 Researchers have created a machine-learning algorithm that can characterise graphene properties and quality within 14 minutes.
Researchers have created a machine-learning algorithm that can characterise graphene properties and quality within 14 minutes.
Tuesday, August 25, 2020
New technology extracts potential to identify quality graphene cheaper and faster
 Researchers have created a machine-learning algorithm that can characterise graphene properties and quality within 14 minutes.
Researchers have created a machine-learning algorithm that can characterise graphene properties and quality within 14 minutes.
Faster, more efficient energy storage could stem from holistic study of MXenes
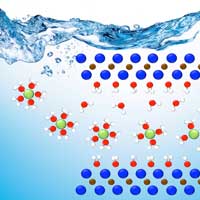 Researchers developed a novel, integrated approach to track energy-transporting ions within an ultra-thin material, which could unlock its energy storage potential leading toward faster charging, longer-lasting devices.
Researchers developed a novel, integrated approach to track energy-transporting ions within an ultra-thin material, which could unlock its energy storage potential leading toward faster charging, longer-lasting devices.
New method to track ultrafast change of magnetic state
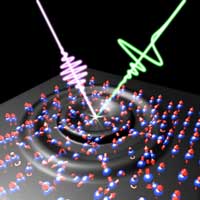 Scientists have developed a precise method to measure the ultrafast change of a magnetic state in materials. They do this by observing the emission of terahertz radiation that necessarily accompanies such a magnetization change.
Scientists have developed a precise method to measure the ultrafast change of a magnetic state in materials. They do this by observing the emission of terahertz radiation that necessarily accompanies such a magnetization change.
Using light's properties to indirectly see inside a cell membrane
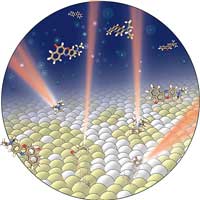 New imaging technique helps resolve nanodomains, chemical composition in cell membranes.
New imaging technique helps resolve nanodomains, chemical composition in cell membranes.
Payper: A new graphene-based contactless payment system
 The role of graphene in the system's printed electronic antenna is to provide high flexibility, conductivity and mechanical strength, which can be imparted onto the tight and variable curvature of the till roll.
The role of graphene in the system's printed electronic antenna is to provide high flexibility, conductivity and mechanical strength, which can be imparted onto the tight and variable curvature of the till roll.
Physicists discover new two-dimensional ferroelectric material just two atoms thick
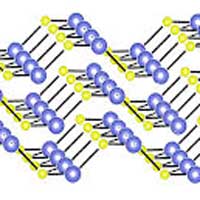 The new material, a tin selenide monolayer, is only the third two-dimensional ferroelectric belonging to the chemical family of group-IV monochalcogenides that has been experimentally grown thus far.
The new material, a tin selenide monolayer, is only the third two-dimensional ferroelectric belonging to the chemical family of group-IV monochalcogenides that has been experimentally grown thus far.
Nanoelectromechanical sensors based on suspended 2D materials
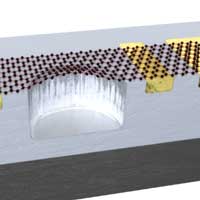 Scientists have published a review article on nanoelectromechanical (NEMS) sensors based on suspended two-dimensional (2D) materials.
Scientists have published a review article on nanoelectromechanical (NEMS) sensors based on suspended two-dimensional (2D) materials.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
