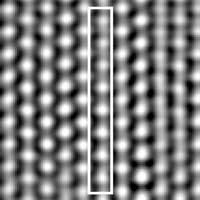
 In a step towards the goal of shrinking electronic devices to the molecular scale, an international team of researchers has developed a stable silver wire that is just one atom wide.
In a step towards the goal of shrinking electronic devices to the molecular scale, an international team of researchers has developed a stable silver wire that is just one atom wide.
Sunday, February 28, 2021
Researchers develop stable silver wire that is just one atom wide
 In a step towards the goal of shrinking electronic devices to the molecular scale, an international team of researchers has developed a stable silver wire that is just one atom wide.
In a step towards the goal of shrinking electronic devices to the molecular scale, an international team of researchers has developed a stable silver wire that is just one atom wide.
How photoblueing disturbs microscopy
 The latest developments in fluorescence microscopy make it possible to image individual molecules in cells or molecular complexes with a spatial resolution of up to 20 nanometres. However, under certain circumstances, an effect occurs that falsifies the results: the laser light used can cause very reactive oxygen molecules to form in the sample.
The latest developments in fluorescence microscopy make it possible to image individual molecules in cells or molecular complexes with a spatial resolution of up to 20 nanometres. However, under certain circumstances, an effect occurs that falsifies the results: the laser light used can cause very reactive oxygen molecules to form in the sample.
Friday, February 26, 2021
Engineering the boundary between 2D and 3D materials
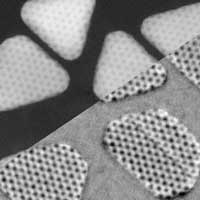 Cutting-edge microscope helps reveal ways to control the electronic properties of atomically thin materials.
Cutting-edge microscope helps reveal ways to control the electronic properties of atomically thin materials.
Light-emitting tattoo engineered for the first time
 Researchers have created a temporary tattoo with light-emitting technology used in TV and smartphone screens, paving the way for a new type of 'smart tattoo'.
Researchers have created a temporary tattoo with light-emitting technology used in TV and smartphone screens, paving the way for a new type of 'smart tattoo'.
Sub-diffraction optical writing enables data storage at the nanoscale
 Researchers have overcome the limitation of laser-enabled optical data storage by using earth-rich lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide flakes.
Researchers have overcome the limitation of laser-enabled optical data storage by using earth-rich lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide flakes.
From microsaws to nanodrills: laser pulses act as subtle machining tools
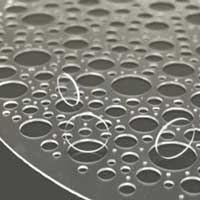 Industrial-grade materials processing on the sub-micron scale is enabled by spatially structured ultrashort laser pulses.
Industrial-grade materials processing on the sub-micron scale is enabled by spatially structured ultrashort laser pulses.
A more effective nanomedicine developed for the treatment of rare Fabry disease
 The results have been made possible thanks to nanotechnology and the approach developed could be applied to other drugs in the future. The new drug improves on current treatments, helps reduce costs and improve patients' quality of life.
The results have been made possible thanks to nanotechnology and the approach developed could be applied to other drugs in the future. The new drug improves on current treatments, helps reduce costs and improve patients' quality of life.
Physicists develop a new method for counting molecules
 Picosecond time-resolved photon antibunching measures nanoscale exciton motion and the true number of chromophores.
Picosecond time-resolved photon antibunching measures nanoscale exciton motion and the true number of chromophores.
Weakness is strength for this low-temperature battery
 Nanoengineers have discovered new fundamental insights for developing lithium metal batteries that perform well at ultra-low temperatures; mainly, that the weaker the electrolyte holds on to lithium ions, the better.
Nanoengineers have discovered new fundamental insights for developing lithium metal batteries that perform well at ultra-low temperatures; mainly, that the weaker the electrolyte holds on to lithium ions, the better.
Sustainable harvesting of electrical energy with nanoporous materials
 Scientists are investigating whether phase transitions of water in nanopores can be used to generate electrical energy on a larger scale.
Scientists are investigating whether phase transitions of water in nanopores can be used to generate electrical energy on a larger scale.
