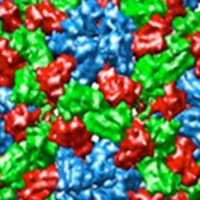
 In nature, viruses use nanocages to protect their genome. Some of these viruses can be disassembled into protein units to remove their genome. These protein units can then be reassembled into nanocages by other templates, the so-called virus-like particles.
In nature, viruses use nanocages to protect their genome. Some of these viruses can be disassembled into protein units to remove their genome. These protein units can then be reassembled into nanocages by other templates, the so-called virus-like particles.
Friday, February 28, 2020
A new template for nonspherical viral nanocage
 In nature, viruses use nanocages to protect their genome. Some of these viruses can be disassembled into protein units to remove their genome. These protein units can then be reassembled into nanocages by other templates, the so-called virus-like particles.
In nature, viruses use nanocages to protect their genome. Some of these viruses can be disassembled into protein units to remove their genome. These protein units can then be reassembled into nanocages by other templates, the so-called virus-like particles.
Stress-relief substrate helps OLED stretch two-dimensionally
 Researchers have created stretchable OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes) that are compliant and maintain their performance under high-strain deformation. Their stress-relief substrates have a unique structure and utilize pillar arrays to reduce the stress on the active areas of devices when strain is applied.
Researchers have created stretchable OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes) that are compliant and maintain their performance under high-strain deformation. Their stress-relief substrates have a unique structure and utilize pillar arrays to reduce the stress on the active areas of devices when strain is applied.
New study explains why superconductivity takes place in graphene
 Theoretical physicists take important step in development of high temperature superconductors.
Theoretical physicists take important step in development of high temperature superconductors.
A nanoconcrete for casting under negative temperature conditions
 Engineers have developed concrete mixture with nano additives for monolithic construction up to ten stories high. The concrete casting is possible within a very humid climate and negative temperature down to minus 5-degree centigrade.
Engineers have developed concrete mixture with nano additives for monolithic construction up to ten stories high. The concrete casting is possible within a very humid climate and negative temperature down to minus 5-degree centigrade.
Thursday, February 27, 2020
Freestanding microwire arrays for transparent solar cells with flexibility
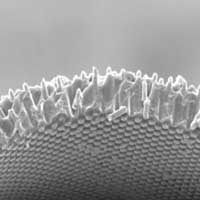 The new solar cell takes a structure in which cylindrical silicon rods are embedded in a flexible and transparent polymer material. As the visible lights passes between polymer materials without silicon rods, it appears entirely transparent to the human eye.
The new solar cell takes a structure in which cylindrical silicon rods are embedded in a flexible and transparent polymer material. As the visible lights passes between polymer materials without silicon rods, it appears entirely transparent to the human eye.
New state-of-the-MOF materials
 Converting crystalline metal-organic frameworks into glass or liquid could give them unique properties and lead to the design of new materials.
Converting crystalline metal-organic frameworks into glass or liquid could give them unique properties and lead to the design of new materials.
Oil separation made easier with 2D material membrane
 Researchers have made a leap forward in overcoming one of the biggest problems in membrane technology - membrane fouling.
Researchers have made a leap forward in overcoming one of the biggest problems in membrane technology - membrane fouling.
Assessing the risks associated with nanoparticles in medical applications
 Researchers have conducted an environmental hazard assessment for a class of substances used in drug delivery.
Researchers have conducted an environmental hazard assessment for a class of substances used in drug delivery.
Tying up molecules as easily as you tie up your laces
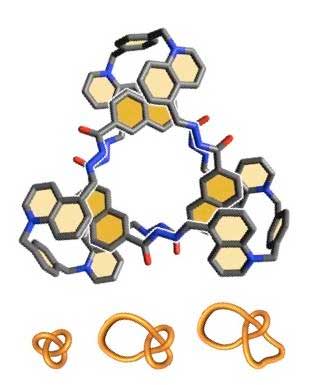 Researchers have developed a simple and effective technique for tying knots in molecules, and have for the first time observed the changes in properties that result from these interlockings. The results open up new perspectives for designing materials and transferring information molecularly.
Researchers have developed a simple and effective technique for tying knots in molecules, and have for the first time observed the changes in properties that result from these interlockings. The results open up new perspectives for designing materials and transferring information molecularly.
