 Inspired by how human bone and colorful coral reefs adjust mineral deposits in response to their surrounding environments, researchers have created a self-adapting material that can change its stiffness in response to the applied force.
Inspired by how human bone and colorful coral reefs adjust mineral deposits in response to their surrounding environments, researchers have created a self-adapting material that can change its stiffness in response to the applied force.
Friday, April 17, 2020
Under pressure: New bioinspired material can 'shapeshift' to external forces
 Inspired by how human bone and colorful coral reefs adjust mineral deposits in response to their surrounding environments, researchers have created a self-adapting material that can change its stiffness in response to the applied force.
Inspired by how human bone and colorful coral reefs adjust mineral deposits in response to their surrounding environments, researchers have created a self-adapting material that can change its stiffness in response to the applied force.
MOF nanoparticles: Acidic alert
 Researchers have synthesized nanoparticles that can be induced by a change in pH to release a deadly dose of ionized iron within cells. This mechanism could potentially open up new approaches to the targeted elimination of malignant tumors.
Researchers have synthesized nanoparticles that can be induced by a change in pH to release a deadly dose of ionized iron within cells. This mechanism could potentially open up new approaches to the targeted elimination of malignant tumors.
New nanocarrier drug delivery technology crosses the blood-brain barrier
 Researchers developed a cyclic peptide (a chain of amino acids bonded circularly) that enhances blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration. By attaching the cyclic peptide to the surface of nanoparticles, research and development of new drug nanocarriers for drug delivery to the brain becomes possible.
Researchers developed a cyclic peptide (a chain of amino acids bonded circularly) that enhances blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration. By attaching the cyclic peptide to the surface of nanoparticles, research and development of new drug nanocarriers for drug delivery to the brain becomes possible.
Single atom layer trap for lithium-ion migration
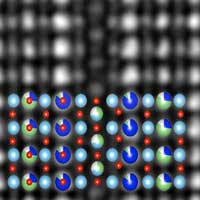 Scientists have observed a new type of microscopic feature that can significantly influence ionic transport.
Scientists have observed a new type of microscopic feature that can significantly influence ionic transport.
Flatter graphene, faster electrons
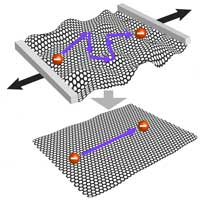 Bumps on a road slow down our pace, so do corrugations in graphene to travelling electrons. By flattening the corrugations out, we help electrons move effectively faster through a graphene sheet.
Bumps on a road slow down our pace, so do corrugations in graphene to travelling electrons. By flattening the corrugations out, we help electrons move effectively faster through a graphene sheet.
High-capacity nanocarbon battery material uses salmon DNA
 Stabilizing the surface of over-lithiated layered oxides using DNA from salmon and carbon nanotubes. Improved catalyst performance and lifespan found through the use of integrated advanced analytical techniques.
Stabilizing the surface of over-lithiated layered oxides using DNA from salmon and carbon nanotubes. Improved catalyst performance and lifespan found through the use of integrated advanced analytical techniques.
A carbon nanotube adhesive sheet with extremely high thermal conductivity
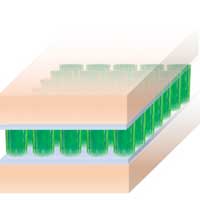 Thermal conductivity three times higher than conventional materials, enabling practical use as a heat dissipation material.
Thermal conductivity three times higher than conventional materials, enabling practical use as a heat dissipation material.
Pushing the limits of 2D supramolecules
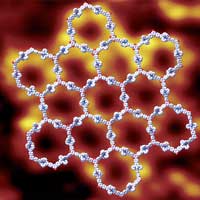 Scientists have reached a new milestone in the development of two-dimensional supramolecules - the building blocks that make areas of nanotechnology and nanomaterial advancement possible.
Scientists have reached a new milestone in the development of two-dimensional supramolecules - the building blocks that make areas of nanotechnology and nanomaterial advancement possible.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
