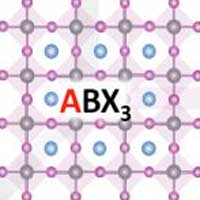
 Scientists have discovered that perovskites, a class of promising materials that could be used for low-cost, high-performance solar cells and LEDs, have a previously unutilized molecular component that can further tune the electronic property of perovskites.
Scientists have discovered that perovskites, a class of promising materials that could be used for low-cost, high-performance solar cells and LEDs, have a previously unutilized molecular component that can further tune the electronic property of perovskites.
Friday, February 5, 2021
New way to power up nanomaterials for electronic applications
 Scientists have discovered that perovskites, a class of promising materials that could be used for low-cost, high-performance solar cells and LEDs, have a previously unutilized molecular component that can further tune the electronic property of perovskites.
Scientists have discovered that perovskites, a class of promising materials that could be used for low-cost, high-performance solar cells and LEDs, have a previously unutilized molecular component that can further tune the electronic property of perovskites.
Tiny sensors reveal cellular forces involved in tissue generation
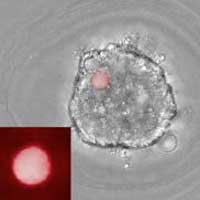 A new technique reveals the forces involved at the cellular level during biological tissue formation and growth processes. The technique could be useful in better understanding how these processes work, and in studying how they may respond to environmental toxins or drug therapies.
A new technique reveals the forces involved at the cellular level during biological tissue formation and growth processes. The technique could be useful in better understanding how these processes work, and in studying how they may respond to environmental toxins or drug therapies.
Crystalline polymers as sensor and detoxifier in one
 A newly developed material not only quickly and selectively indicates the presence of ozone, but also simultaneously renders the gas harmless.
A newly developed material not only quickly and selectively indicates the presence of ozone, but also simultaneously renders the gas harmless.
Trapping gases better with boron nitride nanopores
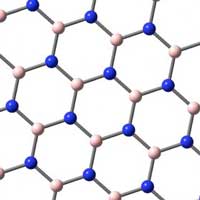 Scientists demonstrate high-performance gas molecule confinement with nanoporous boron nitride, promising to replace standard porous carbon in future.
Scientists demonstrate high-performance gas molecule confinement with nanoporous boron nitride, promising to replace standard porous carbon in future.
A magnetic twist to graphene
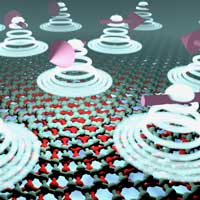 By combining ferromagnets and two rotated layers of graphene, researchers open up a new platform for strongly interacting states using graphene's unique quantum degree of freedom.
By combining ferromagnets and two rotated layers of graphene, researchers open up a new platform for strongly interacting states using graphene's unique quantum degree of freedom.
Inexpensive, printed thermoelectric generators for power generation
 Researchers have developed three-dimensional component architectures based on novel, printable thermoelectric materials. This might be a milestone on the way towards use of inexpensive thermoelectric generators.
Researchers have developed three-dimensional component architectures based on novel, printable thermoelectric materials. This might be a milestone on the way towards use of inexpensive thermoelectric generators.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
