 New mechanophore senses damage to fiber reinforced polymers.
New mechanophore senses damage to fiber reinforced polymers.
Tuesday, February 18, 2020
An early warning system for damage in composite materials
 New mechanophore senses damage to fiber reinforced polymers.
New mechanophore senses damage to fiber reinforced polymers.
Improving the electrical and mechanical properties of carbon-nanotube-based fibers
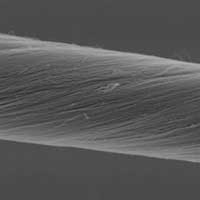 Researchers recently developed a technique that can be used to build carbon-nanotube-based fibers by creating chemical crosslinks; the technique improves the electrical and mechanical properties of these materials.
Researchers recently developed a technique that can be used to build carbon-nanotube-based fibers by creating chemical crosslinks; the technique improves the electrical and mechanical properties of these materials.
Time-resolved measurement in a memory device
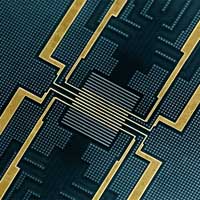 Researchers have measured the timing of single writing events in a novel magnetic memory device with a resolution of less than 100 picoseconds. Their results are relevant for the next generation of main memories based on magnetism.
Researchers have measured the timing of single writing events in a novel magnetic memory device with a resolution of less than 100 picoseconds. Their results are relevant for the next generation of main memories based on magnetism.
Topological materials outperform through quantum periodic motion
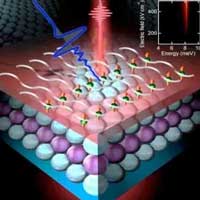 Scientists have discovered that applying vibrational motion in a periodic manner may be the key to preventing dissipations of the desired electron states that would make advanced quantum computing and spintronics possible.
Scientists have discovered that applying vibrational motion in a periodic manner may be the key to preventing dissipations of the desired electron states that would make advanced quantum computing and spintronics possible.
Highly sensitive sensors show promise in enhancing human touch
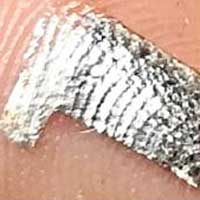 Ultrathin crack-based sensors operate on a principle similar to a spider's sense organ and display remarkable sensitivity to movement.
Ultrathin crack-based sensors operate on a principle similar to a spider's sense organ and display remarkable sensitivity to movement.
Ultrasound device improves charge time and run time in lithium batteries
 A novel ultrasound-emitting device brings lithium metal batteries, or LMBs, one step closer to commercial viability. Although the research team focused on LMBs, the device can be used in any battery, regardless of chemistry.
A novel ultrasound-emitting device brings lithium metal batteries, or LMBs, one step closer to commercial viability. Although the research team focused on LMBs, the device can be used in any battery, regardless of chemistry.
Supersensitive nanomaterials for DNA diagnostics and targeted drug delivery
 Scientists have developed a smart material with unique properties, which holds promise for express DNA analysis and next-generation drugs against cancer and other serious diseases.
Scientists have developed a smart material with unique properties, which holds promise for express DNA analysis and next-generation drugs against cancer and other serious diseases.
Flat lens gets ahead of the optical curve
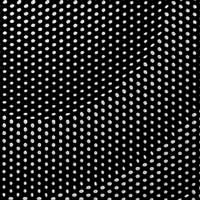 Researchers dotted metasurfaces with 600-nanometer-high silicon cylinders that alters the path and speed of light as it passes through them.
Researchers dotted metasurfaces with 600-nanometer-high silicon cylinders that alters the path and speed of light as it passes through them.
Creating custom light using 2D materials
 Scientists have discovered an entire class of two-dimensional materials that are the thickness of one or a few atoms. When combined together, these atomically thin crystals are capable of forming structures that emit customisable light in the desired colour.
Scientists have discovered an entire class of two-dimensional materials that are the thickness of one or a few atoms. When combined together, these atomically thin crystals are capable of forming structures that emit customisable light in the desired colour.
Power sources for smart contact lenses
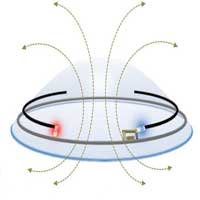 Researchers have demonstrated a multifunctional AC and/or DC power supply on soft, moist contact lenses.
Researchers have demonstrated a multifunctional AC and/or DC power supply on soft, moist contact lenses.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
