Monday, September 10, 2018
Diamond dust enables low-cost, high-efficiency magnetic field detection
Graphene enables clock rates in the terahertz range
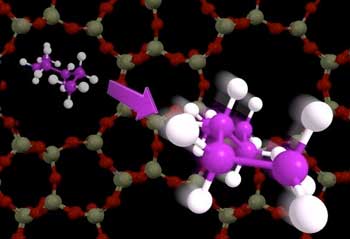
Researchers discover how caged molecules 'rattle and sing'
First truly black solar modules roll off industrial production line

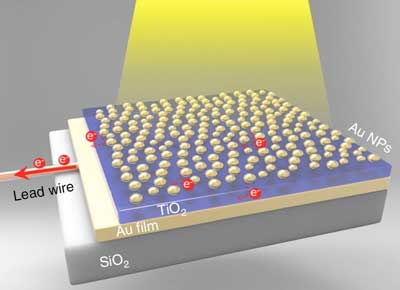
Golden sandwich could make the world more sustainable
Researchers develop a solid material with mobile nanoparticles that react to the environment

Novel cascadable magnetic majority gate (CMMG) that is based on magnetic tunneling junctions
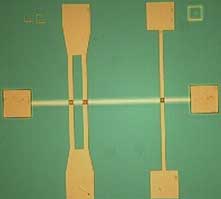
Understanding origami in 2D materials

Algorithm accurately predicts how electromagnetic waves and magnetic materials interact
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