Adding nanofibers to the silkworm's diet makes them spin stronger silk
 Researchers tweaked the diet of silkworms by adding cellulose nanofiber to their food. The resultant silk was stronger and more durable. This new method of realizing cellulose nanofiber synthesized silk is a sustainable way to produce biomaterials.
Researchers tweaked the diet of silkworms by adding cellulose nanofiber to their food. The resultant silk was stronger and more durable. This new method of realizing cellulose nanofiber synthesized silk is a sustainable way to produce biomaterials.
Thursday, February 25, 2021
Putting graphene in a spin
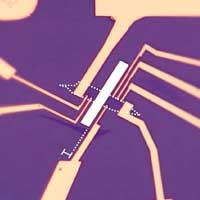 Researchers induce artificial 'magnetic texture' in graphene, a quantum science advancement that could help lead to more powerful semiconductors, computers.
Researchers induce artificial 'magnetic texture' in graphene, a quantum science advancement that could help lead to more powerful semiconductors, computers.
Developing 2D polymers
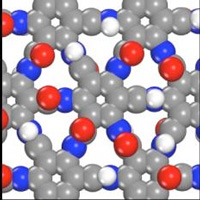 Scientists used computer simulations to compare the thermal stability of the 1D polymer Kevlar, a 2D polymer called an amide covalent organic framework, and a hypothetical 2D polymer designed by the laboratory called graphamid.
Scientists used computer simulations to compare the thermal stability of the 1D polymer Kevlar, a 2D polymer called an amide covalent organic framework, and a hypothetical 2D polymer designed by the laboratory called graphamid.
Molecular bridges power up printed electronics
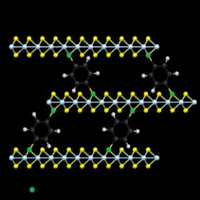 Researchers boost the efficiency of conductive inks and devices connecting layered materials flakes with small molecules.
Researchers boost the efficiency of conductive inks and devices connecting layered materials flakes with small molecules.
Chip simplifies COVID-19 testing, delivers results on a phone
 Programmed magnetic nanobeads enable diagnostic device.
Programmed magnetic nanobeads enable diagnostic device.
Graphene filter makes carbon capture more efficient and cheaper
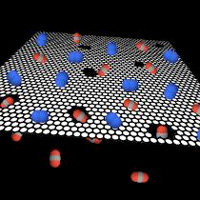 Chemical engineers have developed a graphene filter for carbon capture that surpasses the efficiency of commercial capture technologies, and can reduce the cost carbon capture down to $30 per ton of carbon dioxide.
Chemical engineers have developed a graphene filter for carbon capture that surpasses the efficiency of commercial capture technologies, and can reduce the cost carbon capture down to $30 per ton of carbon dioxide.
Nanobubbles could improve dentists' tools
 People's teeth-chattering experiences in the dentist's chair could be improved by fresh insights into how tiny, powerful bubbles are formed by ultra-fast vibrations, a study suggests.
People's teeth-chattering experiences in the dentist's chair could be improved by fresh insights into how tiny, powerful bubbles are formed by ultra-fast vibrations, a study suggests.
Bio-based membranes with ocular stem cells to treat corneal disorders
 The production, preparation, and use of bacterial nanocellulose as corneal bandages could be the key to help delicate stem cells to migrate to the cornea and heal the eye from a range of ocular disorders.
The production, preparation, and use of bacterial nanocellulose as corneal bandages could be the key to help delicate stem cells to migrate to the cornea and heal the eye from a range of ocular disorders.
Biobattery-powered microneedle patch can deliver drugs and procure testing samples
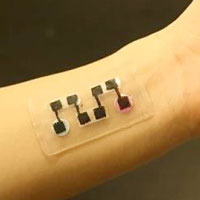 Researchers have developed a biobattery-powered device capable of both delivering large molecule pharmaceuticals across the skin barrier and extracting interstitial fluid for diagnostic purposes.
Researchers have developed a biobattery-powered device capable of both delivering large molecule pharmaceuticals across the skin barrier and extracting interstitial fluid for diagnostic purposes.
