 Study demonstrates the efficacy and therapeutic potential of select ionizable lipid nanoparticles for delivering mRNA to treat genetic diseases before birth.
Study demonstrates the efficacy and therapeutic potential of select ionizable lipid nanoparticles for delivering mRNA to treat genetic diseases before birth.
Wednesday, January 13, 2021
Scientists identify nanoparticles that could deliver therapeutic mRNA before birth
 Study demonstrates the efficacy and therapeutic potential of select ionizable lipid nanoparticles for delivering mRNA to treat genetic diseases before birth.
Study demonstrates the efficacy and therapeutic potential of select ionizable lipid nanoparticles for delivering mRNA to treat genetic diseases before birth.
Turning pyrolyzed ash into graphene for improving concrete, other compounds
 Scientists have turned their attention to Joule heating of the material, a byproduct of plastic recycling processes. A strong jolt of energy flashes it into graphene.
Scientists have turned their attention to Joule heating of the material, a byproduct of plastic recycling processes. A strong jolt of energy flashes it into graphene.
Spice up your solar panels by adding a touch of chili
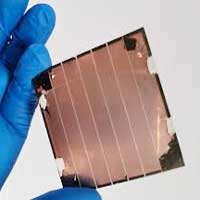 The compound that makes chili peppers spicy also boosts perovskite solar cell performance.
The compound that makes chili peppers spicy also boosts perovskite solar cell performance.
Catalysts: worth taking a closer look
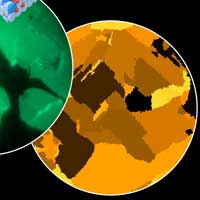 Why do metal oxide surfaces behave differently? Scientists found a new research method to answer important questions.
Why do metal oxide surfaces behave differently? Scientists found a new research method to answer important questions.
Avalanching nanoparticles break barriers to imaging cells in real time
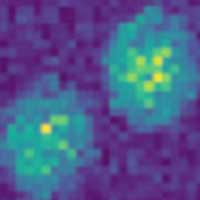 Study could lead to simple, high-resolution bioimaging in real time by overcoming a fundamental property of light.
Study could lead to simple, high-resolution bioimaging in real time by overcoming a fundamental property of light.
High-sensitivity nanophotonic sensors with passive trapping of analyte molecules in hot-spots
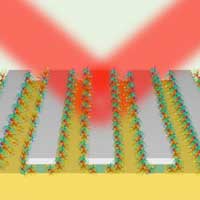 Scientists have demonstrated an optical sensor design which utilizes nano-scale trenches to passively concentrate and trap trace analytes in a solution, leading to the capability of detecting picogram level biomolecules such as glucose and amino acids. The devices also achieved effective trapping of nanoparticles.
Scientists have demonstrated an optical sensor design which utilizes nano-scale trenches to passively concentrate and trap trace analytes in a solution, leading to the capability of detecting picogram level biomolecules such as glucose and amino acids. The devices also achieved effective trapping of nanoparticles.
Physicists discover unifying pattern in two-dimensional ferroelectrics
 Physicists have discovered a unifying framework in the dipolar patterns of two-dimensional ferroelectrics, a finding which could help advance the development of high-density information coding systems in computers and other electronics.
Physicists have discovered a unifying framework in the dipolar patterns of two-dimensional ferroelectrics, a finding which could help advance the development of high-density information coding systems in computers and other electronics.
Tomorrow's structural materials: As hard as a diamond and as deformable as metal
 A supercrystal made of nanoparticles.
A supercrystal made of nanoparticles.
Using neural networks for faster X-ray imaging
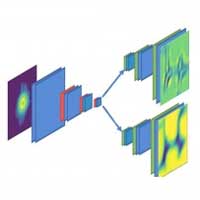 Scientists are using artificial intelligence to decode X-ray images faster, which could aid innovations in medicine, materials and energy.
Scientists are using artificial intelligence to decode X-ray images faster, which could aid innovations in medicine, materials and energy.
Researchers report quantum-limit-approaching chemical sensing chip
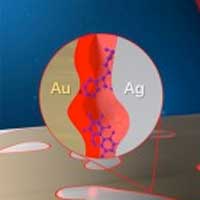 Study shows improvements to chemical sensing chip that aims to quickly and accurately identify drugs and other trace chemicals.
Study shows improvements to chemical sensing chip that aims to quickly and accurately identify drugs and other trace chemicals.
Energy harvesting made possible with skin temperature
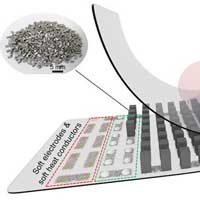 Development of flexible thermoelectric devices with maximized flexibility and high efficiency; enabling mass production with high yield by automated process, commercialization of self-powered wearable devices.
Development of flexible thermoelectric devices with maximized flexibility and high efficiency; enabling mass production with high yield by automated process, commercialization of self-powered wearable devices.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
