Wednesday, November 14, 2018
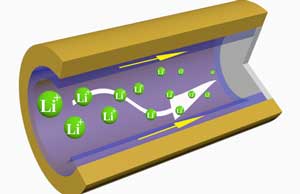
Next gen batteries possible with engineering breakthrough
Physicists discover a new way of resonance tuning for nonlinear optics
Thermal nanotransistor can conduct heat away from electronic components

Epoxy compound gets a graphene bump

The slower they turn, the brighter they glow

When electric fields make spins swirl
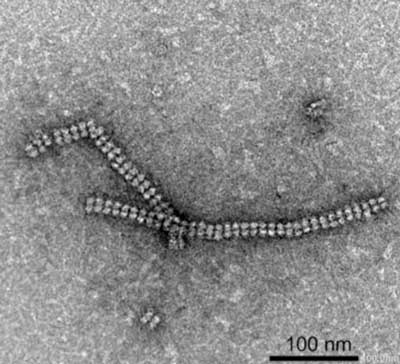
Nanotubes built from protein crystals: Breakthrough in biomolecular engineering
Scientists engineer a functional optical lens out of 2D materials
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
