 Migrating cells must overcome physical barriers such as tight pores in finely meshed tissues. A recent study by a team of biophysicists provides a new theory to describe how cells manoeuvre such confining environments.
Migrating cells must overcome physical barriers such as tight pores in finely meshed tissues. A recent study by a team of biophysicists provides a new theory to describe how cells manoeuvre such confining environments.
Friday, March 8, 2019
Cells in a tight spot
 Migrating cells must overcome physical barriers such as tight pores in finely meshed tissues. A recent study by a team of biophysicists provides a new theory to describe how cells manoeuvre such confining environments.
Migrating cells must overcome physical barriers such as tight pores in finely meshed tissues. A recent study by a team of biophysicists provides a new theory to describe how cells manoeuvre such confining environments.
New method opens the way for cutting tools with longer lifetime
 Researchers have developed a theoretical model that enables simulations for showing what happens in hard cutting materials as they degrade. The model will enable manufacturing industry to save both time and money.
Researchers have developed a theoretical model that enables simulations for showing what happens in hard cutting materials as they degrade. The model will enable manufacturing industry to save both time and money.
Scientists take a deep dive into the imperfect world of 2D materials
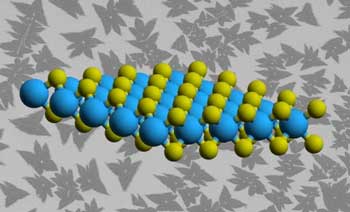 Team combines several nanoscale techniques to gain new insights on the effects of defects in a well-studied monolayer material.
Team combines several nanoscale techniques to gain new insights on the effects of defects in a well-studied monolayer material.
Listening to quantum radio
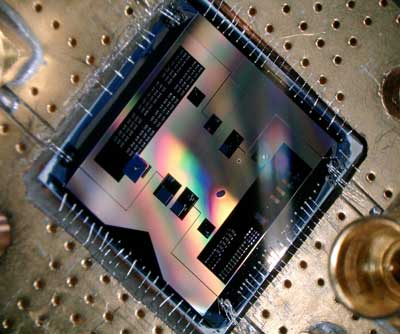 Researchers have created a quantum circuit that enables them to listen to the weakest radio signal allowed by quantum mechanics. This new quantum circuit opens the door to possible future applications in areas such as radio astronomy and medicine (MRI).
Researchers have created a quantum circuit that enables them to listen to the weakest radio signal allowed by quantum mechanics. This new quantum circuit opens the door to possible future applications in areas such as radio astronomy and medicine (MRI).
Researchers simulate the process of adhesive wear
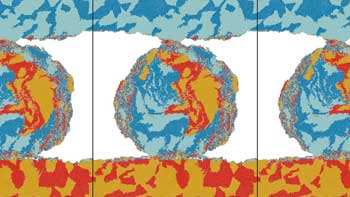 Using high-performance computer simulations, researchers were able to observe how surface roughness changes when two materials rub together. Their findings, which provide insight into friction and wear mechanisms, have implications for areas ranging from engineering to the study of tectonic faults.
Using high-performance computer simulations, researchers were able to observe how surface roughness changes when two materials rub together. Their findings, which provide insight into friction and wear mechanisms, have implications for areas ranging from engineering to the study of tectonic faults.
Super superlattices: The moire patterns of three layers change the electronic properties of graphene
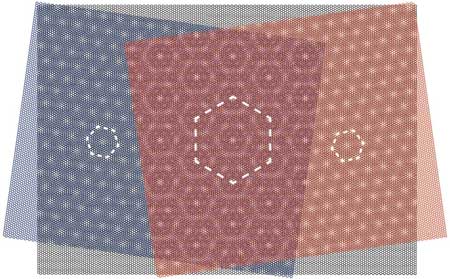 Combining an atomically thin graphene and a boron nitride layer at a slightly rotated angle changes their electrical properties. Physicists have now shown for the first time the combination with a third layer can result in new material properties also in a three-layer sandwich of carbon and boron nitride.
Combining an atomically thin graphene and a boron nitride layer at a slightly rotated angle changes their electrical properties. Physicists have now shown for the first time the combination with a third layer can result in new material properties also in a three-layer sandwich of carbon and boron nitride.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