Wednesday, February 26, 2020
Nanoelectronics enables brain neurons and artificial neurons to communicate with each other
 This study has for the first time shown how three key emerging technologies can work together: brain-computer interfaces, artificial neural networks and advanced memory technologies (also known as memristors).
This study has for the first time shown how three key emerging technologies can work together: brain-computer interfaces, artificial neural networks and advanced memory technologies (also known as memristors).
Nanoscale precipitates make big difference in mitigating strength-ductility tradeoff
 Researchers have found that nanoscale precipitates provide a unique sustainable dislocation source at sufficiently high stress.
Researchers have found that nanoscale precipitates provide a unique sustainable dislocation source at sufficiently high stress.
New technique to create nanomaterials may help detect cancer earlier
 For the first time, a team of scientists has created functional nanomaterials with hollow interiors that can be used to create highly sensitive biosensors for early cancer detection.
For the first time, a team of scientists has created functional nanomaterials with hollow interiors that can be used to create highly sensitive biosensors for early cancer detection.
Light-shrinking device enables detection of ultra-tiny substances
 Engineers have created light-based technology that can detect biological substances with a molecular mass more than two orders of magnitude smaller than previously possible. The advance was made possible by building a device that shrinks light while exploiting mathematical singularities known as exceptional points.
Engineers have created light-based technology that can detect biological substances with a molecular mass more than two orders of magnitude smaller than previously possible. The advance was made possible by building a device that shrinks light while exploiting mathematical singularities known as exceptional points.
Researchers discover new way to control the phase of light using 2D materials
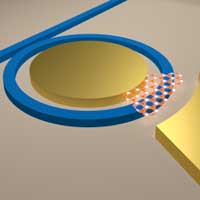 Researchers use atomically thin materials to manipulate the phase of light without changing its amplitude, at extremely low power loss; could enable applications such as LIDAR, phased arrays, optical switching, and quantum and optical neural networks.
Researchers use atomically thin materials to manipulate the phase of light without changing its amplitude, at extremely low power loss; could enable applications such as LIDAR, phased arrays, optical switching, and quantum and optical neural networks.
Metal-organic frameworks can separate gases despite the presence of water
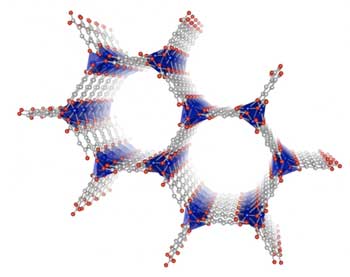 Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising materials for inexpensive and less energy-intensive gas separation even in the presence of impurities such as water.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising materials for inexpensive and less energy-intensive gas separation even in the presence of impurities such as water.
MOF co-catalyst allows selectivity of branched aldehydes of up to 90%
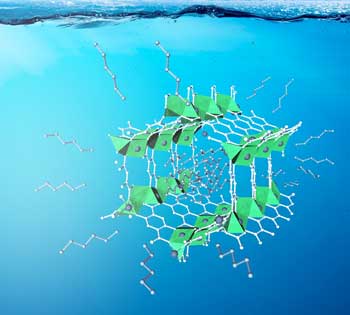 Approach represents a powerful tool for designing selective catalytic heterogeneous processes.
Approach represents a powerful tool for designing selective catalytic heterogeneous processes.
Tuesday, February 25, 2020
When bonding noble metals to 2D materials, interfaces matter
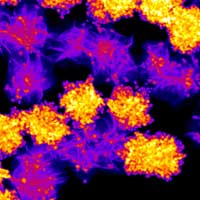 Researchers have developed new materials for improved single-atom catalysis and future electronics.
Researchers have developed new materials for improved single-atom catalysis and future electronics.
Production of high yield Si-C for anodes in Li batteries
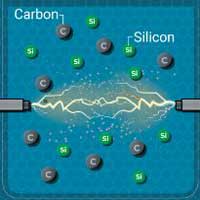 Novel composite combining the high energy storage capacity of silicon and the elastic property of carbon.
Novel composite combining the high energy storage capacity of silicon and the elastic property of carbon.
Safe method of adding metal particles to organic nanomaterials paves way for better batteries
 Novel liquid-based method for safe synthesis of carbon-based materials containing ultrafine metallic atoms.
Novel liquid-based method for safe synthesis of carbon-based materials containing ultrafine metallic atoms.
