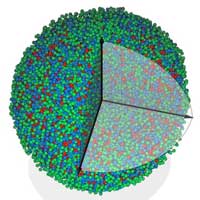
 For more than a century, an important class of matter -- the amorphous solid -- has eluded scientists' ability to depict nature at the level of atoms and molecules. Until now. A study reports the first-ever determination of an amorphous solid's three-dimensional atomic structure.
For more than a century, an important class of matter -- the amorphous solid -- has eluded scientists' ability to depict nature at the level of atoms and molecules. Until now. A study reports the first-ever determination of an amorphous solid's three-dimensional atomic structure.
Wednesday, March 31, 2021
Century-old problem solved with first-ever 3D atomic imaging of an amorphous solid
 For more than a century, an important class of matter -- the amorphous solid -- has eluded scientists' ability to depict nature at the level of atoms and molecules. Until now. A study reports the first-ever determination of an amorphous solid's three-dimensional atomic structure.
For more than a century, an important class of matter -- the amorphous solid -- has eluded scientists' ability to depict nature at the level of atoms and molecules. Until now. A study reports the first-ever determination of an amorphous solid's three-dimensional atomic structure.
Thermal power nanogenerator created without solid moving parts
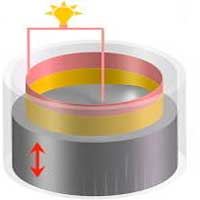 Researchers propose a thermal power nanogenerator, called a thermoacoustically driven liquid-metal-based triboelectric nanogenerator, or TA-LM-TENG, which converts thermal energy into electrical energy.
Researchers propose a thermal power nanogenerator, called a thermoacoustically driven liquid-metal-based triboelectric nanogenerator, or TA-LM-TENG, which converts thermal energy into electrical energy.
'Designer' pore shows selective traffic to and from the cell nucleus
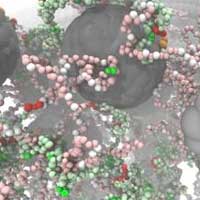 Scientists have developed an artificial model of membrane pores using simple design rules, which enabled them to study how this feat is accomplished.
Scientists have developed an artificial model of membrane pores using simple design rules, which enabled them to study how this feat is accomplished.
A speed limit for spins
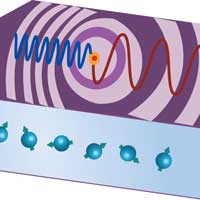 Scientists report that, when driven out of equilibrium by magnetic fields, a universal Doppler effect limits the maximal spin current in magnetic insulators. This finding is a surprising analogy to what happens in superconductors driven by electric fields and could provide a fundamental design principle for future nano-devices with computing science and power applications.
Scientists report that, when driven out of equilibrium by magnetic fields, a universal Doppler effect limits the maximal spin current in magnetic insulators. This finding is a surprising analogy to what happens in superconductors driven by electric fields and could provide a fundamental design principle for future nano-devices with computing science and power applications.
New method helps model the behavior of 2D materials under pressure
 The research will help create pressure sensors based on silicene or other 2D materials.
The research will help create pressure sensors based on silicene or other 2D materials.
Tuesday, March 30, 2021
Faster and less-invasive atomic force microscopy for visualizing biomolecular systems
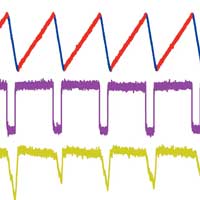 Researchers demonstrate a newly developed atomic force microscopy approach for imaging biological samples and processes. The method offers higher frame rates and less disturbance of samples.
Researchers demonstrate a newly developed atomic force microscopy approach for imaging biological samples and processes. The method offers higher frame rates and less disturbance of samples.
Researchers first to link silicon atoms on surfaces
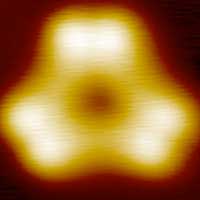 A team consisting of various working groups from the fields of chemistry and physics are now the first to have linked silicon atoms on surfaces. From silicon polymers, the researchers hope for innovative material properties and new, promising candidates for potential applications.
