 For the first time, researchers have been able to observe the way ceramic materials fracture on the atomic scale. They confirm that the arrangement of molecules between grains within a body of ceramic material strongly affects the way a fracture propagates through it.
For the first time, researchers have been able to observe the way ceramic materials fracture on the atomic scale. They confirm that the arrangement of molecules between grains within a body of ceramic material strongly affects the way a fracture propagates through it.
Monday, August 12, 2019
Directly observing the way ceramic materials fracture on the atomic scale
 For the first time, researchers have been able to observe the way ceramic materials fracture on the atomic scale. They confirm that the arrangement of molecules between grains within a body of ceramic material strongly affects the way a fracture propagates through it.
For the first time, researchers have been able to observe the way ceramic materials fracture on the atomic scale. They confirm that the arrangement of molecules between grains within a body of ceramic material strongly affects the way a fracture propagates through it.
Scientists create 20-qubit Schrödinger cat states with superconducting quantum processor
 In addition, they showed that the generated 18-qubit Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state is genuine entangled.
In addition, they showed that the generated 18-qubit Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state is genuine entangled.
New type of electrolyte could enhance supercapacitor performance
 Novel class of 'ionic liquids' may store more energy than conventional electrolytes - with less risk of catching fire.
Novel class of 'ionic liquids' may store more energy than conventional electrolytes - with less risk of catching fire.
Organic semiconductors - No encapsulation needed for unprecedented stability
 The common opinion is that organic semiconductors are sensitive and unstable and hence cannot keep up with their inorganic counterparts. As researchers demonstrate, this impression has to change.
The common opinion is that organic semiconductors are sensitive and unstable and hence cannot keep up with their inorganic counterparts. As researchers demonstrate, this impression has to change.
Researchers turn off backscattering, aim to improve optical data transmission
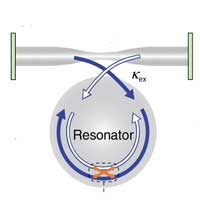 In a study, researchers exploited an interaction between light and sound waves to suppress the scattering of light from material defects - which could lead to improved fiber optic communication.
In a study, researchers exploited an interaction between light and sound waves to suppress the scattering of light from material defects - which could lead to improved fiber optic communication.
How do atoms vibrate in graphene nanostructures?
 Innovative new electron spectroscopy technique pushes the limits of nanospectroscopy for materials design.
Innovative new electron spectroscopy technique pushes the limits of nanospectroscopy for materials design.
Mapping the energetic landscape of solar cells
 A new spectroscopic method now makes it possible to measure and visualise the energetic landscape inside solar cells based on organic materials.
A new spectroscopic method now makes it possible to measure and visualise the energetic landscape inside solar cells based on organic materials.
You're not so tough, h-BN
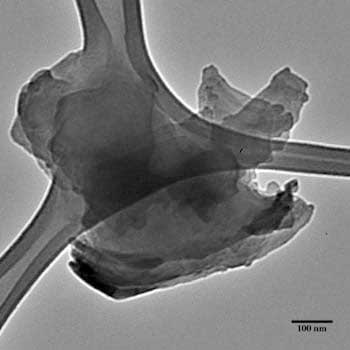 Chemists find new path to make strong 2D material better for applications.
Chemists find new path to make strong 2D material better for applications.
Researchers take a direct image of magic-angle twisted graphene sheets
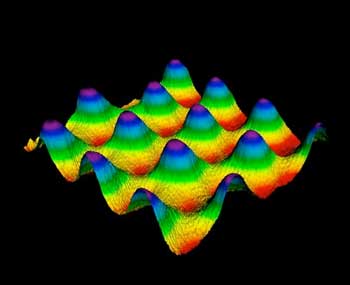 Understanding the 'magic angle' - a specific orientation between the stacked graphene that yields special electric properties - could pave the way to realizing the dream of room-temperature superconductors, which could transmit enormous electric currents while producing zero heat.
Understanding the 'magic angle' - a specific orientation between the stacked graphene that yields special electric properties - could pave the way to realizing the dream of room-temperature superconductors, which could transmit enormous electric currents while producing zero heat.
Sharp meets flat in tunable 2D material
 New atom-flat compounds show promise for optoelectronics, advanced computing.
New atom-flat compounds show promise for optoelectronics, advanced computing.
Dyes and viruses create new composite material for photooxidation reactions
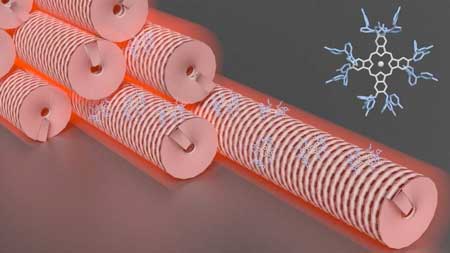 A recent study shows that native viruses can be employed as a scaffold to immobilise photoactive molecules to potentially oxidise organic pollutants present in wastewater, under visible light irradiation.
A recent study shows that native viruses can be employed as a scaffold to immobilise photoactive molecules to potentially oxidise organic pollutants present in wastewater, under visible light irradiation.
Zinc oxide nanowires - novel solution for cheaper, cleaner production of electronic components
 Researchers are offering a novel solution for high-yield nanowire production from zinc oxide - a cheaper and environmentally friendlier material, compared to the rare earth elements such as indium, arsenic or gallium often used in electronics production.
Researchers are offering a novel solution for high-yield nanowire production from zinc oxide - a cheaper and environmentally friendlier material, compared to the rare earth elements such as indium, arsenic or gallium often used in electronics production.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
