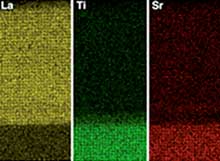
 The oxide ceramic material lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO) retains its magnetic properties in atomically thin layers if it is 'sandwiched' between two layers of a different ceramic oxide, lanthanum strontium chromium oxide. The findings have implications for future use of LSMO in spintronic-based computing and storage devices.
The oxide ceramic material lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO) retains its magnetic properties in atomically thin layers if it is 'sandwiched' between two layers of a different ceramic oxide, lanthanum strontium chromium oxide. The findings have implications for future use of LSMO in spintronic-based computing and storage devices.
Tuesday, June 11, 2019
'Sandwich' structure key to thin LSMO films retaining magnetic properties
 The oxide ceramic material lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO) retains its magnetic properties in atomically thin layers if it is 'sandwiched' between two layers of a different ceramic oxide, lanthanum strontium chromium oxide. The findings have implications for future use of LSMO in spintronic-based computing and storage devices.
The oxide ceramic material lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO) retains its magnetic properties in atomically thin layers if it is 'sandwiched' between two layers of a different ceramic oxide, lanthanum strontium chromium oxide. The findings have implications for future use of LSMO in spintronic-based computing and storage devices.
Engineers design nanostructured diamond metalens for compact quantum technologies
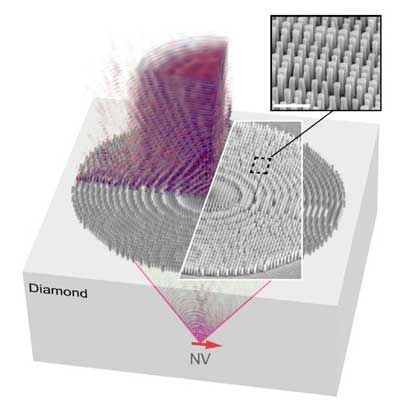 By finding a certain kind of defect inside a block of diamond and fashioning a pattern of nanoscale pillars on the surface above it, researchers can now control the shape of individual photons emitted by the defect.
By finding a certain kind of defect inside a block of diamond and fashioning a pattern of nanoscale pillars on the surface above it, researchers can now control the shape of individual photons emitted by the defect.
iPhone plus nanoscale porous silicon equals cheap, simple home diagnostics
 The simplest home medical tests might look like a deck of various silicon chips coated in special film, one that could detect drugs in the blood, another for proteins in the urine indicating infection, another for bacteria in water and the like. Add the bodily fluid you want to test, take a picture with your smart phone, and a special app lets you know if there is a problem or not.
The simplest home medical tests might look like a deck of various silicon chips coated in special film, one that could detect drugs in the blood, another for proteins in the urine indicating infection, another for bacteria in water and the like. Add the bodily fluid you want to test, take a picture with your smart phone, and a special app lets you know if there is a problem or not.
New material with magnetic shape memory (w/video)
 What is special about the new material is that, unlike previous shape-memory materials, it consists of a polymer and droplets of a so-called magnetorheological fluid embedded in it. Areas of application for this new type of composite material include medicine, aerospace, electronics and robotics.
What is special about the new material is that, unlike previous shape-memory materials, it consists of a polymer and droplets of a so-called magnetorheological fluid embedded in it. Areas of application for this new type of composite material include medicine, aerospace, electronics and robotics.
Plot twist: Straightening single-molecule conductors improves their performance
 Researchers have created single-molecule nanowires, complete with an insulation layer, up to 10 nanometers in length. When they measured the electrical properties of these nanowires, the researchers found that forcing the ribbon-like chains to be flat significantly improved their conductivity compared with a twisted conformation.
Researchers have created single-molecule nanowires, complete with an insulation layer, up to 10 nanometers in length. When they measured the electrical properties of these nanowires, the researchers found that forcing the ribbon-like chains to be flat significantly improved their conductivity compared with a twisted conformation.
The solvent pH controls the interactions of gold nanoclusters
 Simulations reveal that gold nanocluster can bind to viruses by different interactions, and that the strength of the interactions are dependent on pH conditions.
Simulations reveal that gold nanocluster can bind to viruses by different interactions, and that the strength of the interactions are dependent on pH conditions.
An innovative electron microscope overturning common knowledge of 88 years history
 Researchers developed a revolutionary electron microscope that incorporates newly designed magnetic objective lenses, and achieved direct, atom-resolved imaging of materials with sub-Angstrom spatial resolution.
Researchers developed a revolutionary electron microscope that incorporates newly designed magnetic objective lenses, and achieved direct, atom-resolved imaging of materials with sub-Angstrom spatial resolution.
Light-powered nanobio-hybrid organisms consume CO2, create eco-friendly plastics and fuels
 Researchers have developed nanobio-hybrid organisms capable of using airborne carbon dioxide and nitrogen to produce a variety of plastics and fuels, a promising first step toward low-cost carbon sequestration and eco-friendly manufacturing for chemicals.
Researchers have developed nanobio-hybrid organisms capable of using airborne carbon dioxide and nitrogen to produce a variety of plastics and fuels, a promising first step toward low-cost carbon sequestration and eco-friendly manufacturing for chemicals.
A bubbly new way to detect the magnetic fields of nanoparticles
 The method provides manufacturers with a practical way to measure and improve their control of the properties of magnetic nanoparticles for a host of medical and environmental applications.
The method provides manufacturers with a practical way to measure and improve their control of the properties of magnetic nanoparticles for a host of medical and environmental applications.
Tiny light box opens new doors into the nanoworld
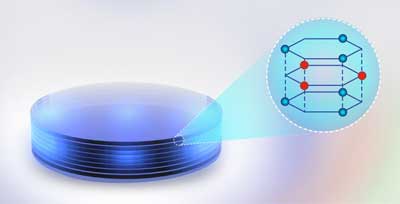 Scientists have discovered a completely new way of capturing, amplifying and linking light to matter at the nanolevel. Using a tiny box, built from stacked atomically thin material, they have succeeded in creating a type of feedback loop in which light and matter become one.
Scientists have discovered a completely new way of capturing, amplifying and linking light to matter at the nanolevel. Using a tiny box, built from stacked atomically thin material, they have succeeded in creating a type of feedback loop in which light and matter become one.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