A team consisting of various working groups from the fields of chemistry and physics are now the first to have linked silicon atoms on surfaces. From silicon polymers, the researchers hope for innovative material properties and new, promising candidates for potential applications.
Monday, March 29, 2021
This nanosensor could turn your smartphone into a supersmart gas sensor
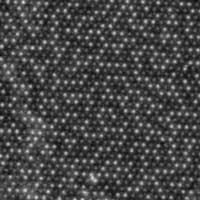 Researchers reported an atomically thin 2D sensor that works at room temperature and thus consumes less power than conventional sensors.
Researchers reported an atomically thin 2D sensor that works at room temperature and thus consumes less power than conventional sensors.
Tires turned into graphene that makes stronger concrete
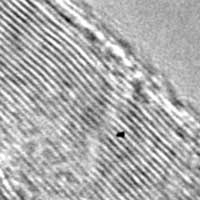 Researchers have optimized a process to convert waste from rubber tires into graphene that can, in turn, be used to strengthen concrete.
Researchers have optimized a process to convert waste from rubber tires into graphene that can, in turn, be used to strengthen concrete.
Standing out: Unusual magnetic transition in perovskite oxide can help boost spintronics
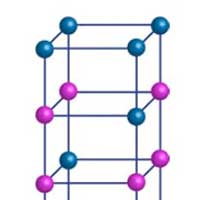 Scientists examined the perovskite oxide PbFeO3, a compound that has evaded inspection until now, owing to difficulties in synthesizing samples and resolving its crystal structure.
Scientists examined the perovskite oxide PbFeO3, a compound that has evaded inspection until now, owing to difficulties in synthesizing samples and resolving its crystal structure.
Method offers inexpensive imaging at the scale of virus particles
 Using an ordinary light microscope, researchers can now obtain images with unprecedented accuracy.
Using an ordinary light microscope, researchers can now obtain images with unprecedented accuracy.
Scientists use nanotechnology to detect bone-healing stem cells
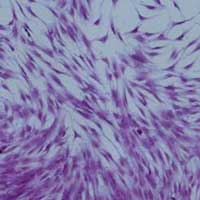 Researchers have developed a new way of using nanomaterials to identify and enrich skeletal stem cells - a discovery which could eventually lead to new treatments for major bone fractures and the repair of lost or damaged bone.
Researchers have developed a new way of using nanomaterials to identify and enrich skeletal stem cells - a discovery which could eventually lead to new treatments for major bone fractures and the repair of lost or damaged bone.
Putting a spin on Heusler alloys
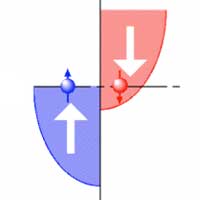 A review on the latest research of the various types of Heusler alloys summarizes the field?s main achievements up to 2020.
A review on the latest research of the various types of Heusler alloys summarizes the field?s main achievements up to 2020.
Kirigami-style nanostructure fabrication may open new world of micro and nanostructures
 Using a technique that mimics the ancient Japanese art of kirigami, a team of researchers may offer an easier way to fabricate complex 3D nanostructures for use in electronics, manufacturing and health care.
Using a technique that mimics the ancient Japanese art of kirigami, a team of researchers may offer an easier way to fabricate complex 3D nanostructures for use in electronics, manufacturing and health care.
The road to quantum computing
 The race for the quantum computer will most likely be decided at the quantum bit (qubit) ? the smallest information unit of the quantum computer. The coupling of several qubits into a computing system is currently one of the greatest challenges in the development of quantum computers.
The race for the quantum computer will most likely be decided at the quantum bit (qubit) ? the smallest information unit of the quantum computer. The coupling of several qubits into a computing system is currently one of the greatest challenges in the development of quantum computers.
Contact lenses poised to detect cancer, treat disease and replace digital screens
 Newly-published 'contact lens technologies of the future' paper reviews innovative uses for disease detection and therapy, drug delivery, vision enhancement and more.
Newly-published 'contact lens technologies of the future' paper reviews innovative uses for disease detection and therapy, drug delivery, vision enhancement and more.