Nanocrystals for high-resolution X-ray imaging of curved 3D objects
 New flexible X-ray sensor suitable for next-generation medical and industrial applications.
New flexible X-ray sensor suitable for next-generation medical and industrial applications.
On the line: Watching nanoparticles get in shape
 New method could advance next-generation applications in medicine, cosmetics, and petroleum recovery.
New method could advance next-generation applications in medicine, cosmetics, and petroleum recovery.
Wednesday, February 24, 2021
An intelligent soft material that curls under pressure or expands when stretched
 Researchers have printed liquid metal circuits onto a single piece of soft polymer, creating an intelligent material that curls under pressure or mechanical strain.
Researchers have printed liquid metal circuits onto a single piece of soft polymer, creating an intelligent material that curls under pressure or mechanical strain.
Treating rheumatoid arthritis with micromotors
 Researchers have developed magnesium-based micromotors propelled by hydrogen bubbles, which improved rheumatoid arthritis symptoms when injected into the joints of rats.
Researchers have developed magnesium-based micromotors propelled by hydrogen bubbles, which improved rheumatoid arthritis symptoms when injected into the joints of rats.
An mRNA nanovaccine for cancer immunotherapy
 Researchers have developed a graphene oxide hydrogel that, when injected into mice with melanoma, slowly released RNA nanovaccines that shrank tumors and kept them from metastasizing.
Researchers have developed a graphene oxide hydrogel that, when injected into mice with melanoma, slowly released RNA nanovaccines that shrank tumors and kept them from metastasizing.
3D-printing perovskites on graphene makes next-gen X-ray detectors
 By using 3D aerosol jet-printing to put perovskites on graphene, scientists have made X-ray detectors with record sensitivity that can greatly improve the efficiency and reduce the cost and health hazard of medical imaging devices.
By using 3D aerosol jet-printing to put perovskites on graphene, scientists have made X-ray detectors with record sensitivity that can greatly improve the efficiency and reduce the cost and health hazard of medical imaging devices.
Measuring carbon nanotubes taken up by plants
 Scientists describe a way to measure levels of a specific kind of carbon nanotube in plant tissues.
Scientists describe a way to measure levels of a specific kind of carbon nanotube in plant tissues.
Tuesday, February 23, 2021
Buckyballs on DNA for harvesting light
 Supramolecular structure boosts efficiency of light harvesting for solar cells.
Supramolecular structure boosts efficiency of light harvesting for solar cells.
Biopolymer-coated nanocatalyst can help realize a hydrogen fuel-driven future
 Scientists demonstrate enhanced hydrogen production from sunlight-assisted water splitting using a polydopamine-coated zinc sulfide nanorod catalyst.
Scientists demonstrate enhanced hydrogen production from sunlight-assisted water splitting using a polydopamine-coated zinc sulfide nanorod catalyst.
Targeted delivery of highly toxic anti-cancer drug to brain tumors
 Researchers develop, tests nano-carrier as potential treatment for glioblastomas.
Researchers develop, tests nano-carrier as potential treatment for glioblastomas.
Liquids that can move on their own
 Scientists are harnessing the power of swirling cellular proteins to create self-propelling fluids.
Scientists are harnessing the power of swirling cellular proteins to create self-propelling fluids.
The magic angle of twisted graphene
 Researchers report hyperspectral optical images, generated by a nano-Raman spectroscope, of the crystal superlattice in reconstructed (low-angle) twisted bilayer graphene.
Researchers report hyperspectral optical images, generated by a nano-Raman spectroscope, of the crystal superlattice in reconstructed (low-angle) twisted bilayer graphene.
Spintronics: New manufacturing process makes crystalline microstructures universally usable
 New storage and information technology requires new higher performance materials. One of these materials is yttrium iron garnet, which has special magnetic properties. Thanks to a new process, it can now be transferred to any material.
New storage and information technology requires new higher performance materials. One of these materials is yttrium iron garnet, which has special magnetic properties. Thanks to a new process, it can now be transferred to any material.
Terahertz imaging of graphene paves the way to industrialisation
 Terahertz spectroscopy penetrates graphene films allowing scientists to make detailed maps of their electrical quality, without damaging or contaminating the material.
