 Researchers have demonstrated resonant absorption of terahertz radiation in commercially available graphene. This is an important step toward designing efficient terahertz detectors, which would enable faster internet and a safe replacement for X-ray body scans.
Researchers have demonstrated resonant absorption of terahertz radiation in commercially available graphene. This is an important step toward designing efficient terahertz detectors, which would enable faster internet and a safe replacement for X-ray body scans.
Sunday, June 30, 2019
Physicists use commercial graphene for T-wave detection
 Researchers have demonstrated resonant absorption of terahertz radiation in commercially available graphene. This is an important step toward designing efficient terahertz detectors, which would enable faster internet and a safe replacement for X-ray body scans.
Researchers have demonstrated resonant absorption of terahertz radiation in commercially available graphene. This is an important step toward designing efficient terahertz detectors, which would enable faster internet and a safe replacement for X-ray body scans.
Friday, June 28, 2019
Atomic 'patchwork' using heteroepitaxy for next generation semiconductor devices
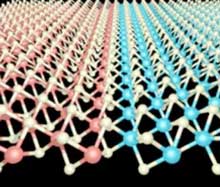 Continuous process for engineering 2D transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDC) heterostructures.
Continuous process for engineering 2D transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDC) heterostructures.
Medicines made of solid gold
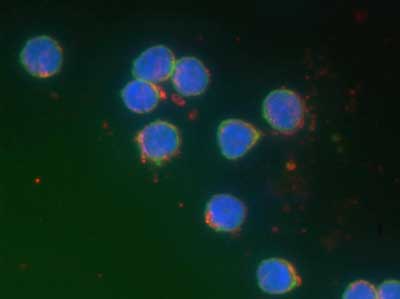 By testing a variety of gold nanoparticles, researchers are providing first evidence of their impact upon human B lymphocytes - the immune cells responsible for antibody production.
By testing a variety of gold nanoparticles, researchers are providing first evidence of their impact upon human B lymphocytes - the immune cells responsible for antibody production.
New material shows high potential for quantum computing
 Researchers are getting closer to confirming the existence of an exotic quantum particle called Majorana fermion, crucial for fault-tolerant quantum computing - the kind of quantum computing that addresses errors during its operation.
Researchers are getting closer to confirming the existence of an exotic quantum particle called Majorana fermion, crucial for fault-tolerant quantum computing - the kind of quantum computing that addresses errors during its operation.
Confirmation of old theory leads to new breakthrough in superconductor science
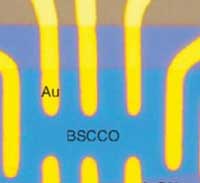 Scientists at Harvard have developed a superconductor that is only one nanometer thick. By studying fluctuations in this ultra-thin material as it transitions into superconductivity, the scientists gained insight into the processes that drive superconductivity.
Scientists at Harvard have developed a superconductor that is only one nanometer thick. By studying fluctuations in this ultra-thin material as it transitions into superconductivity, the scientists gained insight into the processes that drive superconductivity.
Artificial DNA can control release of active ingredients from drugs
 With a combination of hydrogels and artificial DNA, nanoparticles can be released in sequence under conditions similar to those in the human body.
With a combination of hydrogels and artificial DNA, nanoparticles can be released in sequence under conditions similar to those in the human body.
Advanced method for analyzing graphene oxide
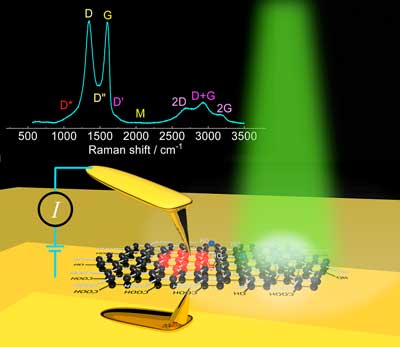 Researchers have developed a reliable method for analyzing the reduction of graphene oxide microregions. In contrast to earlier proposed methods based on Raman spectroscopy, this advanced method provides more exact data about unique properties of certain areas of the material of only a few micrometers in size.
Researchers have developed a reliable method for analyzing the reduction of graphene oxide microregions. In contrast to earlier proposed methods based on Raman spectroscopy, this advanced method provides more exact data about unique properties of certain areas of the material of only a few micrometers in size.