Electromagnetic fields of nanostructures visualized in 3D for the first time
 Scientists have succeeded in imaging so-called surface phonons in three dimensions for the first time. The research success could accelerate the development of new, efficient nanotechnologies.
Scientists have succeeded in imaging so-called surface phonons in three dimensions for the first time. The research success could accelerate the development of new, efficient nanotechnologies.
Friday, March 26, 2021
Controlling bubble formation on electrodes
 Study finds the wettability of porous electrode surfaces is key to making efficient water-splitting or carbon-capturing systems.
Study finds the wettability of porous electrode surfaces is key to making efficient water-splitting or carbon-capturing systems.
Plasmon-coupled gold nanoparticles useful for thermal history sensing
 Researchers have demonstrated that stretching shape-memory polymers embedded with clusters of gold nanoparticles alters their plasmon-coupling, giving rise to desirable optical properties.
Researchers have demonstrated that stretching shape-memory polymers embedded with clusters of gold nanoparticles alters their plasmon-coupling, giving rise to desirable optical properties.
Pressure sensor with high sensitivity and linear response based on soft micropillared electrodes
 Researchers have improved the deformability of the sensor structure by designing a flexible electrode with a surface micropillared structure with a large aspect ratio that is easy to buckle and lose stability.
Researchers have improved the deformability of the sensor structure by designing a flexible electrode with a surface micropillared structure with a large aspect ratio that is easy to buckle and lose stability.
DNA-metal double helix
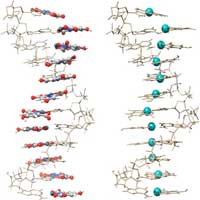 Single-stranded DNA as supramolecular template for highly organized palladium nanowires.
Single-stranded DNA as supramolecular template for highly organized palladium nanowires.
Measuring the topology of a polaritonic analog of graphene
 A recent study reports the measurement of topological invariants in artificial graphene.
A recent study reports the measurement of topological invariants in artificial graphene.
Tuning of one atomic layer unlocks catalytic pathway
 An atomically precise surface probe helped researchers discover that a catalyst can be activated by tuning the composition of just one atomic surface layer.
An atomically precise surface probe helped researchers discover that a catalyst can be activated by tuning the composition of just one atomic surface layer.
How to make atomic-scale superconductors resistant to magnetic fields
 Scientists discovered that a superconductor with atomic-scale thickness can retain its superconductivity even when a strong magnetic field is applied to it.
Scientists discovered that a superconductor with atomic-scale thickness can retain its superconductivity even when a strong magnetic field is applied to it.
Inexpensive tin packs a big punch for the future of supercapacitors
 Researchers have developed a better material to improve connectivity while maintaining recyclability and low cost.
Researchers have developed a better material to improve connectivity while maintaining recyclability and low cost.
Sorting out nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers (w/video)
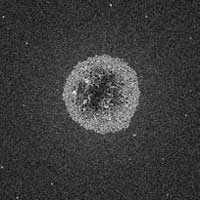 Scientists have developed a method to use lasers to control the movement of nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers.
Scientists have developed a method to use lasers to control the movement of nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers.
Researchers harvest energy from radio waves to power wearable devices
 Researchers developed a stretchable wideband dipole antenna system capable of wirelessly transmitting data that is collected from health-monitoring sensors.
Researchers developed a stretchable wideband dipole antenna system capable of wirelessly transmitting data that is collected from health-monitoring sensors.
Looking at the potential for a new magnetised nanoparticle to treat brain cancer
 Scientists found new magnetised nanoparticle can be used in combination with other therapies, such as magnetic heat therapy, to potentially treat brain cancer.
Scientists found new magnetised nanoparticle can be used in combination with other therapies, such as magnetic heat therapy, to potentially treat brain cancer.
Thursday, March 25, 2021
Scientists uncover a process that stands in the way of making quantum dots brighter
 The results have important implications for today's TV and display screens and for future technologies where light takes the place of electrons and fluids.
The results have important implications for today's TV and display screens and for future technologies where light takes the place of electrons and fluids.
