 An international team of researchers has created the brightest known materials on Earth by designing a new type of material that can protect the properties of fluorescent molecules. The scientists are planning further research to explore the use of these new materials in a range of different applications, from solar energy harvesting to bioimaging to lasers.
An international team of researchers has created the brightest known materials on Earth by designing a new type of material that can protect the properties of fluorescent molecules. The scientists are planning further research to explore the use of these new materials in a range of different applications, from solar energy harvesting to bioimaging to lasers.
Thursday, August 6, 2020
Chemists create the brightest-ever fluorescent materials
 An international team of researchers has created the brightest known materials on Earth by designing a new type of material that can protect the properties of fluorescent molecules. The scientists are planning further research to explore the use of these new materials in a range of different applications, from solar energy harvesting to bioimaging to lasers.
An international team of researchers has created the brightest known materials on Earth by designing a new type of material that can protect the properties of fluorescent molecules. The scientists are planning further research to explore the use of these new materials in a range of different applications, from solar energy harvesting to bioimaging to lasers.
Nanoparticle system captures heart-disease biomarker from blood for in-depth analysis
 Researchers have developed a method combining sticky nanoparticles with high-precision protein measurement to capture and analyze a common marker of heart disease to reveal details that were previously inaccessible.
Researchers have developed a method combining sticky nanoparticles with high-precision protein measurement to capture and analyze a common marker of heart disease to reveal details that were previously inaccessible.
A nanoparticle strategy to evaluate tumor photothermal therapy in real-time
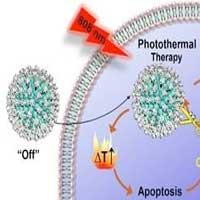 Researchers reported an 'intelligent' strategy of using organic nanoparticles to evaluate photothermal therapy efficiency on tumor in real time.
Researchers reported an 'intelligent' strategy of using organic nanoparticles to evaluate photothermal therapy efficiency on tumor in real time.
Thermal chaos returns quantum system to its unknown past
 Physicists have devised a way to time-reverse the evolution of an object in an arbitrary, unknown state.
Physicists have devised a way to time-reverse the evolution of an object in an arbitrary, unknown state.
Scientists zero in on bismuth vanadate's role in renewable energy at the nanoscale
 Scientists have gained important new insight into what might be happening at the nanoscale to hold bismuth vanadate back as a good candidate for photoelectrical water splitting.
Scientists have gained important new insight into what might be happening at the nanoscale to hold bismuth vanadate back as a good candidate for photoelectrical water splitting.
Scientists see train of photons in a new light
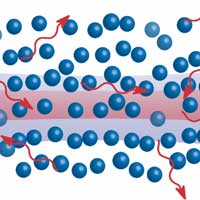 Scientists describe an experiment that investigates how to extract a train of single photons from a laser packed with many photons.
Scientists describe an experiment that investigates how to extract a train of single photons from a laser packed with many photons.
New technology to create chiral light fields
 Unlike previous approaches, the new technology performed on a 4 pi microscopic system and utilized radially or azimuthally polarized beams to generate the chiral light fields.
Unlike previous approaches, the new technology performed on a 4 pi microscopic system and utilized radially or azimuthally polarized beams to generate the chiral light fields.
High-frequency transverse phonons in amorphous materials observed for the first time
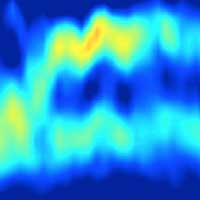 With the help of state-of-the-art neutron scattering instrumentation and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists have demonstrated the existence of high-frequency transverse phonons in metallic glass for the first time.
With the help of state-of-the-art neutron scattering instrumentation and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists have demonstrated the existence of high-frequency transverse phonons in metallic glass for the first time.
Way, shape and form: Synthesis conditions define the nanostructure of manganese dioxide
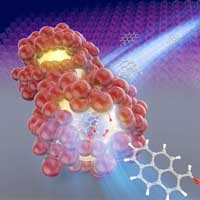 The study sheds light on how different synthesis conditions can produce manganese dioxide with distinct porous structures, hinting at a strategy for the development of highly tuned MnO2 nanomaterials that could serve as catalysts in the fabrication of bioplastics.
The study sheds light on how different synthesis conditions can produce manganese dioxide with distinct porous structures, hinting at a strategy for the development of highly tuned MnO2 nanomaterials that could serve as catalysts in the fabrication of bioplastics.
An electrical switch for magnetism
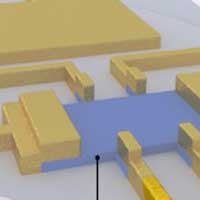 Physicists have demonstrated the control of magnetism in a magnetic semiconductor via electrical means, paving the way for novel spintronic devices.
Physicists have demonstrated the control of magnetism in a magnetic semiconductor via electrical means, paving the way for novel spintronic devices.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