Thursday, June 27, 2019
Novel electrodes enhance battery capacity
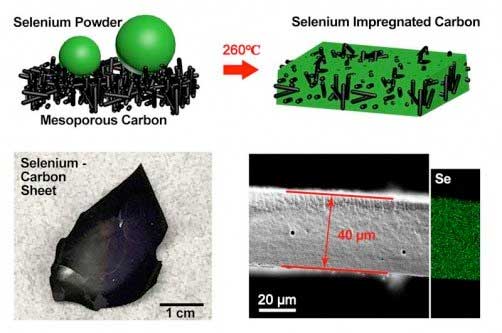 New self-supporting composite metal material doubles the volumetric energy and achieves fast charging rates in batteries.
New self-supporting composite metal material doubles the volumetric energy and achieves fast charging rates in batteries.
New technology gives insight into how nanomaterials form and grow
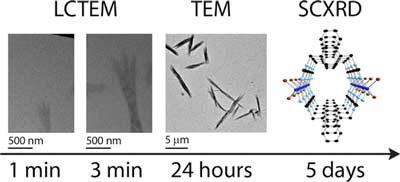 A new form of electron microscopy allows researchers to examine nanoscale tubular materials while they are 'alive' and forming liquids - a first in the field.
A new form of electron microscopy allows researchers to examine nanoscale tubular materials while they are 'alive' and forming liquids - a first in the field.
Portable gas detection shrinks to new dimensions
 The banknote-size sensor can identify each ingredient of a 29-compound mixture in seven seconds. The system also reliably detected compounds that simulate mustard gas and phosphonate-based nerve agents during 40 days of continuous operation.
The banknote-size sensor can identify each ingredient of a 29-compound mixture in seven seconds. The system also reliably detected compounds that simulate mustard gas and phosphonate-based nerve agents during 40 days of continuous operation.
Bursts of light shape walls between waves of charge
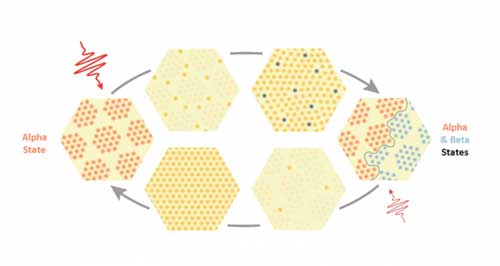 New method provides ultrafast switching of electronic structure and illuminates fundamentals of charge ordering, potentially offering a simple path for next-generation data storage.
New method provides ultrafast switching of electronic structure and illuminates fundamentals of charge ordering, potentially offering a simple path for next-generation data storage.
A new way to make droplets bounce away
 Engineers design surfaces that send rain flying away, potentially preventing icing or soaking.
Engineers design surfaces that send rain flying away, potentially preventing icing or soaking.
Thermoelectric nanomaterial turns waste heat back into electricity
 A low-temperature method for making high-performance thermoelectric materials could recapture lost energy.
A low-temperature method for making high-performance thermoelectric materials could recapture lost energy.
Printing graphene inks in space
 Studying the different self-assembly modes of graphene into functional patterns in zero-gravity will enable the fabrication of graphene electronic devices during long-term space missions, as well as help understand fundamental properties of graphene printing on Earth.
Studying the different self-assembly modes of graphene into functional patterns in zero-gravity will enable the fabrication of graphene electronic devices during long-term space missions, as well as help understand fundamental properties of graphene printing on Earth.
Improved technique for using magnetic nanoclusters to kill hard-to-reach tumors
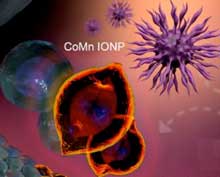 Researchers developed nanoclusters, multiatom collections of nanoparticles, with enhanced heating efficiency. The nanoclusters are hexagon-shaped iron oxide nanoparticles doped with cobalt and manganese and loaded into biodegradable nanocarriers.
Researchers developed nanoclusters, multiatom collections of nanoparticles, with enhanced heating efficiency. The nanoclusters are hexagon-shaped iron oxide nanoparticles doped with cobalt and manganese and loaded into biodegradable nanocarriers.
Wednesday, June 26, 2019
A water repellent 'nanoflower' for biomedical applications
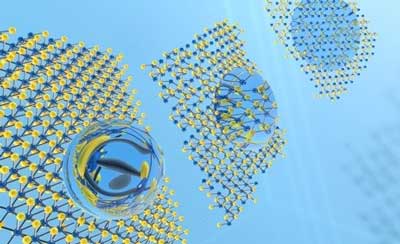 Researchers have developed a 'lotus effect' by incorporating atomic defects in nanomaterials, which could have widespread applications in biomedical field including biosensing, lab-on-a-chip, blood-repellent, anti-fouling and self-cleaning applications.
