
Thursday, January 31, 2019
Novel electron microscopy offers nanoscale, damage-free tracking of isotopes in amino acids
Dynamic aspirin - molecular vibrations drive electrons over large distances
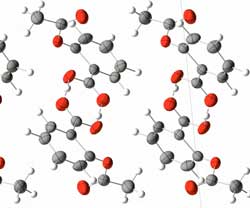
Graphene crinkles can be used as 'molecular zippers'
What keeps spiders on the ceiling?
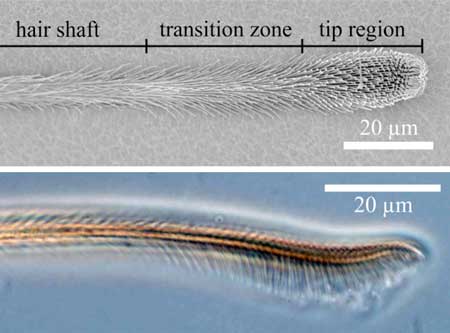
Nano-encapsulation technology enhances DHA absorption for early brain development

To observe photoswitches, stick on a platinum atom

A new topological approach to the next generation of electronic, photonic and phononic devices
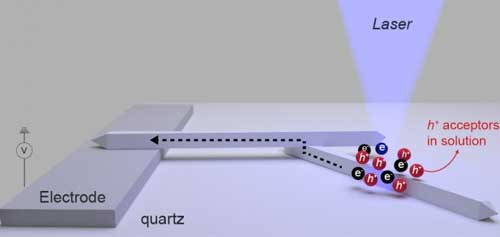
A first: Researchers quantify photocurrent loss in nanoparticle interface
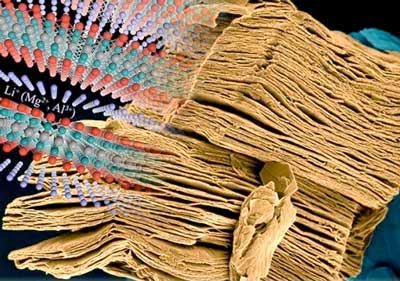
Maximizing the potential of MXenes
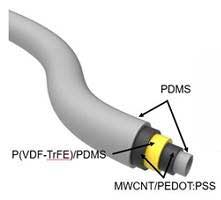
Stretchable multi-functional fiber for energy harvesting and strain sensing
Wednesday, January 30, 2019
Catching atoms in action: watching next-gen materials crystallize
A sustainable and recyclable carbon nanotubes thermoelectric paper

Structural colors, without the shimmer

Scientists use Nobel-prize winning chemistry for clean energy breakthrough

Layered cocktails inspire new form of male birth control

Harnessing light for a solar-powered chemical industry

Ingestible, expanding pill monitors the stomach for up to a month

Artificial intelligence instantly captures materials' properties

Antireflection coating makes plastic invisible

Waterproof graphene electronic circuits
Tuesday, January 29, 2019
Synthesizing single-crystalline hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) film that uniformly self-assembles
Laser-fabricated crystals in glass are ferroelectric
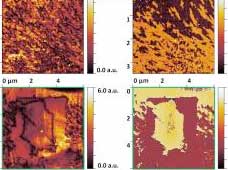
Researchers decipher electrical conductivity in doped organic semiconductors
Thin-film semiconductor fabrication process uses copper(I) iodide at room temperature
Dietary nanoparticulates impact gut microbiome
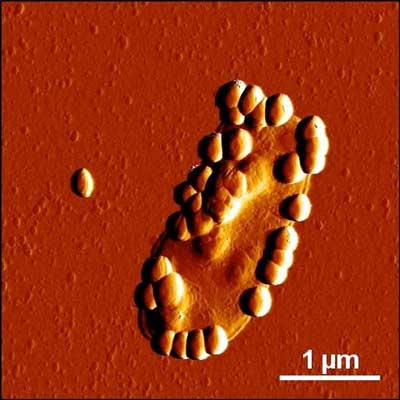
Photovoltaics - versatile in shape and color

