 New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
Thursday, April 30, 2020
'Magnetic drugs' could stay at disease sites longer
 New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
New research suggests that a novel magnetism-based drug delivery approach could help ensure drugs are not removed from where they are needed in the body.
'Breathable' electronics pave the way for more functional wearable tech
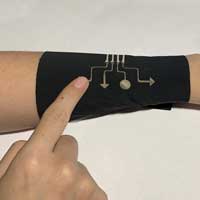 Engineering researchers have created ultrathin, stretchable electronic material that is gas permeable, allowing the material to 'breathe'.
Engineering researchers have created ultrathin, stretchable electronic material that is gas permeable, allowing the material to 'breathe'.
Optical 'nanomixer': Scientists propose new method for mixing liquids
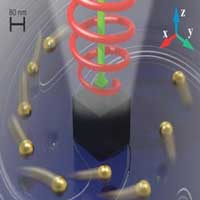 Scientists propose a method that can help solve problem of controlling over the mixing speed: they decided to use the so-called radiation pressure.
Scientists propose a method that can help solve problem of controlling over the mixing speed: they decided to use the so-called radiation pressure.
Groovy photoelectrodes: How a textured surface can dramatically boost their performance
 Researchers find that a promising photoelectrode material for producing hydrogen using sunlight can be made even better by increasing its surface roughness.
Researchers find that a promising photoelectrode material for producing hydrogen using sunlight can be made even better by increasing its surface roughness.
Nanodevices for the brain could thwart formation of Alzheimer's plaques
 In a multidisciplinary study, scientists have developed an approach to prevent plaque formation by engineering a nano-sized device that captures the dangerous peptides before they can self-assemble.
In a multidisciplinary study, scientists have developed an approach to prevent plaque formation by engineering a nano-sized device that captures the dangerous peptides before they can self-assemble.
Scientists reveal the magnetic states of nanoscale gyroids
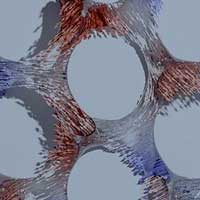 Researchers revealed the magnetic states of nanoscale gyroids, 3D chiral network-like nanostructures. The findings add a new candidate system for research into unconventional information processing and emergent phenomena relevant to spintronics.
Researchers revealed the magnetic states of nanoscale gyroids, 3D chiral network-like nanostructures. The findings add a new candidate system for research into unconventional information processing and emergent phenomena relevant to spintronics.
Scientists prove the existence of Skyrmion tubes
 For the first time, an international team of researchers succeeded in demonstrating the previously unknown structure of magnetic skyrmion tubes in 3D. This knowledge makes it possible to better understand the formation and destruction of skyrmions and to use the magnetic structures in spintronic storage devices.
For the first time, an international team of researchers succeeded in demonstrating the previously unknown structure of magnetic skyrmion tubes in 3D. This knowledge makes it possible to better understand the formation and destruction of skyrmions and to use the magnetic structures in spintronic storage devices.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