Exploring the nanoworld in 3D
 Scientists combined several electron microscopy techniques to map out the phonon-polariton excitations across the surface of magnesium oxide nanostructures with high spatial, spectral, and angular resolution. The reconstruction of the surface excitation maps in three dimensions will be useful for understanding and optimizing the properties of the nanostructured materials for advanced functionality.
Scientists combined several electron microscopy techniques to map out the phonon-polariton excitations across the surface of magnesium oxide nanostructures with high spatial, spectral, and angular resolution. The reconstruction of the surface excitation maps in three dimensions will be useful for understanding and optimizing the properties of the nanostructured materials for advanced functionality.
New class of versatile, high-performance quantum dots primed for medical imaging, quantum computing
 An atomically defined interlayer embedded into a quantum dot emits single photons at room temperature and allows tuning a wavelength in discrete quantized jumps.
An atomically defined interlayer embedded into a quantum dot emits single photons at room temperature and allows tuning a wavelength in discrete quantized jumps.
New nanotransistors keep their cool at high voltages
 Power converters play an essential role in electric vehicles and solar panels, for example, but tend to lose a lot of power in the form of heat in the electricity conversion process. Thanks to a new type of transistor, these converters can perform at substantially improved efficiencies, especially in high-power applications.
Power converters play an essential role in electric vehicles and solar panels, for example, but tend to lose a lot of power in the form of heat in the electricity conversion process. Thanks to a new type of transistor, these converters can perform at substantially improved efficiencies, especially in high-power applications.
'Climbing droplets' could lead to more efficient water harvesting
 Researchers' novel surface encourages droplets to move spontaneously into larger droplets.
Researchers' novel surface encourages droplets to move spontaneously into larger droplets.
A new European infrastructure will facilitate the transfer of nano-pharmaceuticals from lab to the clinic
 The PHOENIX project will provide a new infrastructure available to research laboratories, SMEs and start-ups to facilitate the transfer of nano-pharmaceuticals from the laboratory to clinical practice.
The PHOENIX project will provide a new infrastructure available to research laboratories, SMEs and start-ups to facilitate the transfer of nano-pharmaceuticals from the laboratory to clinical practice.
Nickel-platinum nanoparticles give boost to detection of cancer and disease
 The technique uses nickel-platinum nanoparticles to increase the sensitivity of an ELISA, which is used to test for the presence of cancers, HIV and more.
The technique uses nickel-platinum nanoparticles to increase the sensitivity of an ELISA, which is used to test for the presence of cancers, HIV and more.
Gearing up nanoscale machines
 Scientists are advancing the science of molecular-scale gear trains for transmitting rotational force.
Scientists are advancing the science of molecular-scale gear trains for transmitting rotational force.
Researchers discover new organic conductor
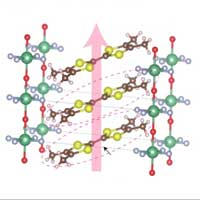 Researchers have discovered a one-dimensional charge transfer salt with an infinite anion chain. This one-dimensional substance exhibits unique physical phenomena and functionality.
Researchers have discovered a one-dimensional charge transfer salt with an infinite anion chain. This one-dimensional substance exhibits unique physical phenomena and functionality.
Revealing nano Big Bang - Scientists observe the first milliseconds of crystal formation (w/video)
 New study shows how stable materials have unstable beginnings.
New study shows how stable materials have unstable beginnings.
Technology uses 'single' approach to develop electronics, acoustics
 Researchers have developed a new approach to creating popular thin films used for devices across a broad range of fields, including optics, acoustics and electronics.
Researchers have developed a new approach to creating popular thin films used for devices across a broad range of fields, including optics, acoustics and electronics.
Microswimmers to be made capable of learning with machine learning algorithms
 A team of physicists have developed a method for giving tiny artificial microswimmers a certain ability to learn using machine learning algorithms.
A team of physicists have developed a method for giving tiny artificial microswimmers a certain ability to learn using machine learning algorithms.
