
Wednesday, August 1, 2018
Harmful dyes in lakes, rivers can become colorless with new, sponge-like material
Advanced microscopy technique reveals new aspects of water at the nanoscale level
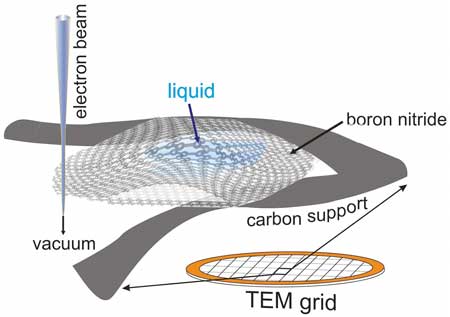
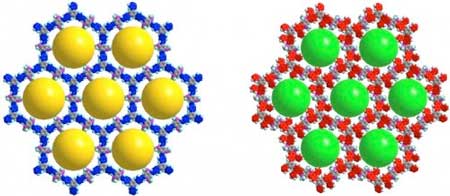
New competition for MOFs: Scientists make stronger COFs
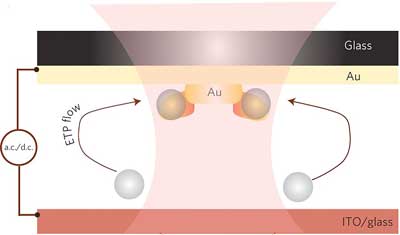
Researchers develop 'tornado' lab-on-a-chip technology with micro tweezers to detect dangerous viruses, biological contaminants
Fast, cheap and colorful 3D printing with nanomaterials

Researchers disclose optical secrets of disulfide nanotubes
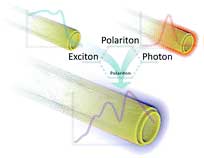
Scientists discover a first-of-its-kind material for the quantum age

An elastic puff of air
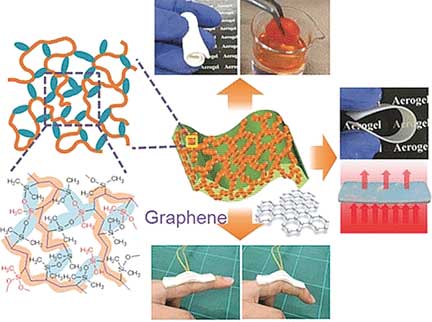
Insight into catalysis through novel study of X-ray absorption spectroscopy

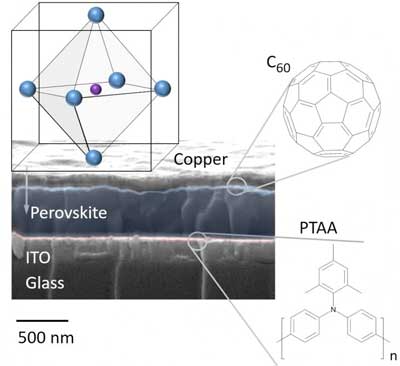
Insight into loss processes in perovskite solar cells enables efficiency improvements
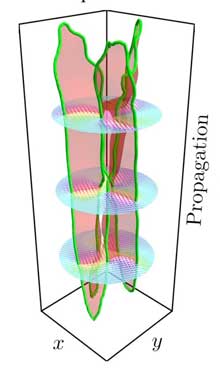
Scientists find holes in light by tying it in knots
Fire-resistant polymer nanocontainers

On-chip optical filter processes wide range of light wavelengths
Sunscreen for dancing molecules

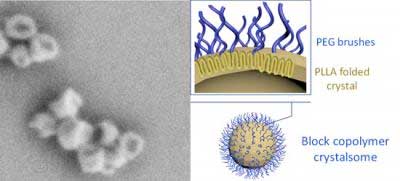
New type of nanoparticle for drug delivery lasts longer in bloodstream
Microscopic antennas to peer into nano-sized worlds

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