Breaking the temperature barrier in small-scale materials testing
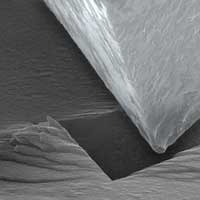 Researchers have demonstrated a new method for testing microscopic aeronautical materials at ultra-high temperatures. By combining electron microscopy and laser heating, scientists can evaluate these materials much more quickly and inexpensively than with traditional testing.
Researchers have demonstrated a new method for testing microscopic aeronautical materials at ultra-high temperatures. By combining electron microscopy and laser heating, scientists can evaluate these materials much more quickly and inexpensively than with traditional testing.
Monday, February 24, 2020
Synthesizing a superatom
 Scientists have demonstrated how superatoms of a desired valency, stability, and volume can be synthesized in a solution medium by altering the number of atoms in a cluster structure. This is an important step in realizing the practical application of superatom clusters as substitutes for elements in chemical reactions.
Scientists have demonstrated how superatoms of a desired valency, stability, and volume can be synthesized in a solution medium by altering the number of atoms in a cluster structure. This is an important step in realizing the practical application of superatom clusters as substitutes for elements in chemical reactions.
Shining a new light on biomimetic materials
 Researchers have merged optical, chemical and materials sciences to utilize light to control the local dynamic behavior within a hydrogel, much like the ability of the iris and pupil in the eye to dynamically respond to incoming light.
Researchers have merged optical, chemical and materials sciences to utilize light to control the local dynamic behavior within a hydrogel, much like the ability of the iris and pupil in the eye to dynamically respond to incoming light.
Defects add color to quantum systems
 Researchers are investigating light-emitting defects in materials that may someday form the basis of quantum-based technologies, such as quantum computers, quantum networks or engines that run on light. Once understood, these defects can become controllable features.
Researchers are investigating light-emitting defects in materials that may someday form the basis of quantum-based technologies, such as quantum computers, quantum networks or engines that run on light. Once understood, these defects can become controllable features.
A simple retrofit transforms electron microscopes into high-speed atom-scale cameras
 Patented 'beam chopper' provides cost-effective way to investigate super-fast processes important for tomorrow's technology.
Patented 'beam chopper' provides cost-effective way to investigate super-fast processes important for tomorrow's technology.
Going super small to get super strong metals
 A new study has resulted in a new understanding of how individual atoms of metal grains interact with each other, as well as a way to use those physics to achieve super-strong metals.
A new study has resulted in a new understanding of how individual atoms of metal grains interact with each other, as well as a way to use those physics to achieve super-strong metals.
Developing lensless imaging at the nanoscale
 Researchers are planning to develop imaging that can look at biological systems at a much higher resolution and definition.
Researchers are planning to develop imaging that can look at biological systems at a much higher resolution and definition.
An exceptionally stable single-atom catalyst
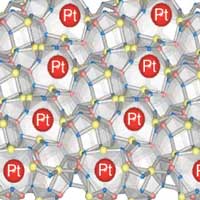 Scientists have shown that single platinum atoms trapped in C12A7 crystals act as a stable and effective catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitroarenes, an essential process in the production of many kinds of fine chemicals.
Scientists have shown that single platinum atoms trapped in C12A7 crystals act as a stable and effective catalyst for the hydrogenation of nitroarenes, an essential process in the production of many kinds of fine chemicals.
Directing nanoparticles straight to tumors
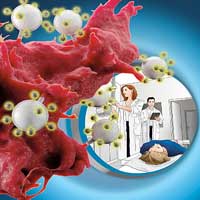 A team of researchers has produced tiny nanoparticles that are designed to specifically target cancer cells. They can navigate directly to the tumor cells and visualize those using advanced imaging techniques.
A team of researchers has produced tiny nanoparticles that are designed to specifically target cancer cells. They can navigate directly to the tumor cells and visualize those using advanced imaging techniques.
Short film of a magnetic nano-vortex
 For the first time, researchers have recorded a '3D film' of magnetic processes on the nanometer scale. This reveals a variety of dynamics inside the material, including the motion of swirling boundaries between different magnetic domains.
For the first time, researchers have recorded a '3D film' of magnetic processes on the nanometer scale. This reveals a variety of dynamics inside the material, including the motion of swirling boundaries between different magnetic domains.