Researchers have developed a 'lotus effect' by incorporating atomic defects in nanomaterials, which could have widespread applications in biomedical field including biosensing, lab-on-a-chip, blood-repellent, anti-fouling and self-cleaning applications.
Experiment reverses the direction of heat flow
 Scientists used quantum correlations to make heat flow from a colder to a hotter medium without adding external energy, affording a deeper understanding of the second law of thermodynamics.
Scientists used quantum correlations to make heat flow from a colder to a hotter medium without adding external energy, affording a deeper understanding of the second law of thermodynamics.
Perfect quantum portal emerges at exotic interface
 A junction between an ordinary metal and a special kind of superconductor has provided a robust platform to observe Klein tunneling.
A junction between an ordinary metal and a special kind of superconductor has provided a robust platform to observe Klein tunneling.
Using nanotechnology to remove diesel fuel from water and soil
 Researchers have developed a hydrophobic nanosponge to remove diesel fuel from contaminated water and soil.
Researchers have developed a hydrophobic nanosponge to remove diesel fuel from contaminated water and soil.
Atomic Motion is captured in 4D for the first time
 Scientists have gained a never-before-seen view of nucleation - capturing how the atoms rearrange at 4D atomic resolution (that is, in three dimensions of space and across time). The findings differ from predictions based on the classical theory of nucleation that has long appeared in textbooks.
Scientists have gained a never-before-seen view of nucleation - capturing how the atoms rearrange at 4D atomic resolution (that is, in three dimensions of space and across time). The findings differ from predictions based on the classical theory of nucleation that has long appeared in textbooks.
The fundamental physics of frequency combs sheds light on nature's problem-solving skills
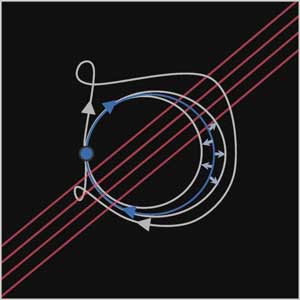 Insight into laser frequency combs improves understanding, advances technology.
Insight into laser frequency combs improves understanding, advances technology.
Shell increases versatility of nanowires
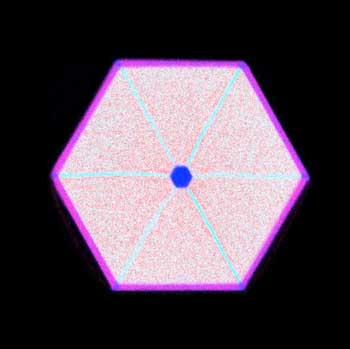 Researchers have managed to produce nanowires with operating wavelengths that can be freely selected over a wide range - simply by altering the shell structure.
Researchers have managed to produce nanowires with operating wavelengths that can be freely selected over a wide range - simply by altering the shell structure.
Bleach-induced transformation for humidity-durable MOF air filters
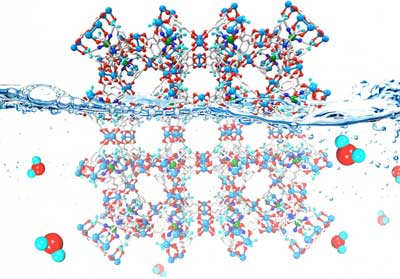 Adding hydroquinone, a skin-bleaching ingredient, to a well-known metal organic framework (MOF) changes its copper ions in a way that makes this porous material exceptionally stable in water.
Adding hydroquinone, a skin-bleaching ingredient, to a well-known metal organic framework (MOF) changes its copper ions in a way that makes this porous material exceptionally stable in water.
Translating proteins into music, and back
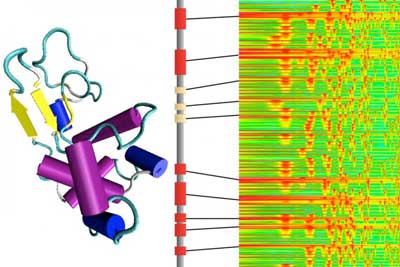 By turning molecular structures into sounds, researchers gain insight into protein structures and create new variations.
