials created by bacteria
 Scientists have developed a method to produce graphene materials using a novel technique: mixing oxidized graphite with bacteria.
Scientists have developed a method to produce graphene materials using a novel technique: mixing oxidized graphite with bacteria.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

 Single molecules measure electrical potentials.
Single molecules measure electrical potentials.