
Monday, January 14, 2019
Brilliant glow of paint-on semiconductors comes from ornate quantum physics
Pore size influences nature of complex nanostructures
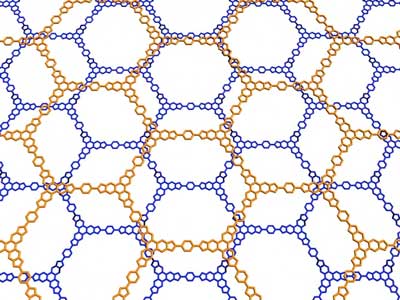
Bioinspired nanoscale drug delivery method
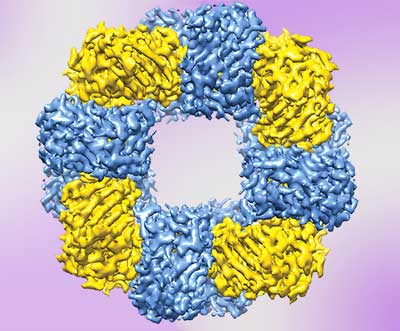
Discovery of single atom structure leads to more efficient catalyst

Researchers catalog defects that give 2-D materials amazing properties

DNA origami: A precise measuring tool for optimal antibody effectiveness
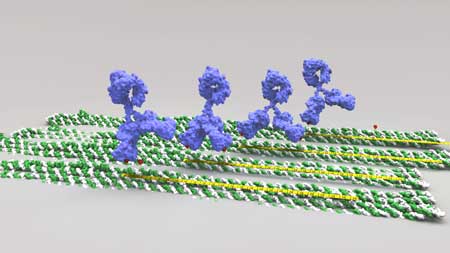
Scientists coax proteins to form synthetic structures with method that mimics nature
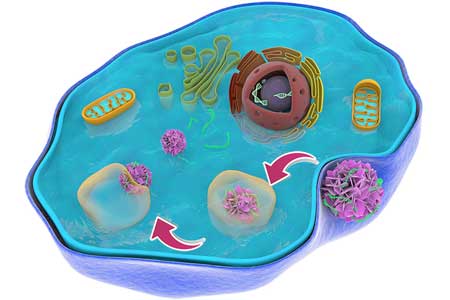
New immune system understanding may lead to safer nanomedicines
Scientists develop promising new type of polymers

Next generation photonic memory devices are light-written, ultrafast and energy efficient
5000 times faster than a computer - interatomic light rectifier generates directed electric currents
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
