 New process targets improvements for defense, vehicles and health products.
New process targets improvements for defense, vehicles and health products.
Thursday, March 7, 2019
Design treatment of advanced metals producing better sculpting
 New process targets improvements for defense, vehicles and health products.
New process targets improvements for defense, vehicles and health products.
Fireflies, heart beats, and the science of sync
 In lessons for nanomachines, physicists have discovered surprisingly complex states emerging out of simple synchronized networks.
In lessons for nanomachines, physicists have discovered surprisingly complex states emerging out of simple synchronized networks.
Tiny DNA reader to advance development of anticancer drugs
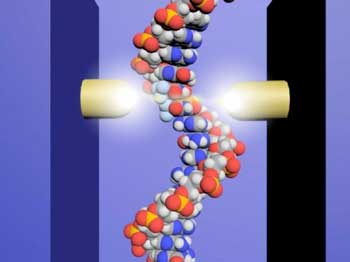 Researchers use tiny probes and an electrical current to locate anticancer drug molecules incorporated into single strands of DNA.
Researchers use tiny probes and an electrical current to locate anticancer drug molecules incorporated into single strands of DNA.
Using laser 'tweezers', scientists grab and study tiny protein droplets
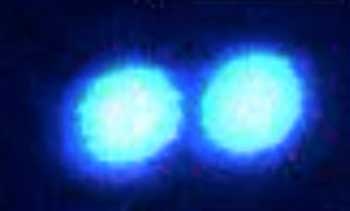 New research illuminates some basic properties of these eccentric marvels of biology.
New research illuminates some basic properties of these eccentric marvels of biology.
Breakthrough could enable cheaper infrared cameras
 Quantum dots could make technology available for self-driving cars, consumer electronics.
Quantum dots could make technology available for self-driving cars, consumer electronics.
New cell-sized microrobots might make incredible journeys
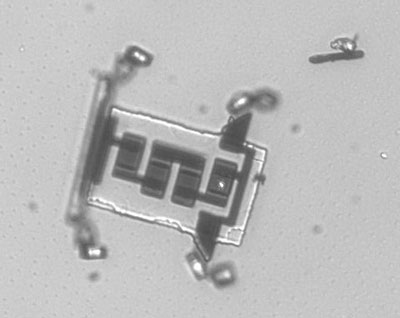 A million functional microscopic robots produced from a 4-inch silicon wafer in new nanofabrication process.
A million functional microscopic robots produced from a 4-inch silicon wafer in new nanofabrication process.
New graphene-based device is first step toward ultrasensitive biosensors
Device could detect disease biomarkers at the molecular level and lead to new sensor technology.
When semiconductors stick together, materials go quantum
 A new study reveals how aligned layers of atomically thin semiconductors can yield an exotic new quantum material.
A new study reveals how aligned layers of atomically thin semiconductors can yield an exotic new quantum material.
Combs of light for molecules
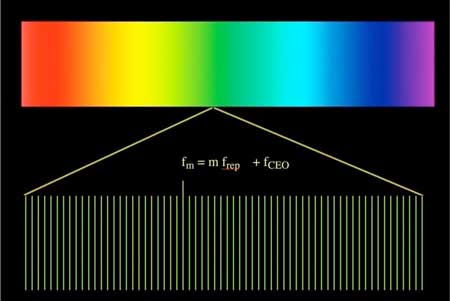 Developments and prospects in the field of atomic and molecular broadband spectroscopy with frequency combs.
Developments and prospects in the field of atomic and molecular broadband spectroscopy with frequency combs.
Smoothing out the wrinkles in graphene
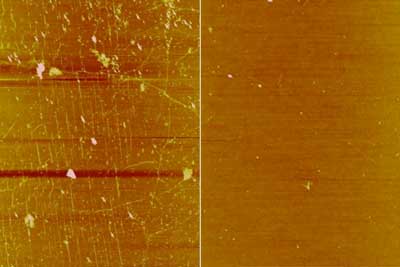 Coating graphene with wax makes for a less contaminated surface during device manufacturing.
Coating graphene with wax makes for a less contaminated surface during device manufacturing.
New optical imaging system could be deployed to find tiny tumors
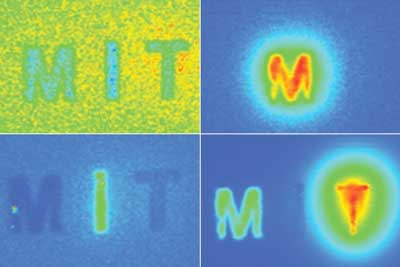 Near-infrared technology pinpoints fluorescent probes deep within living tissue; may be used to detect cancer earlier.
Near-infrared technology pinpoints fluorescent probes deep within living tissue; may be used to detect cancer earlier.
New approach facilitates spectroscopy on individual molecules
 While spectroscopic measurements are normally averaged over myriad molecules, a new method provides precise information about the interaction of individual molecules with their environment.
While spectroscopic measurements are normally averaged over myriad molecules, a new method provides precise information about the interaction of individual molecules with their environment.
Two dimensional ?Lego? shows new methods for creating electronics
 Physicists have discovered that when two atomically thin (two-dimensional) materials like graphene are placed on top of each other like a ?Lego? tower, their properties change and a material with novel hybrid properties emerges, paving the way for design of new materials and nano devices.
Physicists have discovered that when two atomically thin (two-dimensional) materials like graphene are placed on top of each other like a ?Lego? tower, their properties change and a material with novel hybrid properties emerges, paving the way for design of new materials and nano devices.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
