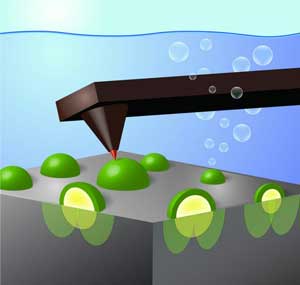
 Researchers find that smaller catalytic nanoparticles may be vital for many kinds of devices that convert solar energy into chemical fuels like hydrogen gas.
Researchers find that smaller catalytic nanoparticles may be vital for many kinds of devices that convert solar energy into chemical fuels like hydrogen gas.
Monday, October 7, 2019
Electrode-fitted microscope points to better designed devices that make fuel from sunlight
 Researchers find that smaller catalytic nanoparticles may be vital for many kinds of devices that convert solar energy into chemical fuels like hydrogen gas.
Researchers find that smaller catalytic nanoparticles may be vital for many kinds of devices that convert solar energy into chemical fuels like hydrogen gas.
Bacteria trapped - and terminated - by graphene filter
 Research team adapts laser-induced graphene to remove pathogens from the air.
Research team adapts laser-induced graphene to remove pathogens from the air.
First video of viruses assembling (w/video)
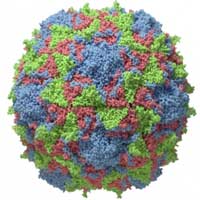 For the first time, researchers have captured images of the formation of individual viruses, offering a real-time view into the kinetics of viral assembly. The research provides new insights into how to fight viruses and engineer self-assembling particles.
For the first time, researchers have captured images of the formation of individual viruses, offering a real-time view into the kinetics of viral assembly. The research provides new insights into how to fight viruses and engineer self-assembling particles.
Picoscience and a plethora of new materials
 The revolutionary tech discoveries of the next few decades, the ones that will change daily life, may come from new materials so small they make nanomaterials look like lumpy behemoths.
The revolutionary tech discoveries of the next few decades, the ones that will change daily life, may come from new materials so small they make nanomaterials look like lumpy behemoths.
Physicists unlock the mystery of thermionic emission in graphene
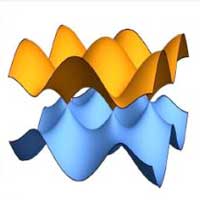 Researchers discover a new theory that paves the way for the design of better graphene electronics and energy converters.
Researchers discover a new theory that paves the way for the design of better graphene electronics and energy converters.
Researchers develop unique material from marine bath sponge skeleton
 Researchers have deciphered the structure of a marine sponge skeleton and developed a novel three-dimensional composite material for the modern materials industry.
Researchers have deciphered the structure of a marine sponge skeleton and developed a novel three-dimensional composite material for the modern materials industry.
Microscope prints patterns at the nanoscale
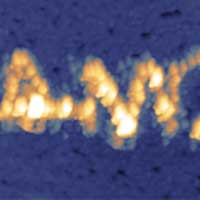 Researchers have successfully used an atomic force microscope to electrochemically print at the nanoscale. This technique can print structures for a new generation of solar cells on chips.
Researchers have successfully used an atomic force microscope to electrochemically print at the nanoscale. This technique can print structures for a new generation of solar cells on chips.
Molecular nanocarbons with mechanical bonds
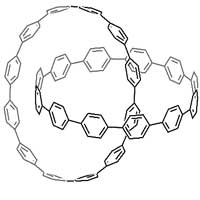 As the first step of precise synthesis of nanocarbons with complex topology, researchers have proposed 'topological molecular nanocarbons'.
As the first step of precise synthesis of nanocarbons with complex topology, researchers have proposed 'topological molecular nanocarbons'.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