By turning molecular structures into sounds, researchers gain insight into protein structures and create new variations.
Hubble finds electrically-charged buckyballs in interstellar space
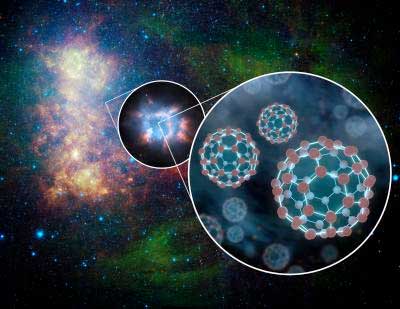 Scientists using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have confirmed the presence of electrically-charged molecules in space shaped like soccer balls, shedding light on the mysterious contents of the interstellar medium (ISM) - the gas and dust that fills interstellar space.
Scientists using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have confirmed the presence of electrically-charged molecules in space shaped like soccer balls, shedding light on the mysterious contents of the interstellar medium (ISM) - the gas and dust that fills interstellar space.
Tuesday, June 25, 2019
Research reveals exotic quantum states in double-layer graphene
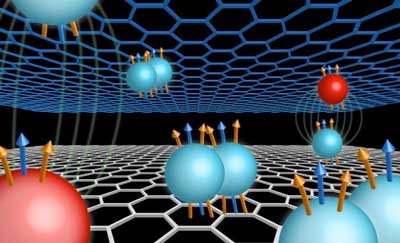 Findings shed new light on the nature of electron interactions in quantum systems and establishing a potential new platform for future quantum computers.
Findings shed new light on the nature of electron interactions in quantum systems and establishing a potential new platform for future quantum computers.
Machine learning reveals how strongly interacting electrons behave at atomic level
 A team of scientists, collaborating across theoretical and experimental physics and computer science, have developed and trained a new Machine Learning technique, to finally understand how electrons behave in important quantum materials.
A team of scientists, collaborating across theoretical and experimental physics and computer science, have developed and trained a new Machine Learning technique, to finally understand how electrons behave in important quantum materials.
A new 'golden' age for electronics?
 Materials that shrink when heated - changing color from black to golden - could save expensive electronics from heat damage.
Materials that shrink when heated - changing color from black to golden - could save expensive electronics from heat damage.
Novel approach to self-assembling mobile micromachines
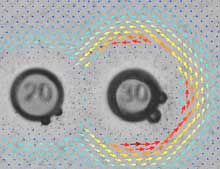 How the components come together depends on their design and shape and the resulting dielectrophoretic forces when exposed to an electric field.
How the components come together depends on their design and shape and the resulting dielectrophoretic forces when exposed to an electric field.
Monday, June 24, 2019
Researchers explain visible light from 2D lead halide perovskites
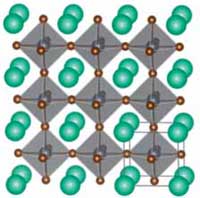 Work resolves mystery and offers new path for light-emitting and other devices.
Work resolves mystery and offers new path for light-emitting and other devices.
Researchers reduce toxic lead in perovskite solar cells
 Researchers detail how they have produced a solar cell which contains 50 percent less lead with the more innocuous tin.
Researchers detail how they have produced a solar cell which contains 50 percent less lead with the more innocuous tin.
Researchers unveil how soft materials react to deformation at molecular level
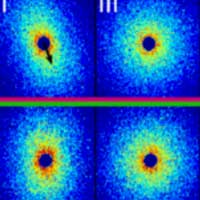 Before designing the next generation of soft materials, researchers must first understand how they behave during rapidly changing deformation. In a new study, researchers challenged previous assumptions regarding polymer behavior with newly developed laboratory techniques that measure polymer flow at the molecular level.
Before designing the next generation of soft materials, researchers must first understand how they behave during rapidly changing deformation. In a new study, researchers challenged previous assumptions regarding polymer behavior with newly developed laboratory techniques that measure polymer flow at the molecular level.
Branching out: Making graphene from gum trees
 Researchers have developed a cost-effective and eco-friendly way of producing graphene using one of Australia's most abundant resources, eucalyptus trees.
Researchers have developed a cost-effective and eco-friendly way of producing graphene using one of Australia's most abundant resources, eucalyptus trees.
Bionic underwater nanogenerator takes cues from electric eels
 Researchers have developed a bionic stretchable nanogenerator that takes inspiration from electric eels.
