Friday, December 7, 2018
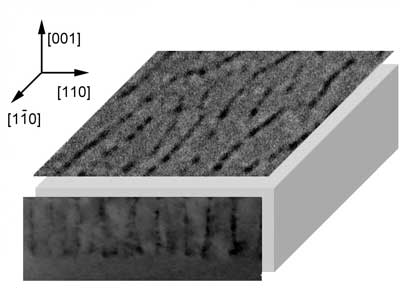
A new 'spin' on kagome lattices
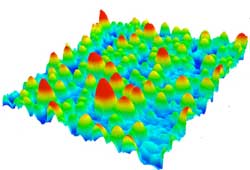
Seeing and avoiding the 'blind spot' in atomic force measurements
Fast storage material in neutron light

An embellished coat for bone implants
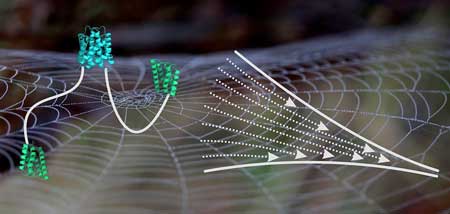
Molecular insights into spider silk
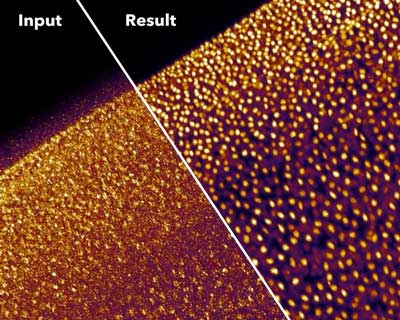
Neural networks let microscopists see more
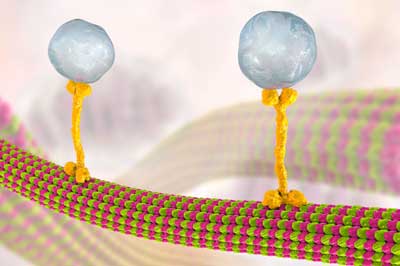
Cryo-electron microscopy shows how stabilizing proteins bind to microtubules
Molecularly thin hybrid perovskite for advanced optoelectronic applications
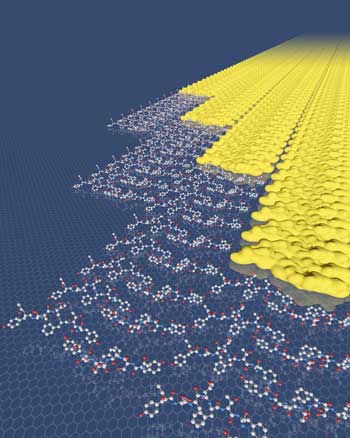
Two-dimensional materials skip the energy barrier by growing one row at a time
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)