Tuesday, May 22, 2018
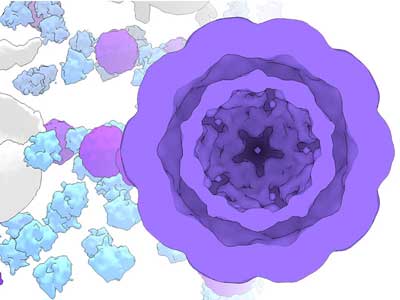
Mimicking biology to shape nanomaterials
Researchers utilize cellular proteins to shape silver nanoplates, suggesting an efficient strategy for controlling the nanostructure of inorganic materials.
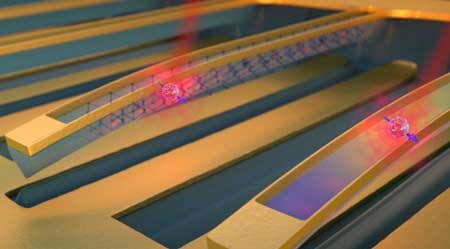
Tunable diamond string may hold key to quantum memory
A process similar to guitar tuning improves storage time of quantum memory.
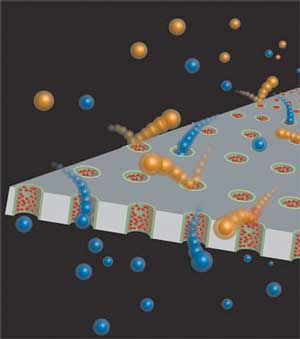
Remote control of transport through nanopores
New study outlines key factors affecting the transfer of molecules through biological channels.
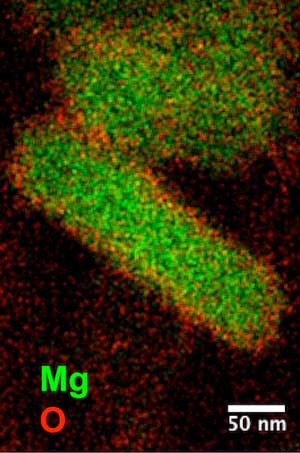
Magnesium magnificent for plasmonic applications
Researchers have synthesized and isolated plasmonic magnesium nanoparticles that show all the promise of their gold, silver and aluminum cousins with none of the drawbacks.
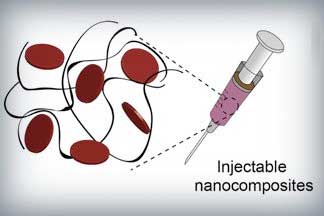
Injectable nanoengineered bandage targets fatal internal bleeding
Self-administered hydrogel designed to stem fatal blood loss, activate wound healing process.
Nanovalves for nanoparticles
Newly-developed nanovalves allow the flow of individual nanoparticles in liquids to be controlled in tiny channels. This is of interest for lab-on-a-chip applications such as in materials science and biomedicine.
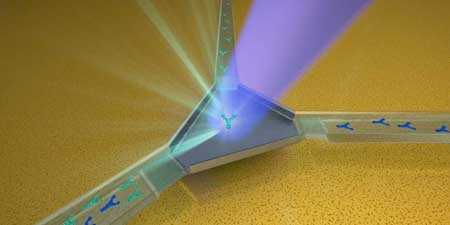
One-way roads for spin currents
Researchers have shown a completely new approach to controlling spin currents based on strong spin-spin interactions, which results in diodes for spin current with a giant rectification.
Nanotechnology food packaging releases preservatives on demand
Researchers demonstrate fruit preservative delivery from a nanocomposite packing in response to the signal from the fruit stimuli.

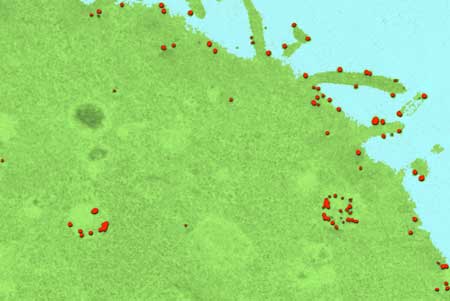
Quantum dot technique can track drug and gene delivery to cells
The new tracking technique uses single-molecule imaging, which allows to observe individual molecules over time, and quantum dots, which act like tiny beacons inside cells.
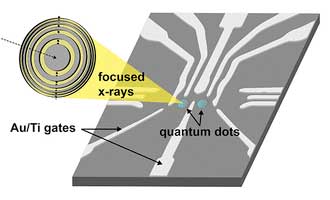
Leveraging imperfections to create better-behaved quantum dots
Potentially paving the way toward advanced computers, lasers or optical devices, researchers have revealed new effects in tiny electronic devices called quantum dots.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)