Researchers have developed a bionic stretchable nanogenerator that takes inspiration from electric eels.
How to bend waves to arrive at the right place
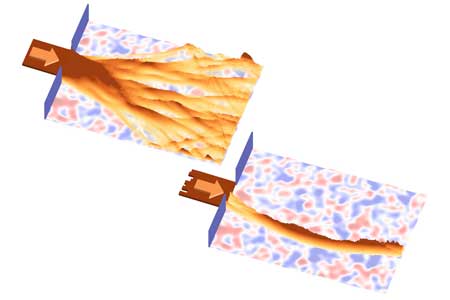 Waves do not always spread uniformly into all directions, but can form a remarkable 'branched flow'. Researchers now have developed a method to control this phenomenon.
Waves do not always spread uniformly into all directions, but can form a remarkable 'branched flow'. Researchers now have developed a method to control this phenomenon.
Friday, June 21, 2019
Researchers take atomic-scale look at metallic glasses
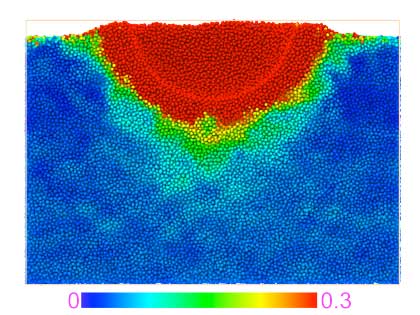 Researchers plan to get an atomic-scale look at bulk metallic glasses to better understand their structure - in particular, the mechanisms that cause them to break.
Researchers plan to get an atomic-scale look at bulk metallic glasses to better understand their structure - in particular, the mechanisms that cause them to break.
Ice lithography: opportunities and challenges in 3D nanofabrication
 The history and progress of ice lithography (IL), and its applications in 3D nanofabrication are reviewed.
The history and progress of ice lithography (IL), and its applications in 3D nanofabrication are reviewed.
Next-gen solar cells spin in new direction with phosphorene
 A nanomaterial made from phosphorus, known as phosphorene, is shaping up as a key ingredient for more sustainable and efficient next-generation perovskite solar cells.
A nanomaterial made from phosphorus, known as phosphorene, is shaping up as a key ingredient for more sustainable and efficient next-generation perovskite solar cells.
Washable electronic textiles to usher in an era of even smarter wearable products
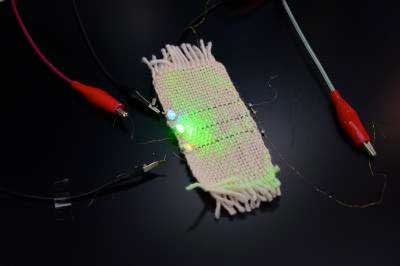 Transistors connected with twisted electrodes maintain functionality even after being bent and washed over 1,000 times and can activate LED or detect electrocardiogram signals.
Transistors connected with twisted electrodes maintain functionality even after being bent and washed over 1,000 times and can activate LED or detect electrocardiogram signals.
New method allows the spin of a quantum dot to be measured without changing it
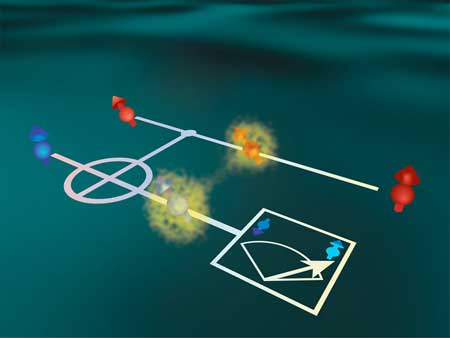 Accurate quantum computing is closer to reality, thanks to quantum non-demolition measurements.
Accurate quantum computing is closer to reality, thanks to quantum non-demolition measurements.
Advanced NMR captures new details in nanoparticle structures
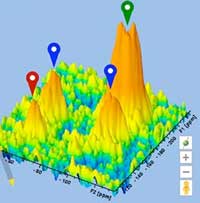 Advanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques have revealed surprising details about the structure of a key group of materials in nanotechology, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, and the placement of their active chemical sites.
Advanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques have revealed surprising details about the structure of a key group of materials in nanotechology, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, and the placement of their active chemical sites.
Nanoemulsion gels offer new way to deliver drugs through the skin
 Novel materials made with FDA-approved components could deliver large payloads of active ingredients.
