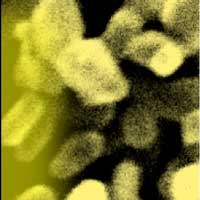
 Insight into charge generation induced by light could enable the design of better photocatalysts made from nanomaterials.
Insight into charge generation induced by light could enable the design of better photocatalysts made from nanomaterials.
Monday, August 17, 2020
Watching electrons harvest light at the nanoscale
 Insight into charge generation induced by light could enable the design of better photocatalysts made from nanomaterials.
Insight into charge generation induced by light could enable the design of better photocatalysts made from nanomaterials.
New superlattice material for future energy efficient devices
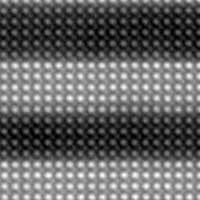 Physicists have created a new material layered by two structures, forming a superlattice, that at a high temperature is a super-efficient insulator conducting current without dissipation and lost energy.
Physicists have created a new material layered by two structures, forming a superlattice, that at a high temperature is a super-efficient insulator conducting current without dissipation and lost energy.
First ever observation of 'time crystals' interacting
 The discovery may lead to applications in quantum information processing because time crystals automatically remain intact - coherent - in varying conditions. Protecting coherence is the main difficulty hindering the development of powerful quantum computers.
The discovery may lead to applications in quantum information processing because time crystals automatically remain intact - coherent - in varying conditions. Protecting coherence is the main difficulty hindering the development of powerful quantum computers.
Scientists develop approach to synthesize unconventional nanoalloys for electrocatalytic application
 A novel synthetic approach broke through the limitation of wet-chemistry methods for synthesizing immiscible and high entropy nanoalloys. The composition and size of the obtained nanoalloys were also controllable by varying the experimental conditions/parameters.
A novel synthetic approach broke through the limitation of wet-chemistry methods for synthesizing immiscible and high entropy nanoalloys. The composition and size of the obtained nanoalloys were also controllable by varying the experimental conditions/parameters.
No limit yet for carbon nanotube fibers
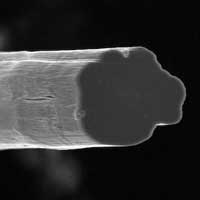 Researchers have made their strongest and most conductive fibers yet, made of long carbon nanotubes through a wet spinning process.
Researchers have made their strongest and most conductive fibers yet, made of long carbon nanotubes through a wet spinning process.
Coupled nanoscale antennas pave the way for lightwave electronics
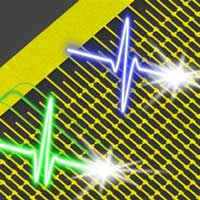 Integrated lightwave electronic circuits allow the absolute phase of a light wave to be determined.
Integrated lightwave electronic circuits allow the absolute phase of a light wave to be determined.
Scientists use photons as threads to weave novel forms of matter
 Researchers have discovered a way to bind two negatively charged electron-like particles which could create opportunities to form novel materials for use in new technological developments.
Researchers have discovered a way to bind two negatively charged electron-like particles which could create opportunities to form novel materials for use in new technological developments.
'Simulation microscope' examines transistors of the future
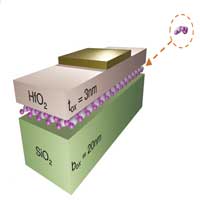 Scientists have now simulated and evaluated one hundred possible 2D materials for building high-performance transistors and discovered 13 promising candidates.
Scientists have now simulated and evaluated one hundred possible 2D materials for building high-performance transistors and discovered 13 promising candidates.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