Watching magnetic nano 'tornadoes' in 3-D
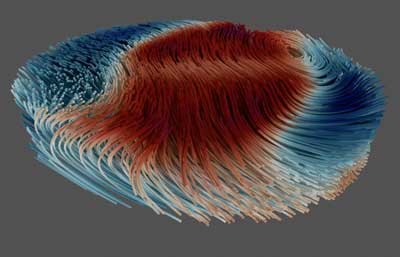 Scientists have developed a three-dimensional imaging technique to observe complex behaviours in magnets, including fast-moving waves and 'tornadoes' thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
Scientists have developed a three-dimensional imaging technique to observe complex behaviours in magnets, including fast-moving waves and 'tornadoes' thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
Novel gold nanocatalyst with high activity and excellent stability
 Researchers prepared a SiO2 modified gold nanocatalyst through co-deposition of gold and silica precursors on the TiO2 support and subsequent high temperature calcination.
Researchers prepared a SiO2 modified gold nanocatalyst through co-deposition of gold and silica precursors on the TiO2 support and subsequent high temperature calcination.
DNA nanostructures suit up for future missions
 A broadly applicable and simple chemical protection strategy removes a major roadblock in the development of therapeutic and diagnostic DNA nanostructures.
A broadly applicable and simple chemical protection strategy removes a major roadblock in the development of therapeutic and diagnostic DNA nanostructures.
When plasmons reach atomic flatland
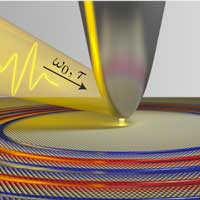 Researchers have discovered a significant new fundamental kind of quantum electronic oscillations, or plasmons, in atomically thin materials. Their work has potential implications for novel imaging techniques and photochemical reactions at the nanoscale.
Researchers have discovered a significant new fundamental kind of quantum electronic oscillations, or plasmons, in atomically thin materials. Their work has potential implications for novel imaging techniques and photochemical reactions at the nanoscale.
Sneaking up on nanocrystals with electron diffraction
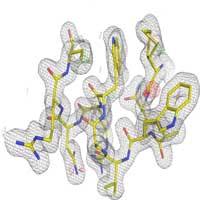 Scientists present a method for serial electron diffraction of protein nanocrystals combining the benefits of serial X-ray crystallography and rotation electron diffraction.
Scientists present a method for serial electron diffraction of protein nanocrystals combining the benefits of serial X-ray crystallography and rotation electron diffraction.
Cellulose nanocrystals and water form an 'eco' super-glue
 Plant-based cellulose nanocrystals have remarkable inherent properties, and when combined with water, a powerful adhesive is formed that competes in strength with Superglue, without the need for toxic solvents.
Plant-based cellulose nanocrystals have remarkable inherent properties, and when combined with water, a powerful adhesive is formed that competes in strength with Superglue, without the need for toxic solvents.
Printable organic photodiodes that can distinguish wavelengths
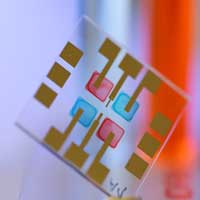 Researchers develop printable organic photodiodes that can distinguish wavelengths and, hence, enable data transmission by light.
Researchers develop printable organic photodiodes that can distinguish wavelengths and, hence, enable data transmission by light.
Friday, February 21, 2020
Researchers develop high-capacity EV battery materials that double driving range
 Newly developed silicon anode materials can increase battery capacity four-fold in comparison to graphite anode materials and enable rapid charging to more than 80% capacity in only five minutes. When applied to batteries for electric vehicles, the new materials are expected to more than double their driving range.
Newly developed silicon anode materials can increase battery capacity four-fold in comparison to graphite anode materials and enable rapid charging to more than 80% capacity in only five minutes. When applied to batteries for electric vehicles, the new materials are expected to more than double their driving range.
Black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor as an ultra-low power switch
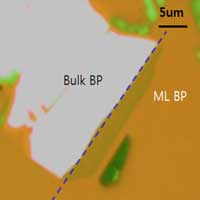 Researchers have developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
Researchers have developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
Thursday, February 20, 2020
Scientists develop new method to isolate atomic sheets and create new materials
 New exfoliation method makes large-area atomically thin layers that can be stacked in any desired order and orientation to generate a whole new class of artificial materials; opens the door to new research and commercialization.
New exfoliation method makes large-area atomically thin layers that can be stacked in any desired order and orientation to generate a whole new class of artificial materials; opens the door to new research and commercialization.