Terahertz spectroscopy penetrates graphene films allowing scientists to make detailed maps of their electrical quality, without damaging or contaminating the material.
Monday, February 22, 2021
Graphene oxide membranes could reduce paper industry energy costs
 Paper industry wastewater recycling is among the most energy-intensive chemical processes in the world. Researchers have found a method to engineer membranes made from graphene oxide that allow water to get through it much faster than through conventional membranes and, in the process, can save the paper industry more than 30% in energy costs of water separation.
Paper industry wastewater recycling is among the most energy-intensive chemical processes in the world. Researchers have found a method to engineer membranes made from graphene oxide that allow water to get through it much faster than through conventional membranes and, in the process, can save the paper industry more than 30% in energy costs of water separation.
Polymer film protects from electromagnetic radiation, signal interference
 Engineers describe a flexible film using a quasi-one-dimensional nanomaterial filler that combines excellent electromagnetic shielding with ease of manufacture.
Engineers describe a flexible film using a quasi-one-dimensional nanomaterial filler that combines excellent electromagnetic shielding with ease of manufacture.
CSI Solid-State: The fingerprints of quantum effects
 In solid-state physics the precise interactions of electrons are analyzed in meticulous detective work to ultimately gain a better understanding of fundamental physical phenomena.
In solid-state physics the precise interactions of electrons are analyzed in meticulous detective work to ultimately gain a better understanding of fundamental physical phenomena.
Silver and gold nanowires open the way to better electrochromic devices
 Researchers have developed a new approach with a cost-effective and easy electrode fabrication that is completely ITO-free.
Researchers have developed a new approach with a cost-effective and easy electrode fabrication that is completely ITO-free.
New 'metalens' shifts focus without tilting or moving
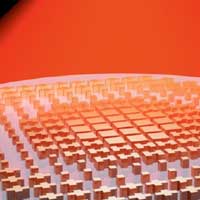 The design may enable miniature zoom lenses for drones, cellphones, or night-vision goggles.
The design may enable miniature zoom lenses for drones, cellphones, or night-vision goggles.
A sponge to soak up carbon dioxide in the air
 A promising technology under development for negative emissions technologies is carbon capture using a material called a MOF, or metal-organic framework.
A promising technology under development for negative emissions technologies is carbon capture using a material called a MOF, or metal-organic framework.
Magnetic effect without a magnet
 Scientists have made a surprising discovery: an exotic metal made of cerium, bismuth and palladium was examined and a giant Hall effect was found to be produced by the material, in the total absence of any magnetic field.
Scientists have made a surprising discovery: an exotic metal made of cerium, bismuth and palladium was examined and a giant Hall effect was found to be produced by the material, in the total absence of any magnetic field.
Concept for a new storage medium
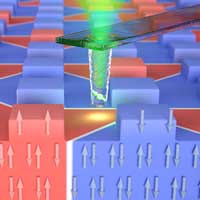 Physicists have proposed an innovative new data storage medium. The technique is based on specific properties of antiferromagnetic materials that had previously resisted experimental examination.
Physicists have proposed an innovative new data storage medium. The technique is based on specific properties of antiferromagnetic materials that had previously resisted experimental examination.
Attachable skin monitors that wick the sweat away
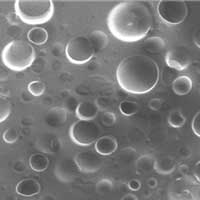 A silicone membrane for wearable devices is more comfortable and breathable thanks to better-sized pores made with the help of citric acid crystals.
A silicone membrane for wearable devices is more comfortable and breathable thanks to better-sized pores made with the help of citric acid crystals.
Sunday, February 21, 2021
Optical frequency combs found a new dimension
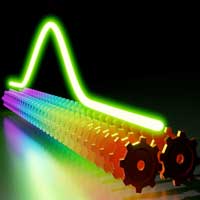 Scientists have demonstrated the generation of tunable and coherent frequency combs in a pair of hybridized optical microresonators.
Scientists have demonstrated the generation of tunable and coherent frequency combs in a pair of hybridized optical microresonators.