Scientists develop sensor with nanopores for definition doping in blood
 Researchers have developed a new sensor with two layers of nanopores. In the conducted experiments, this sensor showed its efficiency as a sensor for one of the doping substances from chiral molecules.
Researchers have developed a new sensor with two layers of nanopores. In the conducted experiments, this sensor showed its efficiency as a sensor for one of the doping substances from chiral molecules.
Wednesday, March 24, 2021
Shining a healing light on the brain with nanoscintillators
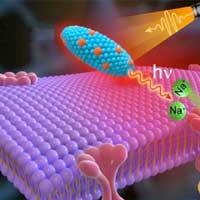 This new treatment involves stimulation of neurons deep within the brain by means of injected nanoparticles that light up when exposed to X-rays (nanoscintillators) and would eliminate an invasive brain surgery currently in use.
This new treatment involves stimulation of neurons deep within the brain by means of injected nanoparticles that light up when exposed to X-rays (nanoscintillators) and would eliminate an invasive brain surgery currently in use.
Semiconductor qubits scale in two dimensions
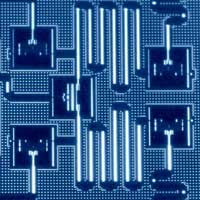 Researchers have shown that semiconductor technology can be used to build a two-dimensional array of qubits to function as a quantum processor.
Researchers have shown that semiconductor technology can be used to build a two-dimensional array of qubits to function as a quantum processor.
Shining light to make hydrogen
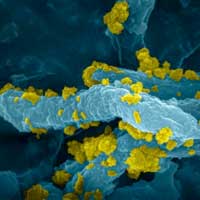 Researchers engineer light-driven bacterial factories to produce hydrogen.
Researchers engineer light-driven bacterial factories to produce hydrogen.
Small robot swimmers that heal themselves from damage (w/video)
 Researchers have developed small, swimming robots that can magnetically heal themselves on-the-fly after breaking into two or three pieces.
Researchers have developed small, swimming robots that can magnetically heal themselves on-the-fly after breaking into two or three pieces.
Fighting cancer with DNA origami
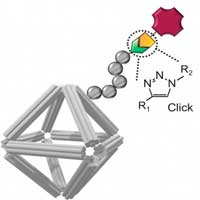 A new approach to functional and physiologically stable DNA origami for biomedical applications.
A new approach to functional and physiologically stable DNA origami for biomedical applications.
Copper foam as a highly efficient, durable filter for reusable masks and air cleaners
 Researchers have transformed copper nanowires into metal foams that could be used in facemasks and air filtration systems. The foams filter efficiently, decontaminate easily for reuse and are recyclable.
Researchers have transformed copper nanowires into metal foams that could be used in facemasks and air filtration systems. The foams filter efficiently, decontaminate easily for reuse and are recyclable.
Coated zinc sulfide nanoparticles are catalytically active
 Scientists discovered a way to retain zinc sulfide's brilliant color and also enable its use as a catalyst; for example, to convert sunlight into usable energy.
Scientists discovered a way to retain zinc sulfide's brilliant color and also enable its use as a catalyst; for example, to convert sunlight into usable energy.
The arrangement matters: how to design advanced thermoelectrics
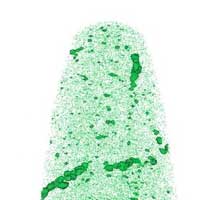 Researchers were able to significantly reduce the thermal conductivity of lead-tellurium thermoelectrics without increasing the dislocation density. For the first time, it is demonstrated that the arrangement of the dislocations and their composition are as important as their amount.
Researchers were able to significantly reduce the thermal conductivity of lead-tellurium thermoelectrics without increasing the dislocation density. For the first time, it is demonstrated that the arrangement of the dislocations and their composition are as important as their amount.
Scientists finds new inroads in fast charging for lithium-ion batteries
 Scientists have long thought the laws of physics limited how fast you could safely recharge a battery, but new research has opened the door to creating a battery that can be recharged in just a fraction of the time.
Scientists have long thought the laws of physics limited how fast you could safely recharge a battery, but new research has opened the door to creating a battery that can be recharged in just a fraction of the time.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