MoS nanoparticles provide a cheaper way to obtain hydrogen
 Researchers propose molybdenum sulfide as a material for the catalysts which is, firstly, more effective than molybdenum, and, secondly, much cheaper since the total amount of expensive metal in catalysts is reduced, and the sulfur is not scarce and very cheap.
Researchers propose molybdenum sulfide as a material for the catalysts which is, firstly, more effective than molybdenum, and, secondly, much cheaper since the total amount of expensive metal in catalysts is reduced, and the sulfur is not scarce and very cheap.
New graphene-based metasurface capable of independent amplitude and phase control of light
 Researchers describe a new strategy of designing metamolecules that incorporates two independently controllable subwavelength meta-atoms. This two-parametric control of the metamolecule secures the complete control of both amplitude and the phase of light.
Researchers describe a new strategy of designing metamolecules that incorporates two independently controllable subwavelength meta-atoms. This two-parametric control of the metamolecule secures the complete control of both amplitude and the phase of light.
In acoustic waves, engineers break reciprocity with 'spacetime-varying metamaterials'
 Scientists have experimentally demonstrated that it?s possible to break reciprocity in acoustic waves with material properties that change simultaneously in time and space.
Scientists have experimentally demonstrated that it?s possible to break reciprocity in acoustic waves with material properties that change simultaneously in time and space.
Plant-based relatives of cholesterol could give boost to nanoparticle gene therapy
 Gene-infused nanoparticles used for combating disease work better when they include plant-based relatives of cholesterol because their shape and structure help the genes get where they need to be inside cells.
Gene-infused nanoparticles used for combating disease work better when they include plant-based relatives of cholesterol because their shape and structure help the genes get where they need to be inside cells.
Wednesday, February 19, 2020
Smart contact lens has potential to improve sight for many
 Researchers have inserted a microchip into an electrically powered contact lens. This technological feat could improve the lives of many suffering from a range of sight-related ailments and lead to more groundbreaking medical applications.
Researchers have inserted a microchip into an electrically powered contact lens. This technological feat could improve the lives of many suffering from a range of sight-related ailments and lead to more groundbreaking medical applications.
A green chemistry preparation of fullerene films
 The method enables fabrication of organic electronics without using toxic organic solvents and costly vacuum technologies, thus reducing the environmental risks and making organic electronics more accessible.
The method enables fabrication of organic electronics without using toxic organic solvents and costly vacuum technologies, thus reducing the environmental risks and making organic electronics more accessible.
Cellulose nanomaterials could make renewable energy cheaper
 Researchers have taken to the trees to look for ways to make new sustainable materials from abundant natural resources - specifically, within the chemical structure of microfibers that make up wood.
Researchers have taken to the trees to look for ways to make new sustainable materials from abundant natural resources - specifically, within the chemical structure of microfibers that make up wood.
New world record for the conversion of solar energy to electricity using quantum dots
 The development of next generation solar power technology that has potential to be used as a flexible 'skin' over hard surfaces has moved a step closer, thanks to a significant breakthrough.
The development of next generation solar power technology that has potential to be used as a flexible 'skin' over hard surfaces has moved a step closer, thanks to a significant breakthrough.
Tuesday, February 18, 2020
An early warning system for damage in composite materials
 New mechanophore senses damage to fiber reinforced polymers.
New mechanophore senses damage to fiber reinforced polymers.
Improving the electrical and mechanical properties of carbon-nanotube-based fibers
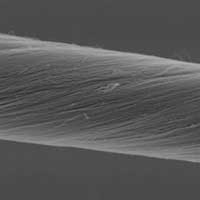 Researchers recently developed a technique that can be used to build carbon-nanotube-based fibers by creating chemical crosslinks; the technique improves the electrical and mechanical properties of these materials.
Researchers recently developed a technique that can be used to build carbon-nanotube-based fibers by creating chemical crosslinks; the technique improves the electrical and mechanical properties of these materials.
Time-resolved measurement in a memory device
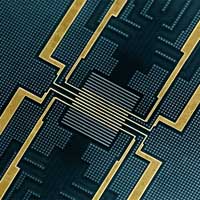 Researchers have measured the timing of single writing events in a novel magnetic memory device with a resolution of less than 100 picoseconds. Their results are relevant for the next generation of main memories based on magnetism.
Researchers have measured the timing of single writing events in a novel magnetic memory device with a resolution of less than 100 picoseconds. Their results are relevant for the next generation of main memories based on magnetism.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