Novel materials made with FDA-approved components could deliver large payloads of active ingredients.
Thursday, June 20, 2019
Electron-behaving nanoparticles rock current understanding of matter
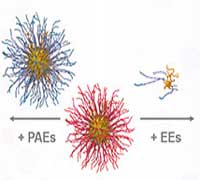 Discovery will lead to new methods for materials design.
Discovery will lead to new methods for materials design.
Researchers study super-repellent nanosurfaces for safer fruits, vegetables
 The National Institute of Food and Agriculture in the U.S. awarded a grant to study and develop super-repellent and anti-fouling surfaces for foods.
The National Institute of Food and Agriculture in the U.S. awarded a grant to study and develop super-repellent and anti-fouling surfaces for foods.
'DNA microscopy' offers entirely new way to image cells
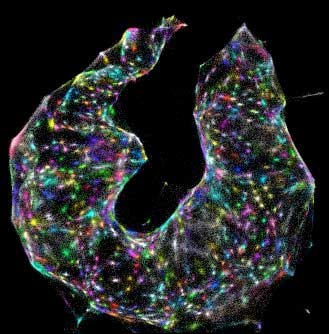 Instead of relying on light (or any kind of optics at all), scientists use DNA 'bar codes' to help pinpoint molecules' relative positions within a sample.
Instead of relying on light (or any kind of optics at all), scientists use DNA 'bar codes' to help pinpoint molecules' relative positions within a sample.
Using graphene and tiny droplets to detect stomach-cancer causing bacteria
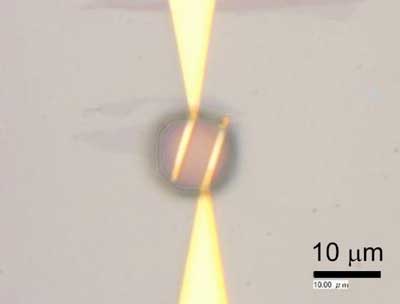 Scientists have invented a new biosensor using graphene to detect bacteria such as those that attack the stomach lining and that have been linked to stomach cancer. When the bacteria interact with the biosensor, chemical reactions are triggered which are detected by the graphene.
Scientists have invented a new biosensor using graphene to detect bacteria such as those that attack the stomach lining and that have been linked to stomach cancer. When the bacteria interact with the biosensor, chemical reactions are triggered which are detected by the graphene.
Crystal with a twist: scientists grow spiraling new material
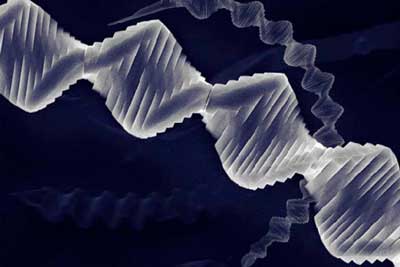 Researchers have created new inorganic crystals made of stacks of atomically thin sheets that unexpectedly spiral like a nanoscale card deck.
Researchers have created new inorganic crystals made of stacks of atomically thin sheets that unexpectedly spiral like a nanoscale card deck.
Current-induced multilevel storage without initialization for high density magnetic memory
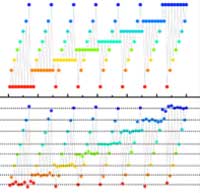 Researchers present an experimental characterization of a multilevel spin-orbit-torque magnetic random access memory (SOT-MRAM) cell based on a perpendicularly magnetized heterostructure and addressed the initialization-free issue of multilevel storage schemes.
Researchers present an experimental characterization of a multilevel spin-orbit-torque magnetic random access memory (SOT-MRAM) cell based on a perpendicularly magnetized heterostructure and addressed the initialization-free issue of multilevel storage schemes.
A ferromagnetic memristor based on conventional magnetic memory
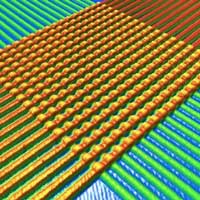 A team of researchers has proposed a spin-orbit-torque memristive device based upon Ta/CoFeB/MgO heterostructures with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy.
A team of researchers has proposed a spin-orbit-torque memristive device based upon Ta/CoFeB/MgO heterostructures with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy.
Graphene could prevent degradation of neurostimulation electrodes
 Millions with neurological diseases could find new option in neurostimulation devices.
Millions with neurological diseases could find new option in neurostimulation devices.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
