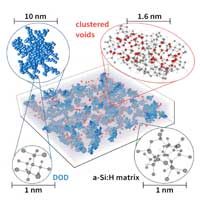
 For the first time, scientists have identified the atomic substructure of amorphous silicon with a resolution of 0.8 nanometres. The results show that three different phases form within the amorphous matrix, which dramatically influences the quality and lifetime of the semiconductor layer.
For the first time, scientists have identified the atomic substructure of amorphous silicon with a resolution of 0.8 nanometres. The results show that three different phases form within the amorphous matrix, which dramatically influences the quality and lifetime of the semiconductor layer.
Thursday, October 29, 2020
Order in the disorder: density fluctuations in amorphous silicon discovered
 For the first time, scientists have identified the atomic substructure of amorphous silicon with a resolution of 0.8 nanometres. The results show that three different phases form within the amorphous matrix, which dramatically influences the quality and lifetime of the semiconductor layer.
For the first time, scientists have identified the atomic substructure of amorphous silicon with a resolution of 0.8 nanometres. The results show that three different phases form within the amorphous matrix, which dramatically influences the quality and lifetime of the semiconductor layer.
Scientists launch quest to develop quantum sensors for probing quantum materials
 The newly created Center for Quantum Sensing and Quantum Materials aims to unravel mysteries associated with exotic superconductors, topological insulators and strange metals.
The newly created Center for Quantum Sensing and Quantum Materials aims to unravel mysteries associated with exotic superconductors, topological insulators and strange metals.
Researchers find path to nanodiamond from graphene
 A spot of pressure enables chemical conversion to hardened 2D material.
A spot of pressure enables chemical conversion to hardened 2D material.
Predictive model reveals function of promising energy harvester device
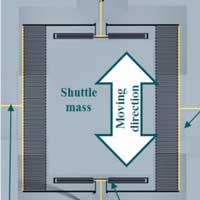 A small energy harvesting device that can transform subtle mechanical vibrations into electrical energy could be used to power wireless sensors and actuators for use in anything from temperature and occupancy monitoring in smart environments, to biosensing within the human body.
A small energy harvesting device that can transform subtle mechanical vibrations into electrical energy could be used to power wireless sensors and actuators for use in anything from temperature and occupancy monitoring in smart environments, to biosensing within the human body.
Breakthrough quantum-dot transistors create a flexible alternative to conventional electronics
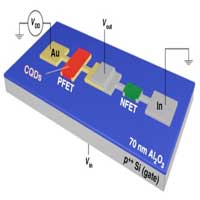 Quantum dot logic circuits provide the long-sought building blocks for innovative devices, including printable electronics, flexible displays, and medical diagnostics.
Quantum dot logic circuits provide the long-sought building blocks for innovative devices, including printable electronics, flexible displays, and medical diagnostics.
Scientists discover new structures in the smallest ice cube
 Scientists have revealed the coexistence of five cubic isomers in the smallest ice cube, including two with chirality.
Scientists have revealed the coexistence of five cubic isomers in the smallest ice cube, including two with chirality.
Chemical scissors snip 2D transition metal dichalcogenides into nanoribbon
 Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative - and an innovative way to produce them using chemical 'scissors' - that could make hydrogen production more economical.
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative - and an innovative way to produce them using chemical 'scissors' - that could make hydrogen production more economical.
Graphene-based memory resistors show promise for brain-based computing
 Engineers are attempting to pioneer a type of computing that mimics the efficiency of the brain's neural networks while exploiting the brain's analog nature.
Engineers are attempting to pioneer a type of computing that mimics the efficiency of the brain's neural networks while exploiting the brain's analog nature.
Smart fluorescent molecular switches based on boron-based compounds
 Scientists have developed extremely stable molecular switches of high luminosity that self-assemble into 1D nanostructures and form gel-like materials. These molecular switches can be used in biomedicine as fluorescent probes for imaging or sensing, in fluorescent displays, or in memories and information processing devices.
Scientists have developed extremely stable molecular switches of high luminosity that self-assemble into 1D nanostructures and form gel-like materials. These molecular switches can be used in biomedicine as fluorescent probes for imaging or sensing, in fluorescent displays, or in memories and information processing devices.
A new method to measure optical absorption in semiconductor crystals
 Scientists reveal more details about omnidirectional photoluminescence (ODPL) spectroscopy - a method for probing semiconducting crystals with light to detect defects and impurities.
Scientists reveal more details about omnidirectional photoluminescence (ODPL) spectroscopy - a method for probing semiconducting crystals with light to detect defects and impurities.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
