 If the stacking structure of a Covalent Organic Framework is even slightly shifted, its properties change dramatically. This happens more often than assumed, as chemists were able to demonstrate.
If the stacking structure of a Covalent Organic Framework is even slightly shifted, its properties change dramatically. This happens more often than assumed, as chemists were able to demonstrate.
Tuesday, January 5, 2021
Nanochemistry: Layers step out of line
 If the stacking structure of a Covalent Organic Framework is even slightly shifted, its properties change dramatically. This happens more often than assumed, as chemists were able to demonstrate.
If the stacking structure of a Covalent Organic Framework is even slightly shifted, its properties change dramatically. This happens more often than assumed, as chemists were able to demonstrate.
A clear path to better insights into biomolecules
 Scientists have obtained some of the sharpest possible 3D images of gold nanoparticles. The resuts lay the foundation for obtaining high resolution images of macromolecules.
Scientists have obtained some of the sharpest possible 3D images of gold nanoparticles. The resuts lay the foundation for obtaining high resolution images of macromolecules.
A polarization-driven guide to making high-performance, versatile solar cells
 Scientists discover 'spontaneously polarizing' materials that can help realize high-performance, lightweight solar cells.
Scientists discover 'spontaneously polarizing' materials that can help realize high-performance, lightweight solar cells.
Convex to concave: More metasurface moire results in wide-range lens
 The odd, wavy pattern that results from viewing certain phone or computer screens through polarized glasses has led researchers to take a step toward thinner, lighter-weight lenses. The pattern is made by laying one material with opaque and translucent parts at an angle over another material of similar contrast.
The odd, wavy pattern that results from viewing certain phone or computer screens through polarized glasses has led researchers to take a step toward thinner, lighter-weight lenses. The pattern is made by laying one material with opaque and translucent parts at an angle over another material of similar contrast.
Super surfaces use terahertz waves to help bounce wireless communication into the next generation
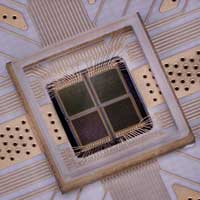 Assembling tiny chips into unique programmable surfaces, researchers have created a key component toward unlocking a communications band that promises to dramatically increase the amount of data wireless systems can transmit.
Assembling tiny chips into unique programmable surfaces, researchers have created a key component toward unlocking a communications band that promises to dramatically increase the amount of data wireless systems can transmit.
Fluorescence microscopy at highest spatial and temporal resolution
 p-MINFLUX is a new implementation of the highly photon-efficient single-molecule localization method with a simplified experimental setup and additional fluorescence lifetime information.
p-MINFLUX is a new implementation of the highly photon-efficient single-molecule localization method with a simplified experimental setup and additional fluorescence lifetime information.
How to untie magnetic nano-knots
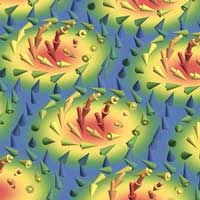 Scientists have discovered that skyrmions untie themselves in two distinct ways. Using a magnetic field, the probability to succeed in untying can be varied by up to a factor of 10,000. This insight might be groundbreaking for future information processing with skyrmions.
Scientists have discovered that skyrmions untie themselves in two distinct ways. Using a magnetic field, the probability to succeed in untying can be varied by up to a factor of 10,000. This insight might be groundbreaking for future information processing with skyrmions.
Putty-like composites of gallium metal with potential for real-world application
 Researchers have invented a new method for incorporating filler particles in liquid gallium to create functional composites of liquid metal. The incorporation of fillers transforms the material from a liquid state into either a paste- or putty-like form depending on the amount of added particles.
Researchers have invented a new method for incorporating filler particles in liquid gallium to create functional composites of liquid metal. The incorporation of fillers transforms the material from a liquid state into either a paste- or putty-like form depending on the amount of added particles.
Hanging by a colored thread - when damaged ropes change color
 Researchers have developed a coating for fibers that changes color when exposed to high temperatures through friction or fire.
Researchers have developed a coating for fibers that changes color when exposed to high temperatures through friction or fire.
Comb of a lifetime: A new method for fluorescence microscopy
 Scientists develop a fluorescence 'lifetime' microscopy technique that uses frequency combs and no mechanical parts to observe dynamic biological phenomena.
Scientists develop a fluorescence 'lifetime' microscopy technique that uses frequency combs and no mechanical parts to observe dynamic biological phenomena.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
