 Study could lead to greater manipulation of quantum materials and deeper understanding of the quantum state for novel electronics.
Study could lead to greater manipulation of quantum materials and deeper understanding of the quantum state for novel electronics.
Tuesday, September 24, 2019
Iridium 'loses its identity' when interfaced with nickel
 Study could lead to greater manipulation of quantum materials and deeper understanding of the quantum state for novel electronics.
Study could lead to greater manipulation of quantum materials and deeper understanding of the quantum state for novel electronics.
Quantum destabilization of a water sandwich
 When a thin layer of water is squeezed between two hydrophobic surfaces, the laws of classical physics break down.
When a thin layer of water is squeezed between two hydrophobic surfaces, the laws of classical physics break down.
Research could help flexible technology last longer, avoid critical failures
 A new study uses the topography of human skin as a model not for preventing cracks but for directing them in the best way possible to avoid critical components and make repairs easy.
A new study uses the topography of human skin as a model not for preventing cracks but for directing them in the best way possible to avoid critical components and make repairs easy.
How molecular footballs burst in an X-ray laser beam
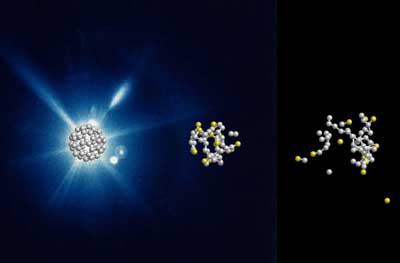 Study shows effect of X-ray flashes on sensitive biomolecules.
Study shows effect of X-ray flashes on sensitive biomolecules.
Highly sensitive nanowire diode converts microwaves to electricity
 The new technology is expected to play a role in harvesting energy from radio waves in the environment, in which electricity is generated from ambient radio waves, such as those emitted from mobile phone base stations.
The new technology is expected to play a role in harvesting energy from radio waves in the environment, in which electricity is generated from ambient radio waves, such as those emitted from mobile phone base stations.
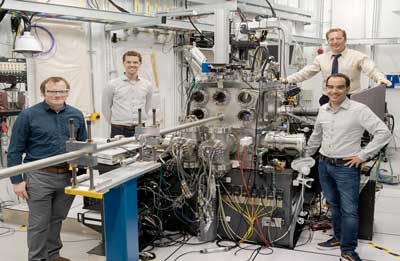
Researchers can now place single ions into solids
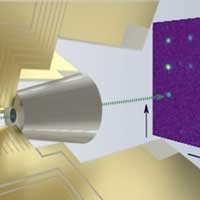 New technique enables implantation of individual ions into crystals with an accuracy of 35 nanometers.
New technique enables implantation of individual ions into crystals with an accuracy of 35 nanometers.
Seeing sound: Scientists observe how acoustic interactions change materials at the atomic level
 Scientists used X-rays to observe spatial changes in a silicon carbide crystal when using sound waves to strain buried defects inside it.
Scientists used X-rays to observe spatial changes in a silicon carbide crystal when using sound waves to strain buried defects inside it.
Converting absorbed photons into twice as many excitons: successful high-efficiency energy conversion with organic monolayer on gold nanocluster surface
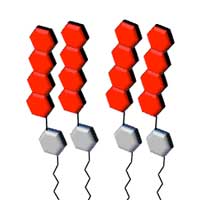 Scientists have found that when light was exposed to the surface of a tetracene alkanethiol-modified gold nanocluster, which they developed themselves, twice as many excitons could be converted compared to the number of photons absorbed by the tetracene molecules.
Scientists have found that when light was exposed to the surface of a tetracene alkanethiol-modified gold nanocluster, which they developed themselves, twice as many excitons could be converted compared to the number of photons absorbed by the tetracene molecules.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
