
Tuesday, December 11, 2018
Scientists developed unique method to calculate transparent materials' porosity
Better biomedical devices, wearable displays may result from tiny light-guiding structures
Chemical engineers develop new theory to build improved nanomaterials
Boron nitride and silver nanoparticles help get rid of carbon monoxide emissions
Custom-made artificial mother-of-pearl
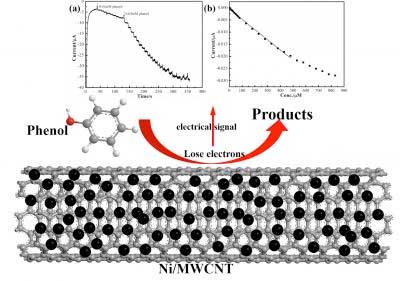
Carbon nanotube based electrochemical sensor for fast detection of phenol in wastewater
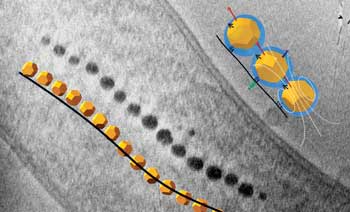
Insights into magnetic bacteria may guide research into medical nanorobots
Copper compound as promising quantum computing unit

Cutting and pasting with graphene

Sprayable gel could help the body fight off cancer after surgery
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