Saturday, February 20, 2021
Researchers create 'beautiful marriage' of quantum enemies
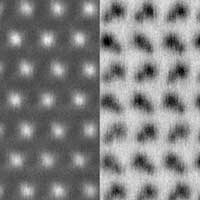 Using nitride-based materials, researchers created a material structure that simultaneously exhibits superconductivity - in which electrical resistance vanishes completely - and the quantum Hall effect, which produces resistance with extreme precision when a magnetic field is applied.
Using nitride-based materials, researchers created a material structure that simultaneously exhibits superconductivity - in which electrical resistance vanishes completely - and the quantum Hall effect, which produces resistance with extreme precision when a magnetic field is applied.
The future of electronics is stretchy (w/video)
 Researchers have developed a material and fabrication process that can rapidly make these devices stretchier, more durable, and closer to being ready for mass manufacturing.
Researchers have developed a material and fabrication process that can rapidly make these devices stretchier, more durable, and closer to being ready for mass manufacturing.
New phenomena for the design of future quantum devices
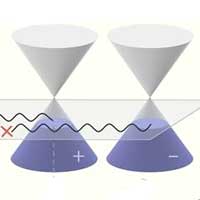 For the first time, Kohn anomaly has been theoretically predicted in a topological material and experimentally observed in a Weyl semimetal. This research revealed how the topological electronic states can alter the phonon spectra in materials, which hold promise for future quantum applications.
For the first time, Kohn anomaly has been theoretically predicted in a topological material and experimentally observed in a Weyl semimetal. This research revealed how the topological electronic states can alter the phonon spectra in materials, which hold promise for future quantum applications.
Scientists find way for mass production of near-zigzag carbon nanotubes
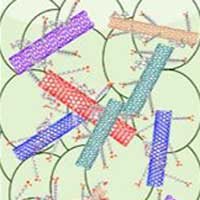 Researchers report a method for submilligram-scale preparation of multiple single-chirality near-zigzag carbon nanotubes such as (9, 1), (9, 2), (10, 2) and (11, 1) nanotubes. This new technique breaks through the bottleneck of mass production of single-chirality near-zigzag single-wall carbon nanotubes, and provides a material basis for the disclosure of their properties and applications.
Researchers report a method for submilligram-scale preparation of multiple single-chirality near-zigzag carbon nanotubes such as (9, 1), (9, 2), (10, 2) and (11, 1) nanotubes. This new technique breaks through the bottleneck of mass production of single-chirality near-zigzag single-wall carbon nanotubes, and provides a material basis for the disclosure of their properties and applications.
A speed limit also applies in the quantum world
 Even in the world of the smallest particles with their own special rules, things cannot proceed infinitely fast. Physicists have now shown what the speed limit is for complex quantum operations.
Even in the world of the smallest particles with their own special rules, things cannot proceed infinitely fast. Physicists have now shown what the speed limit is for complex quantum operations.
Friday, February 19, 2021
Swimming upstream on sound waves (w/video)
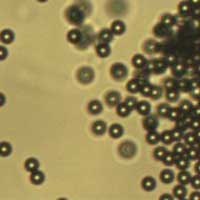 Scientists have succeeded in propelling microvehicles against a fluid flow using ultrasound. In future, these tiny vehicles are set to be introduced into the human bloodstream, thereby revolutionising the field of medicine.
Scientists have succeeded in propelling microvehicles against a fluid flow using ultrasound. In future, these tiny vehicles are set to be introduced into the human bloodstream, thereby revolutionising the field of medicine.
Assessing nanomaterial movements and nanomaterial-induced responses in lymphatic vessels
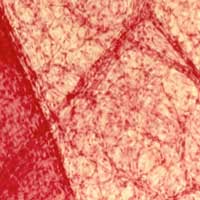 Nanoparticles used in drug delivery systems, bioimaging, and regenerative medicine migrate from tissues to lymphatic vessels after entering the body, so it is necessary to clarify the interaction between nanoparticles and lymphatic vessels.
Nanoparticles used in drug delivery systems, bioimaging, and regenerative medicine migrate from tissues to lymphatic vessels after entering the body, so it is necessary to clarify the interaction between nanoparticles and lymphatic vessels.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