Graphene researchers are wild about zigzags
Monday, January 28, 2019
The energy implications of organic radical polymers
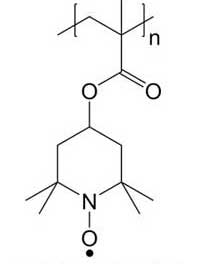
New quantum system could help design better spintronics
Fluid-inspired material self-heals before your eyes (w/video)

Researchers investigate coated Prussian blue nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapies

Engineer's nanostructured 'metallic wood' has the strength of titanium and the density of water
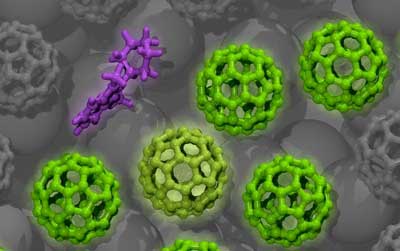
Researchers uncover quantum structure of buckyballs
Plasmonic pioneers fire away in fight over light
Scientists investigate graphene's effect on light-wave interaction
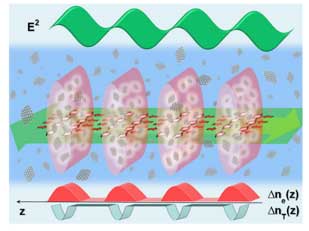
Aerosol-assisted biosynthesis strategy enables functional bulk nanocomposites
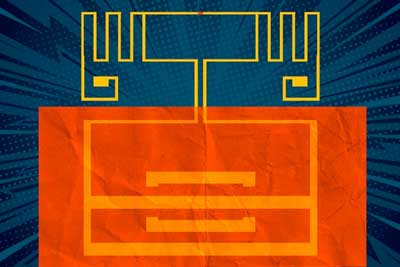
Converting Wi-Fi signals to electricity with new 2-D materials
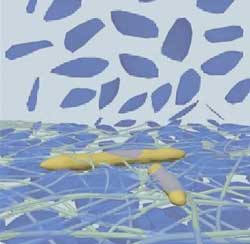
Turning natural gas into carbon nanotubes cuts energy use, carbon dioxide emissions

Insulated molecular wires: the smallest electric power cord
Putting that free energy around you to good use with minuscule energy harvesters
Sunday, January 27, 2019
Using an atomic force microscope as a nanoscopic shovel
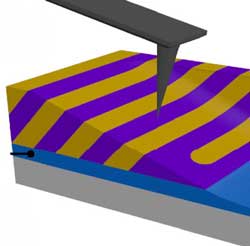
Artificial skin could give superhuman perception

Friday, January 25, 2019
'GO dough' makes graphene easy to shape and mold

Materials that open in the heat of the moment

How the use of different forms of titanium oxide influences perovskite solar cell performance

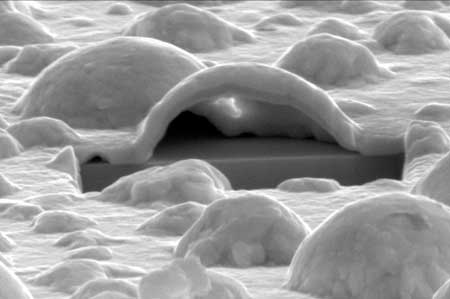
Platinum forms nano-bubbles
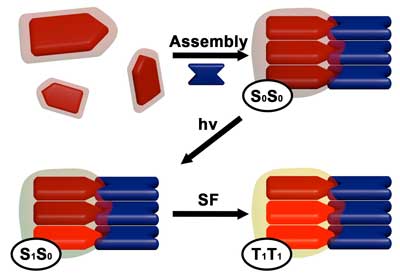
Self-assembling nanomaterial gives pathway to extra environment friendly, reasonably priced harnessing of solar energy
Thursday, January 24, 2019
Engineers develop novel strategy for designing semiconductor nanoparticles for wide-ranging applications
'Green' electronics made from nanocellulose

Engineers eye static electricity to power our electronics
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
